Elementary Number Theory with Programming
Marty Lewinter, Jeanine Meyer
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Elementary Number Theory with Programming
Marty Lewinter, Jeanine Meyer
Über dieses Buch
A highly successful presentation of the fundamental concepts of number theory and computer programming
Bridging an existing gap between mathematics and programming, Elementary Number Theory with Programming provides a unique introduction to elementary number theory with fundamental coverage of computer programming. Written by highly-qualified experts in the fields of computer science and mathematics, the book features accessible coverage for readers with various levels of experience and explores number theory in the context of programming without relying on advanced prerequisite knowledge and concepts in either area.
Elementary Number Theory with Programming features comprehensive coverage of the methodology and applications of the most well-known theorems, problems, and concepts in number theory. Using standard mathematical applications within the programming field, the book presents modular arithmetic and prime decomposition, which are the basis of the public-private key system of cryptography. In addition, the book includes:
- Numerous examples, exercises, and research challenges in each chapter to encourage readers to work through the discussed concepts and ideas
- Select solutions to the chapter exercises in an appendix
- Plentiful sample computer programs to aid comprehension of the presented material for readers who have either never done any programming or need to improve their existing skill set
- A related website with links to select exercises
- An Instructor's Solutions Manual available on a companion website
Elementary Number Theory with Programming is a useful textbook for undergraduate and graduate-level students majoring in mathematics or computer science, as well as an excellent supplement for teachers and students who would like to better understand and appreciate number theory and computer programming. The book is also an ideal reference for computer scientists, programmers, and researchers interested in the mathematical applications of programming.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
1
SPECIAL NUMBERS: TRIANGULAR, OBLONG, PERFECT, DEFICIENT, AND ABUNDANT
We start our introduction to number theory with definitions, properties, and relationships of several categories of numbers.
TRIANGULAR NUMBERS
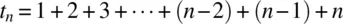
n . This is termed hard-coding. The computation is done using a for-loop. The for-loop adds up the values from 1 to n , exactly following Equation 1.1. The built-in method document.write writes out the result.Date function with the method getTime to get the number of milliseconds from a base date at the start and after the computation. It turns out that computing the millionth triangular number takes 3 ms! You can experiment with different values. Using the formula given in Equation 1.2 would be much, much faster. Give it a try.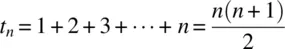
Example: