
Jazz Theory Workbook
From Basic to Advanced Study
Dariusz Terefenko
- 334 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Jazz Theory Workbook
From Basic to Advanced Study
Dariusz Terefenko
Informazioni sul libro
Jazz Theory Workbook accompanies the second edition of the successful Jazz Theory — From Basic to Advanced Study textbook designed for undergraduate and graduate students studying jazz. The overall pedagogy bridges theory and practice, combining theory, aural skills, keyboard skills, and improvisation into a comprehensive whole. While the Companion Website for the textbook features aural and play-along exercises, along with some written exercises and the answer key, this workbook contains brand-new written exercises, as well as as well as four appendices: (1) Rhythmic Exercises, (2) Common-Practice Harmony at the Keyboard, (3) Jazz Harmony at the Keyboard, and (4) Patterns for Jazz Improvisaton. Jazz Theory Workbook works in tandem with its associated textbook in the same format as the 27-chapter book, yet is also designed to be used on its own, providing students and readers with quick access to all relevant exercises without the need to download or print pages that inevitably must be written out. The workbook is sold both on its own as well as discounted in a package with the textbook. Jazz Theory Workbook particularly serves the ever-increasing population of classical students interested in jazz theory or improvisation.
This WORKBOOK is available for individual sale in various formats:
- Print Paperback: 9781138334250
- Print Hardback: 9781138334243
- eBook: 9780429445477
The paperback WORKBOOK is also paired with the corresponding paperback TEXTBOOK in a discounted PACKAGE (9780367321963).
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Part One
Basics
Chapter 1
Music Fundamentals
Master the Fundamentals
- Explain the difference between octave equivalence and enharmonic equivalence.
- List all major sharp keys with their relative partners in the order they appear in the circle of fifths.
- List all major flat keys with their relative partners in the order they appear in the circle of fifths.
- Provide a definition of musical meter. What rhythmic elements are necessary to establish a musical meter?
- Discuss the different types of meter occurring in music.
- What is the difference between the downbeat and the upbeat?
- How many semitones does the major scale have? Where do they occur in the scale?
- How many semitones does the minor scale have (natural, harmonic, and melodic), and between which scale degrees do they occur?
- Describe different methods of labeling intervals.
- Name all diatonic and chromatic intervals within the octave.
- How many semitones does each interval within the octave have?
- Explain the difference between:
- Melodic and harmonic intervals
- Diatonic and chromatic intervals
- Simple and compound intervals
- Describe the pitch and intervallic content of four basic triadic formations.
- Name the lowest pitch of the following triads:
- Am in second inversion
- EM in first inversion
- Fdim in second inversion
- Bm in first inversion

- Aaug in second inversion

- C♯sus in first inversion
- GM in second inversion
- Discuss the unique characteristics of the augmented triad.
- How is the suspended triad different from other types of triadic formations?
Test Your Knowledge
- Write the following pitches in the score.
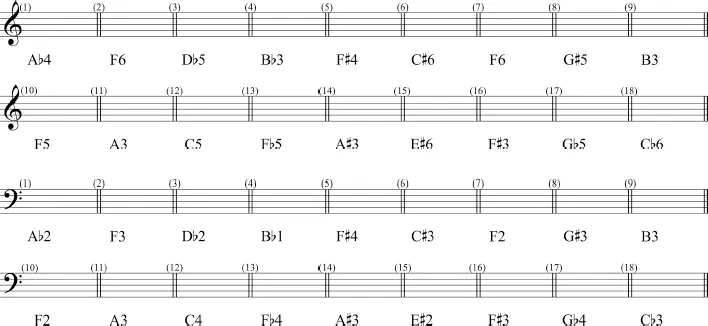
- Label each note on the staff with two different letter names along with their octave designation.
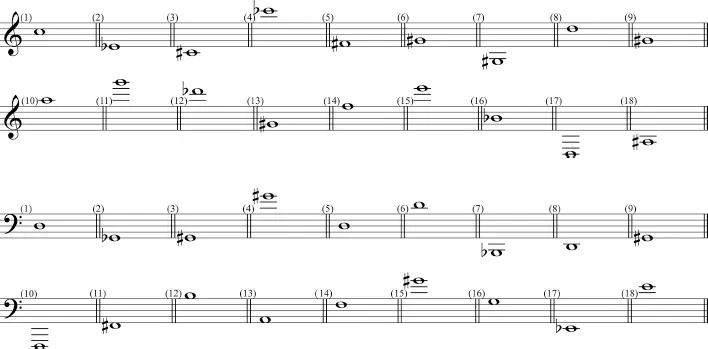
- Write the following scales using accidentals.

- Write the following scales using key signatures.

- Identify the following major keys.

- Identify the following minor keys.

- Identify the following melodic and harmonic intervals.

- Realize the following chord symbols on the staff below.
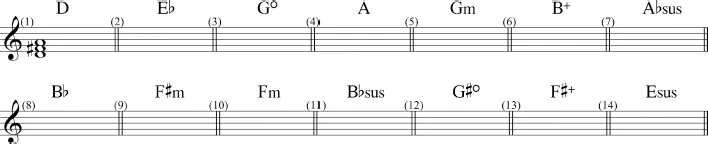
Chapter 2
Jazz Rhythms
Master the Fundamentals
- What is swing? Provide two alternative definitions.
- What musical elements are necessary to convey a “swing feel”?
- Discuss the role of rhythm in jazz.
- What are the main differences between rhythm in jazz and rhythm in common-practice music?
- Name at least three idiomatic rhythmic and metric events that occur in jazz and explain their modus operandi.
- What is the relationship between written “swing 8ths” and their musical interpretation?
- On your instrument, demonstrate the different kinds of swing 8th notes.
- What is the relationship between the tempo of musical performance and the location of swing 8ths within the beat and measure?
- Compare the distribution of metrical accents in jazz as opposed to music from South America.
- Describe the rhythmic organization of music from three different South American countries.
- Provide a definition for the following terms associated with South American music:
- Samba
- Clave
- Partido alto
- Cáscara
- Bossa nova
Test Your Knowledge
- Using the rule of “visible beat 3,” rewrite the incorrectly notated rhythms on the lower staff.


- Based on the specified meter, group the following unmeasured rhythmic values in complete measures.
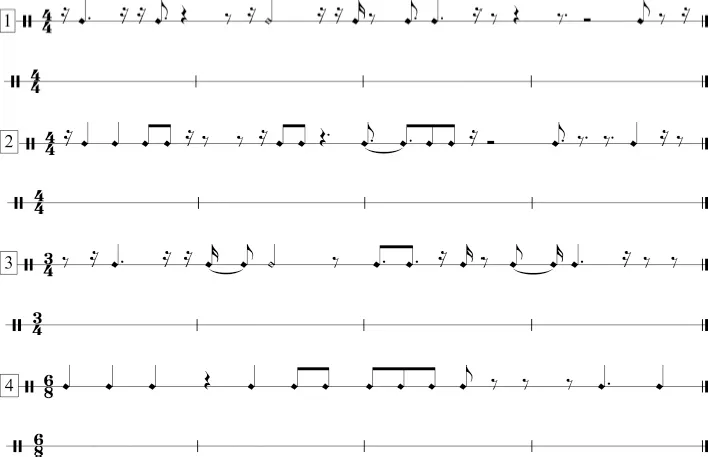


Chapter 3
Harmonic Function
Master the Fundamentals
- What is functional tonality?
- What types of tonal functions exist in common-practice music? What are their main characteristics?
- Provide the name for each scale degree in major and minor keys.
- Explain the difference between primary and secondary chords.
- Assign functional status to secondary triads in major.
- Establish a network of functional relationships between primary and secondary triads in major.
- Assign functional status to secondary triads in minor.
- Establish a network of functional relationships between primary and secondary triads in minor.
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of lead-sheet notation.
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of Roman numeral notation.
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of functional notation.
- What is the difference between musical events occurring at the structural versus surface level? Provide an example.
- What is a pivot chord?
- What role does a pivot chord play in harmonic progressions? Provide an example.
- What is a cadence?
- What types of cadential formulas occur in common-practice music?
- Describe the unfolding of harmonic function in five different cadential formulas.
- What kind of musical event is a prolongation? Provide an example.
- In what ways does musical context determine a chord’s function?
- What are the most fundamental rules of voice leading?
- Explain the main differences between the rules of voice leading in jazz versus common-practice music.
- Draw parallels between voice leading in jazz and common-practice music.
- What types of melodic motions occur in music? Describe their main attributes.
- What type of melodic motion is the most desirable in harmonic progressions and why?
- What are the main characteristics of keyboard style texture?
- What are the main characteristics of chorale style texture?
- Demonstrate the “rule of the nearest way” when connecting chords related by (1) descending/ascending fifths; (2) descending/ascending seconds; and (3) descending/ascending thirds.
- Provide a definition of outer-voice counterpoint. What is its role while realizing harmonic progressions?
Test Your Knowledge
- 1. Using lead-sheet notation, label the following triads.

- 2. Using the “rule of the nearest way,” realize the following progressions in keyboard style.
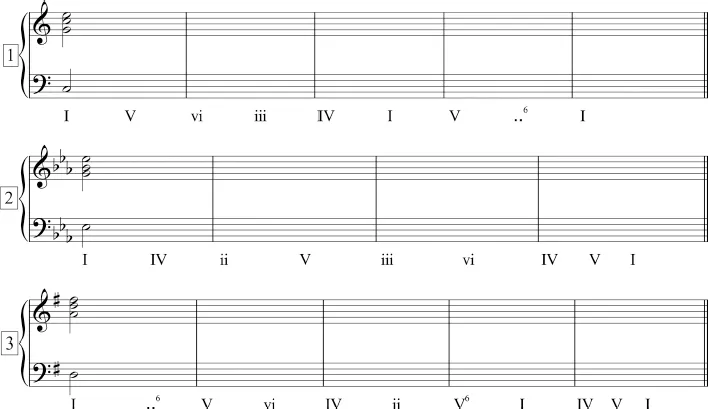

Musical Analysis
- 3. Analyze the following chord progressions using (1) Roman numerals, (2) lead-sheet notation, (3) functional symbols, and (4) scale degrees for the soprano voice.
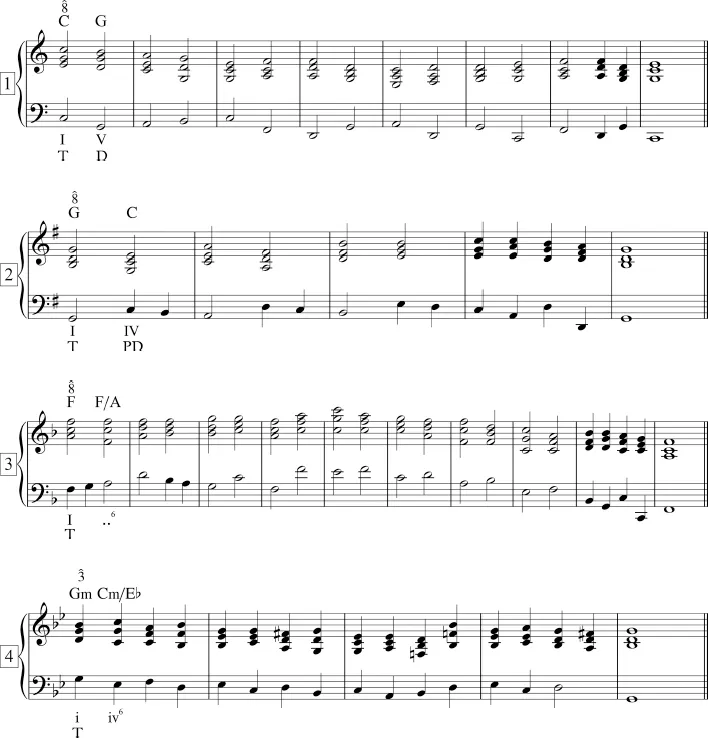

Chapter 4
Four-Part Chords
Master the Fundamentals
- How does the harmonic syntax in jazz differ from that of common-practice music?
- Explain the status of a major 6th and a major 7th within the chord’s structure.
- List all four-part chords belonging to the major category of chords. Describe their pitch content, functional tendencies, and practical applications.
- List all four-part chords belonging to the minor category of chords. Describe their pitch content, functional tendenc...