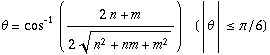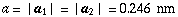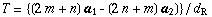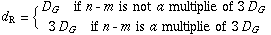![]()
Part I
Preparation and Characterization of Carbon Nanotubes
![]()
1
Structures and Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes
Yahachi Saito
1.1 Structures of Carbon Nanotubes
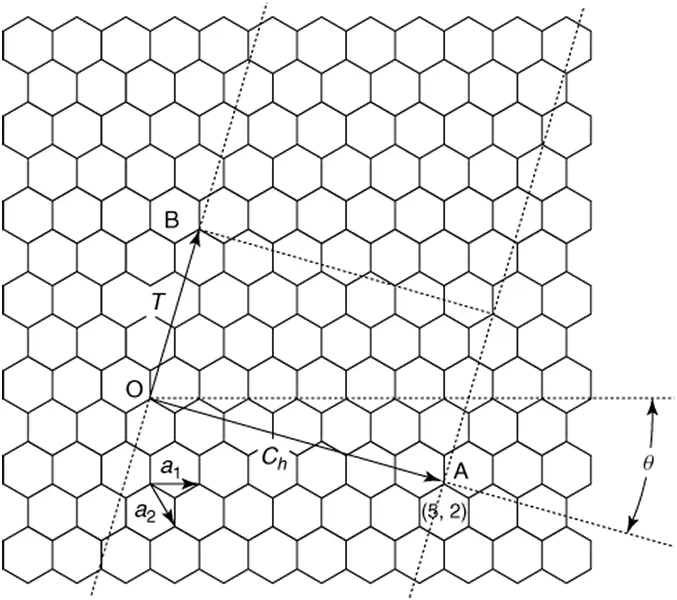
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are hollow cylinders made of seamlessly rolled graphene (honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms, Figure 1.1) with diameters ranging from about 1 over 50 nm, depending on the number of walls comprising the nanotubes. Structurally well-ordered CNTs were discovered and their structures were well characterized by Iijima in 1991 [1]. CNTs composed of one sheet of graphene are called single-wall carbon nanotubes (abbreviated SWCNTs or SWNTs) [2–4], and those made of more than two sheets, multiwall carbon nanotubes (abbreviated MWCNTs or MWNTs). The length of nanotubes exceeds 10 μm, and the longest ones are reportedly on the order of a centimeter [5, 6].
1.1.1 Single-Wall CNTs
There are numerous ways of rolling a sheet of the honeycomb pattern into a seamless cylinder, which give rise to a vast range of diameters and various helical structures. The structure of a CNT is specified (except for handedness) by a vector connecting two lattice points in an unrolled honeycomb lattice (e.g., points O and A in Figure 1.1). When the honeycomb sheet is rolled so as to make the two points coincide, a cylinder whose circumference corresponding to the line AO is formed. Such a vector connecting the crystallographically equivalent lattice points in an unrolled lattice and being perpendicular to the tube axis is called the chiral vector (or wrapping vector), which is expressed using two fundamental translational vectors a1, a2:
where
n and
m are integers with
. The sets of two integers (
n,
m) are called
chiral indices, which are used to specify the structure of SWNTs. The diameter
dt and chiral angle θ (
Figure 1.1) can be expressed in terms of
n and
mA SWNT has translational symmetry along the tube axis. The basic translational vector T is represented by
where dR is defined by using the greatest common divisor DG of n and m as follows:
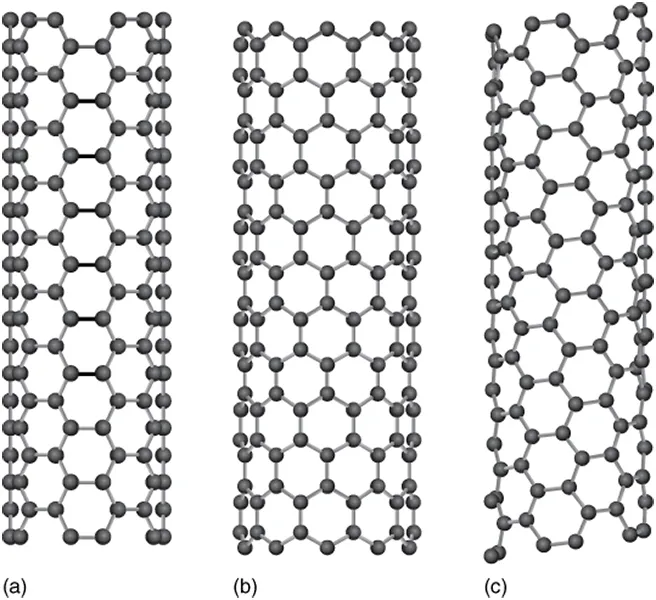
CNTs with n = m(θ = π/6) and m = 0 (θ = 0), called armchair type and zigzag type, respectively, do not have helicity. CNTs with other chiral indices (n ≠ m ≠ 0) have helical structures and are called chiral type. In Figure 1.2a–c, structure models of armchair, zigzag, and chiral type CNTs, respectively, are shown.
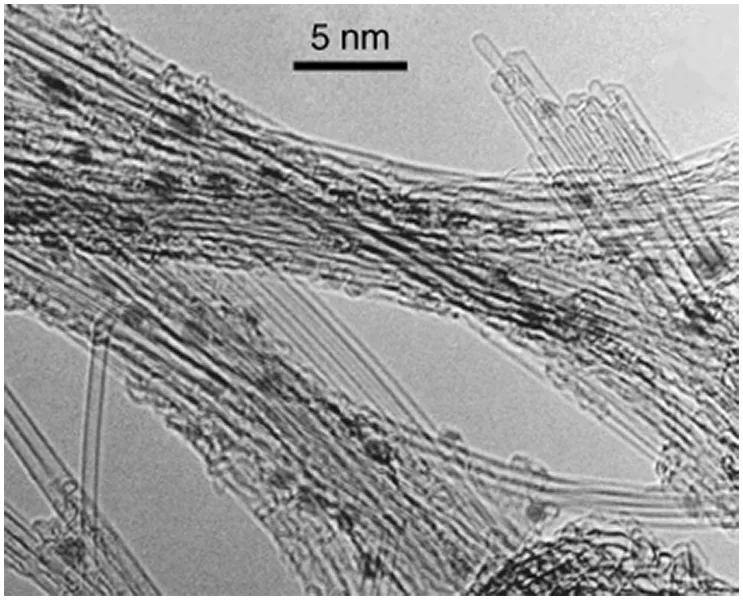
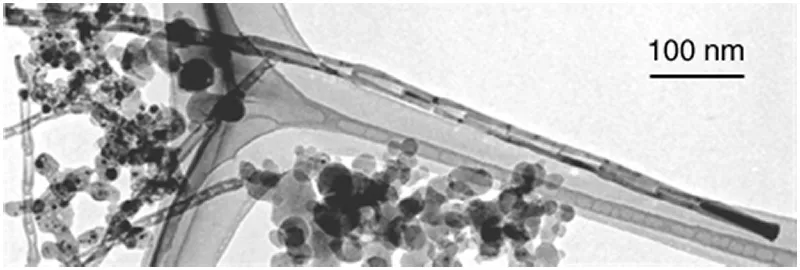
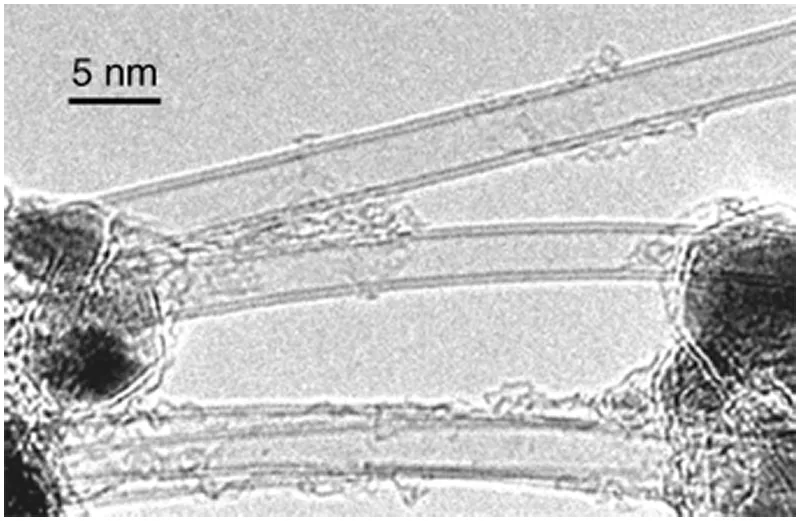
The diameter of SWNTs actually synthesized ranges from 0.7 to about 3 nm, depending on synthesis conditions especially on the diameter of catalyst particles employed for the synthesis. Figure 1.3 shows a transmission electron microscope (TEM) image of SWNTs, with diameter ranging between 1.0 and 1.3 nm, produced by arc discharge with a Ni catalyst. The ends of a tube made from a rolled graphene remain open, but CNTs actually synthesized are capped by a curved graphene (Figure 1.3) or by a metal particle used as catalyst in the synthesis process. Pentagons (five-membered rings) have to be inserted into a graphene sheet in order to render a positive curvature to the sheet. Since one pentagon introduces a + π/6 wedge disclination in the honeycomb lattice, six pentagons are required to from a hemispherical dome of a curved graphene, like the half of the C60 fullerene, and to close one end of a CNT. The caps of CNTs with small diameters (less than about 4 nm in diameter) such as SWNTs look spherical (see the ends of SWNTs in Figure 1.3), while those of thick CNTs (e.g., MWNTs) exhibit polyhedral shapes because the pentagon sites extrude like corners of the polyhedra (see Figure 1.4 in the next section).
1.1.2 Multiwall CNTs
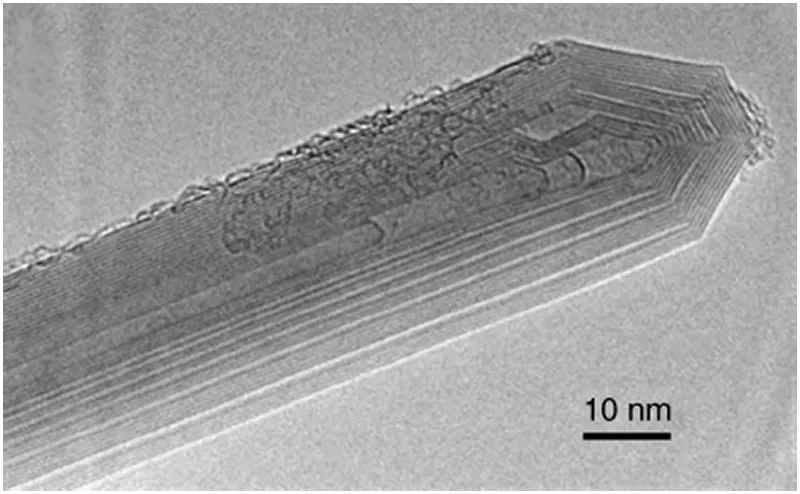
An ideal MWNT consists of graphene sheets stacked in a concentric way. MWNTs produced by the arc-discharge technique (see below) have a high structural perfection and are straight, as shown in
Figure 1.4. The number of sheets ranges from 2 to about 40. For thick MWNTs composed of more than three or four layers, the interlayer spacing between rolled graphene sheets is 0.344 nm on average [7]. The spacing is wider by a small percentage than the ideal graphite value (0.3354 nm), being characteristic of the turbostratic carbon (graphitic layers that are stacked in parallel but without translational and rotational relations between the adjacent layers) [8]. The diameters of MWNTs are in the range 4–50 nm, and the lengths are over
. MWNTs contain narrow cavities (approximately 2–10 nm in diameter) in the center.
On the other hand, MWNTs synthesized by thermal decomposition of hydrocarbon gases (so-called chemical vapor deposition (CVD), see below) are in general comprised of defective graphene sheets and are sometimes curved and curled. Bamboo-like structures composed of a series of compartments with a metal catalyst at their tips are formed as shown in Figure 1.5 [9]. The graphite layers in a bamboo-structured MWNT are not parallel to the tube axis but are inclined to form stacked cones.
1.1.3 Thin-Walled CNTs
Double-wall carbon nanotubes (DWNTs or DWCNTs) consisting of two layers of graphene can be selectively prepared by arc discharge and CVD. Figure 1.6 shows a typical TEM image of DWCNTs produced by arc discharge in a He/H2 gas mixture with Fe–Co–Ni as catalyst and sulfur as promoter [10]. The diameter of DWCNTs is in the range 3–4 nm, that is, intermediate between those of SWNTs and thick MWNTs. The interlayer spacing between the outer and inner walls ranges from 0.37 to 0.39 nm, being about 10% wider than that of thick MWNTs. Due to the small diameter of DWCNTs, the electric voltage required for field emission from DWCNTs is as low as that for SWNTs, though DWCNTs are more robust against degradation during field emission than SWNTs because of the smaller curvature (i.e., more stable with the smaller strains) and the larger cross section (two layers) for electron flow.
1.2 Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes
Production methods of CNTs are roughly divided into three categories: (i) electric arc discharge between carbon electrodes, (ii) laser vaporization of a carbon target, and (iii) thermal decomposition of hydrocarbon gases or CVD. The arc discharge and CVD techniques are briefly described here. Concerning the laser ablation method, which is mainly used for the preparation of high-purity SWNTs, the details can be found in [11].
1.2.1 Arc Discharge
A direct current (DC) arc is almost exclusively used because it is amenable and provides a high yield of nanotubes, even though an alternating current (AC) arc can also evaporate carbon electrodes. Both the anode and the cathode are made of graphite rods for producing MWNTs, while a metal (or metal oxide) powder is impregnated into the anode for the production of SWNTs. The metal catalyzes the formation of SWNTs. Typical catalysts are Fe–Ni, Co–Ni, Y–Ni, and Rh–Pt [12].
Carbon electrodes are evaporated in a buffer gas (usually helium) at a desired pressure (200–600 Torr for helium gas). Since the anode surface is heated to a higher temperature (∼4000 K) than the cathode surface (∼3500 K), the anode is selectively consumed in the arc. The position of the anode tip must be adjusted in order to maintain the proper spacing (about 1 mm) between the electrodes. Approximately half of the evaporated carbon condenses on the tip of the cathode, forming a cylindrical hard deposit. MWNTs are obtained inside the cylindrical cathode deposit even without metal catalysts. The remaining carbon vapor condenses in a gas phase, forming soot. Fullerenes such as C60 and C70 are grown in the soot. When the catalyst metal is co-evaporated with carbon, SWNTs are formed and found in the soot deposited on the walls of the reaction chamber and on the surface of the cathode.
For the production of MWNTs, pure carbon is evaporated mainly in helium gas. Hydrogen gas and even air can also be employed as the working gas. In the latter case, relatively “clean” MWNTs are produced (i.e., the amount of byproducts such as carbon nanoparticles is very small [13]).
Radio frequency (RF) plasma heating of graphite in argon gas can be used to synthesize MWNTs, which are characterized by t...