
eBook - ePub
The Rayleigh-Ritz Method for Structural Analysis
Sinniah Ilanko, Luis Monterrubio, Yusuke Mochida
This is a test
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
The Rayleigh-Ritz Method for Structural Analysis
Sinniah Ilanko, Luis Monterrubio, Yusuke Mochida
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
A presentation of the theory behind the Rayleigh-Ritz (R-R) method, as well as a discussion of the choice of admissible functions and the use of penalty methods, including recent developments such as using negative inertia and bi-penalty terms. While presenting the mathematical basis of the R-R method, the authors also give simple explanations and analogies to make it easier to understand. Examples include calculation of natural frequencies and critical loads of structures and structural components, such as beams, plates, shells and solids. MATLAB codes for some common problems are also supplied.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es The Rayleigh-Ritz Method for Structural Analysis un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a The Rayleigh-Ritz Method for Structural Analysis de Sinniah Ilanko, Luis Monterrubio, Yusuke Mochida en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Sciences physiques y Mécanique. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
1
Principle of Conservation of Energy and Rayleigh’s Principle
The well-known principle of conservation of energy forms the basis of some common convenient analytical techniques in Mechanics. According to this principle, the total energy of a closed system remains unchanged. This means that in the absence of any losses due to friction etc., the sum of the total potential energy and the kinetic energy of a vibratory system will be a constant. Although in practice there will always be some damping, and hence dissipation of energy, for many mechanical systems such losses may be neglected. Such systems are called conservative systems.
The natural frequencies of conservative systems may be obtained by equating the maximum kinetic energy (Tm) to the maximum total potential energy (Vm) associated with vibration. The meaning of these energy terms is very important. To illustrate the principle of conservation of energy, and the meaning of the energy terms let us study some simple vibratory systems.
1.1. A simple pendulum
Consider the oscillatory motion of the simple pendulum consisting of a bob of mass m and a massless string of length L as shown in Figure 1.1. It would be at rest in a vertical configuration under gravity field. If it is given a small disturbance βm and then released, it will tend to vibrate about this equilibrium state. The restoring action of the gravity force will initiate a motion toward the equilibrium state but as the bob approaches the lowest point in its motion it has a velocity and therefore carries on swinging up on the other side until the gravity force causes it to come to a halt momentarily. In the absence of any damping forces, this motion would go on forever, but in reality the damping forces will help to put an end to this vibration after some time.
Figure 1.1. Simple pendulum

Assuming that energy loss associated with mechanical friction and aerodynamic resistance is negligible, we have two types of energy term to consider. These are the kinetic energy (denoted by T1, T2) where the subscripts 1 and 2 refer to states 1 and 2 respectively, and the potential energy (denoted by V1, V2). The kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the velocity and the potential energy is dependent on the vertical position of the bob.
The pendulum will have the maximum kinetic energy as the bob passes through the equilibrium state (state 1) at which time it will have the lowest potential energy. At the time of maximum excursion (state 2), the bob will be at its highest point, and therefore the system will have the maximum potential energy, but since it has no velocity its kinetic energy will be minimum. The potential energy can be defined arbitrarily by selecting a datum. In our example, the increase in the potential energy as the system changes from state 1 to state 2 is entirely associated with the vibration, and will be referred to as the maximum potential energy hereafter. As the bob returns to state 1 from state 2, it loses potential energy and gains kinetic energy. The maximum kinetic energy associated with vibration is the kinetic energy at state 1 minus the kinetic energy at state 2. (The latter is not necessarily absolutely zero, as the support point may have a velocity. In rotating systems care must be taken to ensure that the kinetic energy terms are calculated correctly.) Since the total energy is conserved, the maximum kinetic energy associated with vibration must be equal to the maximum total potential energy associated with vibration. The inclusion of the phrase “associated with vibration” is used here since terms such as “maximum” and “total” can otherwise cause confusion.
From the principle of conservation of energy:
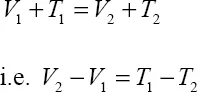
The gain in potential energy as the bob moves from state 1 to state 2 is the maximum potential energy associated with vibration and may be denoted by Vm.
V2–V1 = Vm
Similarly the maximum kinetic energy associated with vibration is:
[1.1] T1–T2 = Tm
From the above equations we have Vm = Tm
In applying the principle of conservation of energy for vibratory systems, it is sufficient to equate the maximum potential and kinetic energy terms associated with vibration.
To find the circu...