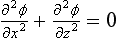![]()
Chapter 1
Introduction
The history of wind wave research is relatively short. Although there were basic developments last century (Airy, 1845; Stokes, 1847), a concerted effort really only began as a result of the military imperative of the Second World War. The work of Sverdrup, Munk and Bretschneider (Sverdrup and Munk, 1944a,b; Bretschneider, 1952a) provided the first observational data base, upon which, to base theories for the evolution of wind generated waves. This work was, however, largely empirical. A theoretical framework began to develop with the studies of wind-wave generation by Miles and Phillips (Miles, 1957; Phillips, 1957). A more complete understanding of the full evolution process, however, awaited the insight into nonlinear interactions provided by Hasselmann (Hasselmann, 1962).
By the mid 60s, the basic processes responsible for the evolution of the wind wave spectrum had been identified. An ability to accurately predict the evolution of the spectrum awaited an increase in the observational data base and advances in computational speed.
The goals of wind wave research are relatively well defined: to be able to predict the wind wave field and its effect on the environment. That environment could be natural (beaches, the atmosphere etc.) or imposed by human endeavour (ports, harbours, coastal settlements etc.). Although the goals are similar, the specific requirements of these various fields differ. For instance, coastal engineering activity may only require knowledge of the integral parameters of significant wave height and peak period, whereas studies of air-sea interaction will generally require a very detailed description of the full spectrum.
This book attempts to summarise the current state of this knowledge and to place this understanding into a common frame work. There are still many aspects of wind waves which are not fully understood. A notable example being wave breaking. Despite this, an impressive ability now exists to predict waves on both global and regional scales. Indeed, it is the author’s belief that the most significant source of error in deep water wave models is the driving wind. Further advances in our understanding of the physics of wave evolution will result in only marginal improvements in the prediction capability. In finite depth regions, knowledge is still relatively poor and further work is clearly required.
The past 20 years has also brought enormous advances in our abilities to measure the ocean wave field. In particular, satellite based remote sensing instruments can now provide a global, real time view of the wave field. The analysis of this growing observational data base is beginning to yield the first global wave climatologies needed for activities such as shipping and ocean engineering. In addition, the assimilation of these data into wave prediction models will begin to address the deficiencies of the forcing wind fields.
This book attempts to take a balanced approach between the pragmatic engineering view of requiring a short term result and the scientific quest for detailed understanding. Thus, it attempts to provide a rigorous description of the physical processes involved as well as practical predictive tools.
A basic assumption which is made throughout the text is that, to first order, waves can be assumed linear. Nonlinearities can be considered as perturbations to this linear solution. It follows from this assumption that waves can be considered in a spectral sense. As a result, fundamentally nonlinear descriptions have been largely ignored. This approach stems from the pragmatic view that the spectral representation of waves is the only approach which has developed a comprehensive predictive capability, even in shallow water where nonlinearities increase.
![]()
Chapter 2
Wave Theory
2.1 Introduction
As a pre-curser to the investigation of the properties of waves under the active forcing of the wind, it is essential to consider the more idealized case of the wave field propagating in the absence of any forcing. Even this highly idealized situation presents formidable mathematical difficulties and thus requires many simplifying assumptions to form a tractable solution. As the restrictions of these simplifying assumptions are gradually reduced the complexity of the solution increases. Only the simplest of these solutions will be considered here. Interest will focus on linear or Airy wave theory (Airy, 1845). Despite the apparently restrictive simplifying assumptions associated with this theory, its range of application is extensive. Linear wave theory will form the basic theoretical rationale for the remainder of this book.
2.2 Small Amplitude or Linear Theory
2.2.1 Governing Equations
In order to form a tractable solution the following simplifying assumptions are made:
1. The water is of constant depth, d and wave length, L (or period, T).
2. The wave motion is two-dimensional, which leads to long crested waves with constant height along the crests.
3. The waves are of constant form, that is, they do not change with time.
4. The fluid (water) is incompressible.
5. Effects of viscosity, turbulence, and surface tension are neglected.
6. The wave height, H is small compared to the wave length, L and the water depth, d (i.e. H/L < < 1 and H/d < < 1).
The limitations which these assumptions place on the resulting theory will be investigated in Section (2.4)
The governing equations to be solved represent the equations for conservation of mass and momentum. Conservation of mass can be written in terms of the Laplace Equation
where x and z are the horizontal and vertical coordinates, respectively, of the two-dimensional solution domain. The velocity potential, φ is defined in terms of the horizontal and vertical co...