
- 440 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This best-selling review guide consolidates the plethora of study materials and scattered information available into a single comprehensive source designed to prepare students for periodontal examinations as well as clinical practice. The material is presented in a clear question and answer format, with references to both classic and more recent literature on topics such as diagnosis, nonsurgical therapy, surgical therapy, regeneration, and implants, and answers are supplemented with relevant tables, illustrations, and pictures throughout. This revised second edition includes new figures, tables, and treatment planning cases, as well as a comprehensive review of the new classifications of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions, providing the most up to date information for those seeking board certification.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information

Background
Q: What is the evidence-based approach?
Evidence-based dentistry is the merging of clinically pertinent scientific evidence to the patient’s oral and medical condition and history as well as the dentist’s experience (Fig 1-1). The dentist uses the evidence to make sound decisions about diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Evidence-based decision making consists of formulating patient-centered questions (Population-Intervention-Comparison-Outcome [PICO]); examining and critically evaluating the evidence; and relating the evidence to practice.1
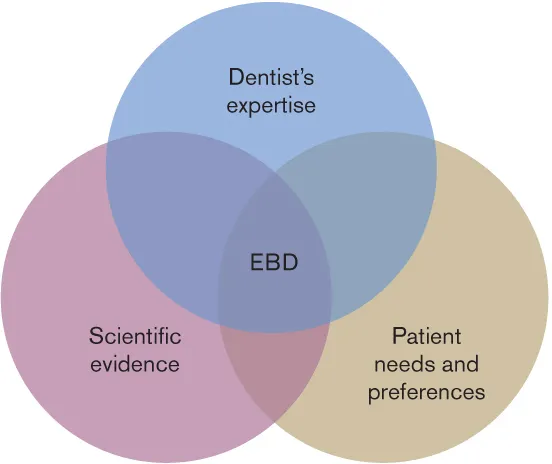
Fig 1-1 Three parts of the decision-making process. (Redrawn from the American Dental Association1 with permission.)
Q: What is the PICO question?
The PICO question is a question that includes a population to be examined, the nature of the intervention to be inspected, a comparison statement, and the type of outcome to be evaluated. It should be problem-focused and concise.
Example: In patients with horizontal alveolar ridge deficiencies (population), what is the effect of horizontal bone augmentation procedures (intervention) compared with controls (comparison) on peri-implant health (outcome)?
Q: What is the step-by-step process for making an evidence-based decision in a dental practice?
The steps involved in evidence-based decision making in a dental practice are shown in Fig 1-2.

Fig 1-2 Evidence-based decision making. (Based on data in Chiappelli et al.2)
Studies
Q: What are the different study types (ranked from highest level of evidence to lowest)?
The different types of studies are shown, ranked in order of highest to lowest level of evidence, in Fig 1-3.
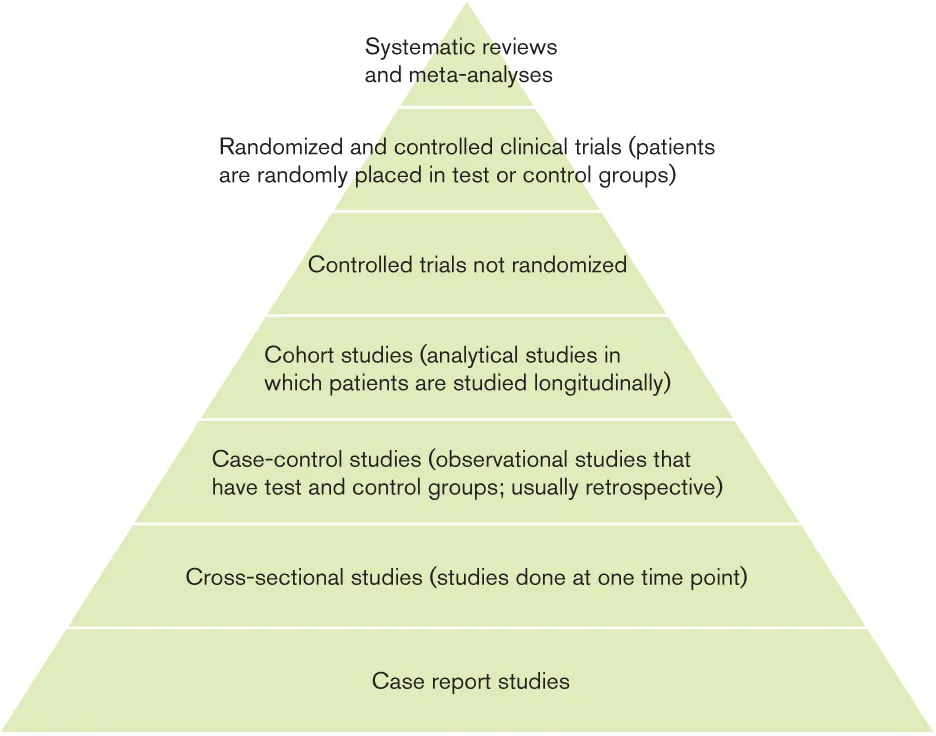
Fig 1-3 Different studies ranked from highest level of evidence to lowest. (Based on Nocini et al.3)
Q: Describe the difference between a cross-sectional study and a longitudinal study.
A cross-sectional study is done at one time point, whereas a longitudinal study ranges over a period, allowing temporal relationships to be investigated.
Q: What is the P value?
The P value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. The smaller the P value, the less likely the effect was due to chance. A P value less than or equal to .05 usually indicates statistical significance.
Q: What is the difference between sensitivity and specificity?
Sensitivity is the ability of a test to correctly identify diseased individuals. Specificity is the ability of a test to correctly identify a healthy individual.
For instance, the diagnostic sensitivity of a clinical parameter (suppuration, gingival plaque) in predicting disease was expressed as the proportion of sites showing attachment loss that also exhibited the given parameter. Diagnostic specificity was expressed as the proportion of sites not exhibiting the clinical parameter and not showing attachment loss.4
Q: What is the difference between internal and external validity?
The difference between internal and external validity is shown in Fig 1-4.
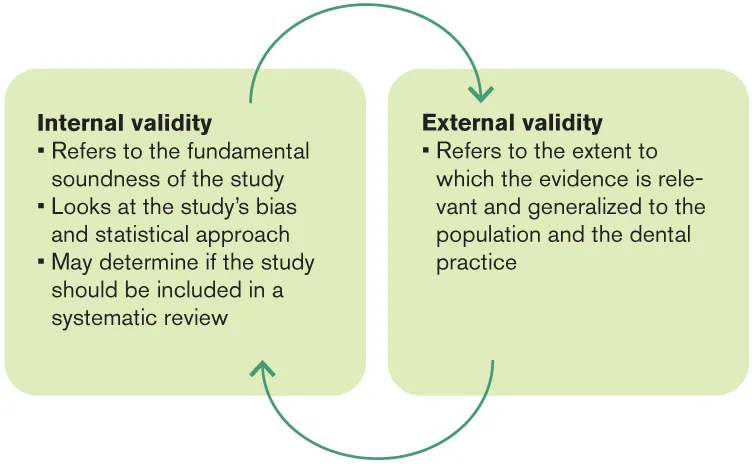
Fig 1-4 Internal and external validity.
Q: Why practice evidence-based dentistry?5
1. There are thousands of articles published monthly in dental magazines. It would take hundreds of hours to read the dental literature. Using evidence-based review databases eases the necessary time spent evaluating dental literature.
2. Practicing evidence-based dentistry keeps dentists current on recent evidence and practice standards.
3. A thorough and analytical literature review should be carried out before proceeding in clinical research.
References
1. American Dental Association. About EBD. https://ebd.ada.org/en/about. Accessed 10 October 2019.
2. Chiappelli F, Brant XMC, Oluwadara OO, Neagos N, Ramchandani MH. Introduction: Research synthesis in evidence-based clinical decision-making. In: Chiappelli F, Brant XMC, Neagos N, Oluwadara OO, Ramchandani MH (eds). Evidence-Based Practice: Toward Optimizing Clinical Outcomes. London: Springer, 2010:5.
3. Nocini PF, Verlato G, De Santis D, et al. Strengths and limitations of the evidence-based movement aimed to improve clinical outcomes in dentistry and oral surgery. In: Chiappelli F, Brant XMC, Neagos N, Oluwadara OO, Ramchandani MH (eds). Evidence-Based Practice: Toward Optimizing Clinical Outcomes. London: Springer, 2010:151.
4. Haffajee AD, Socransky SS, Goodson JM. Clinical parameters as predictors of destructive periodontal disease activity. J Clin Periodontol 1983;10:257–265.
5. Boston University Alumni Medical Library website. Why practice EBM? www.bumc.bu.edu/medlib/resources/...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Copyright Page
- Title Page
- About the Author
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Evidence-Based Dentistry
- 2 Periodontal Anatomy
- 3 Furcations
- 4 Epidemiology and Etiology
- 5 Pharmacology
- 6 Diagnosis
- 7 Prognosis
- 8 Occlusion
- 9 Nonsurgical Therapy
- 10 Surgical Therapy
- 11 Mucogingival Therapy
- 12 Regeneration
- 13 Implants
- 14 Inflammation
- 15 Oral Medicine
- 16 Oral Pathology
- 17 Lasers
- 18 Medical Emergencies
- 19 Treatment Planning
- Appendix
- Index
- Backcover
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Periodontal Review Q&A by Deborah A. Termeie in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Dentistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.