
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
David Jiles
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 626 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
David Jiles
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
A long overdue update, this edition of Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials is a complete revision of its predecessor. While it provides relatively minor updates to the first two sections, the third section contains vast updates to reflect the enormous progress made in applications in the past 15 years, particularly in magnetic recordin
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials von David Jiles im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Sciences physiques & Matière condensée. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Section II
Magnetism in Materials
Magnetic Phenomena on the Microscopic Scale
5 Magnetic Properties
We will now look at the causes of hysteresis in ferromagnets and how the variation of magnetization with magnetic field can be quantified in restricted cases such as at low field and in the approach to saturation. High-resolution measurements of the variation of M with H indicate that there are discontinuities. This is known as the Barkhausen effect. We will also consider the change in length of a ferromagnet as it is magnetized, that is, the magnetostriction, and discuss anisotropy in relation to magnetostriction.
We have shown in the previous chapter that most of the important macroscopic magnetic properties of ferromagnets can be represented on a B-H plot or hysteresis loop. From this, the magnetization can be calculated at every point on the hysteresis curve using the general formula B = μ0(H + M). As the magnetization curve is traversed, there are discontinuous, irreversible changes in the magnetization known as the Barkhausen effect after its discoverer. In recent years, the Barkhausen effect has become an important tool for investigating the microstructural properties of ferromagnetic materials.
One important bulk property of interest, which is not contained in the hysteresis plot, is the magnetostriction. This is the change in length of a material either as a result of a magnetic order (spontaneous magnetostriction) or under the action of a magnetic field (field-induced magnetostriction). This will also be discussed in this chapter.
5.1 HYSTERESIS AND RELATED PROPERTIES
5.1.1 INFORMATION FROM THE HYSTERESIS CURVE
Which are the most important macroscopic magnetic properties of ferromagnets?
From the hysteresis curve such as the one shown in Figure 5.1, we can define a number of magnetic properties of the material, which can be used to characterize the hysteresis loop. A question immediately arises: How many degrees of freedom are there in a hysteresis loop? Or to put the question another way: How many parameters are needed to characterize a hysteresis loop? Clearly, there is no general answer to this, but for the commonly encountered sigmoid-shaped hysteresis loop such as the one in Figure 5.1, we can start to enumerate the important properties and thereby make an estimate.
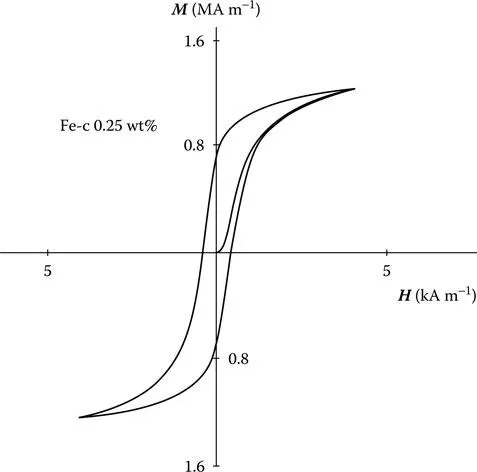
5.1.2 PARAMETRIC CHARACTERIZATION OF HYSTERESIS
Which are the parameters that can be used to define hysteresis?
First of all, the saturation magnetization M0 will give us an upper limit to the magnetization that can be achieved. At temperatures well below the Curie point, the technical saturation Ms can be used instead. The width of the loop across the H axis, which is twice the coercivity Hc, is also an independent parameter since this can be altered by heat treatment and hence is not dependent on Ms. The height of the curve along the B-axis, that is, the remanence is also an independent parameter since it is not wholly dependent on Ms and Hc. The orientation of the hysteresis curve on the B-H plane, which can be represented by , the slope of the curve at the coercive point, is also independent of the other parameters.
The hysteresis loss WH may also be an independent parameter as may the initial permeability . Finally, the curvature of the sides of the hysteresis loop, which although not immediately obvious as an independent parameter, is clearly not dependent on factors such ...