
Rheologische Messungen an Baustoffen 2019
Tagungsband zum 28. Workshop und Kolloquium, 13. und 14. März an der OTH Regensburg
- 116 Seiten
- German
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Rheologische Messungen an Baustoffen 2019
Tagungsband zum 28. Workshop und Kolloquium, 13. und 14. März an der OTH Regensburg
Über dieses Buch
Rheological measurements help to optimize the robust application of building materials. For the past few years applied rheology has been moving increasingly into the center of attention of the civil engineering society. Advanced testing equipment, intensive research and development work have all helped to deepen the understanding of this field. Last but not least, different conferences, such as the 28th Conference on the Rheology of Building Materials at the OTH, have helped to exchange the findings and establish valuable new contacts. Finding a compromise between rheological theory and its practical application has been the main topic of these 28 conferences.In these proceedings important rheological topics are addressed: specific applications of concrete such as self-compacting concrete, tremie concrete and sprayed concrete and mortar mixes for 3D printing, which all may be classified as self-compacting concretes. The consideration of time- and temperature-dependent changes in workability are essential for a successful application of these materials. Furthermore, the influence of the mixing energy used and the way of casting/spraying is of high importance for the rheological properties. The rheology of other concrete types is drastically changed due to the compaction by vibrators.Concrete rheology is controlled by its paste content and the rheology of the paste. Tests on pastes are easier to perform, as particle migration of aggregates is not present. However, one has to ask whether it is sufficient to use the results from the paste-measurements for the assessment of concrete and how the optimized paste content will be predetermined. The other question is which admixtures or additives may help to improve the very different application processes. Apart from using superplasticizer and stabilizers, entrained air is a powerful tool to influence rheology.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
production techniques | component geometry | textile | component |
laminate | 2D components | 2D textile, uncoated, degree of reinforcement almost arbitrarily controllable | facades, slabs |
pouring | 2D and simple 3D components | 2D or 3D textile, uncoated and coated, reinforcement content limited by tightness ofthe structure, spacers necessary | facades, formwork elements, sandwich panels |
shotcreting | 2D and 3D components | 2D textile, uncoated, degree of reinforcement almost arbitrarily controllable | plates in horizontal and vertical position, shells |
centrifuging | circular hollow sections | 2D or 3D textile, uncoated and coated, degree of reinforcement almost arbitrarily controllable | tubes, masts, piles |
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Cover
- Urheberrecht
- Inhalt
- Preface
- Scherinduzierte Partikelmigration: Relevanz bei Theologischen Messungen an Mörteln und Betonen
- Effect of the mixing time on the rheological parameters of cement pastes
- Advanced Admixtures to control Rheology of Tremie Concrete for Deep Foundations
- Analysis of the effect of various limestones in the cement composition on rheological properties of mortar
- Investigations on the influence of paste composition on the rheological properties of flowable mortars and concretes
- Rotatorische und oszillatorische Scherversuche zur Ermittlung steifigkeitsrelevanter Kenngrößen von Offshore-Vergussmörteln unterdem Einfluss des Early-Age Movement
- Rheology as a Tool to Characterize Dissolution and Reappearance of Air under Pressure in Cement Pastes
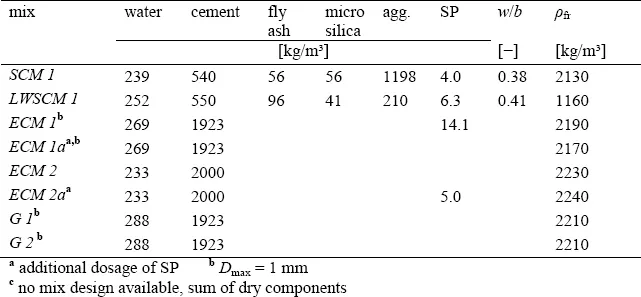
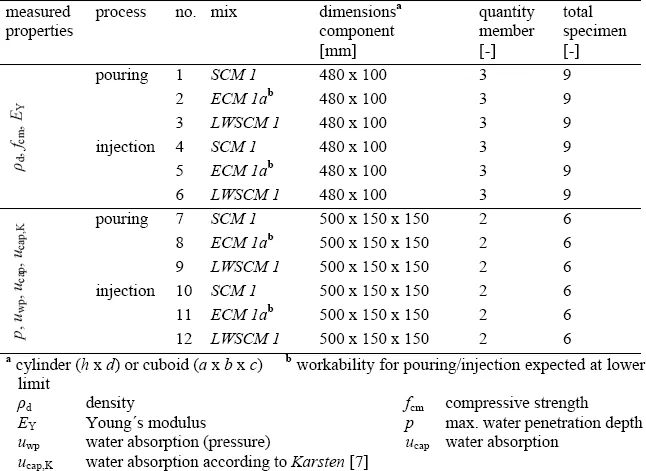
- The injection process - effecting mechanical properties?
- Adhesive mortars properties: Squeeze Flow and Contact Visualization
- Rheologische Unters, an Frischbetonmischungen für Spritzbeton