
eBook - ePub
Equine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding and Stud Management
Mina Davies Morel
This is a test
Buch teilen
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Equine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding and Stud Management
Mina Davies Morel
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Fully updated and revised, the fourth edition of this popular textbook provides a complete and comprehensive account of how to successfully breed horses. Beginning with a grounding in reproductive anatomy, it reviews endocrine control and selection for breeding mares and stallions, pregnancy, parturition and lactation.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Equine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding and Stud Management als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Equine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding and Stud Management von Mina Davies Morel im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Medicine & Equine Veterinary Science. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
1 The Reproductive Anatomy of the Mare
1.1 Introduction
This chapter details the anatomy and function of the mare’s reproductive system. Further accounts may be found in other texts, such as Ashdown and Done (1987), Frandson and Spurgen (1992), Ginther (1992), Kainer (1993), Dyce et al. (1996), Bone (1998), Senger (1999), Bergfelt (2000), Hafez and Hafez (2000), LeBlanc et al. (2004), Dascanio (2011) and Kainer (2011). The reproductive tract of the mare may be considered as a Y-shaped tubular organ with a series of constrictions along its length. The wall of the tract remains largely the same throughout: the outer perimetrium (serosa layer); the central myometrium (outer longitudinal and inner circular muscle layer); the inner endometrium (outer submucosa, inner mucosa and epithelial cell layer) lying against the lumen of the tract. The perineum, vulva, vagina and cervix can be considered as the outer protective structures, and lie mainly within the pelvic cavity, providing protection for the inner, more vital structures, the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries, which lie in the abdominal cavity and are responsible for fertilization and embryo development. Figure 1.1, taken after slaughter, shows the reproductive structures of the mare, and Figs 1.2 and 1.3 illustrate these diagrammatically. Each of these structures will be dealt with in turn in the following account.
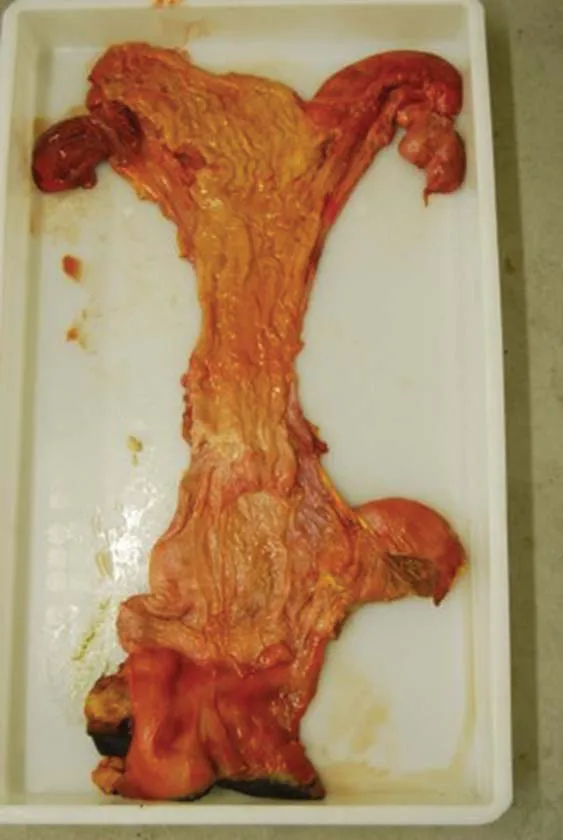
Fig. 1.1 The mare’s reproductive tract after slaughter and dissection (see also Fig. 1.2).
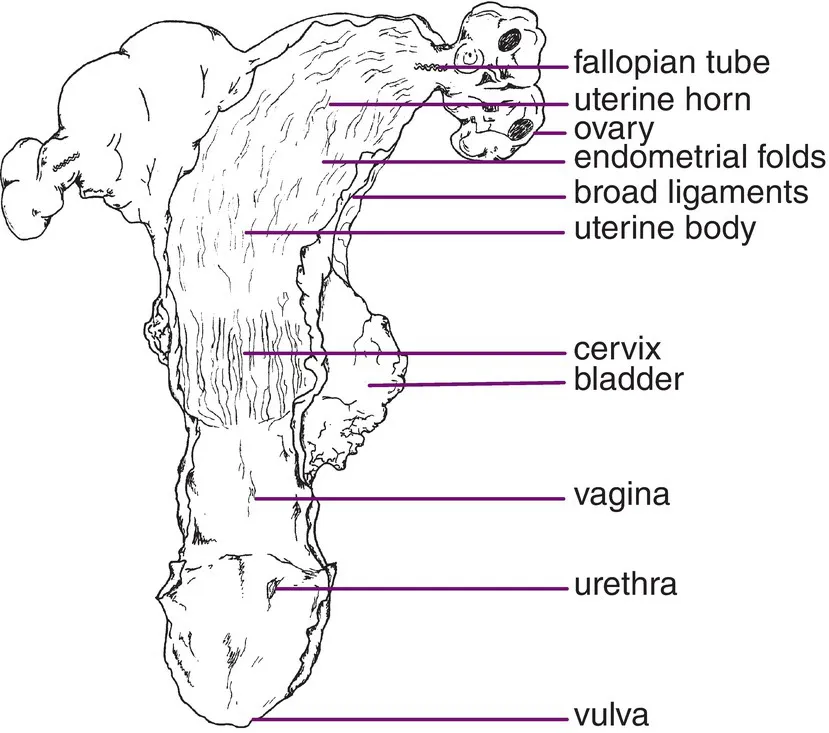
Fig. 1.2 The mare’s reproductive tract: a diagrammatic representation of Fig. 1.1.

Fig. 1.3 A lateral view (from the side) of the mare’s reproductive tract.
1.2 The Vulva
The vulva (Fig. 1.4) is the external area of the mare’s reproductive system, protecting the entrance to the vagina. The outer area is pigmented skin with the normal sebaceous and sweat glands along with the nerve and blood supply normally associated with the skin of the mare. The inner area, where the vulva is continuous with the vagina, is lined by stratified squamous epithelium plus mucous secreting cells enabling it to accommodate abrasion at mating. The upper limit of the vulva (the dorsal commissure) is situated approximately 7 cm below the anus. Below the entrance to the vagina, in the lower part of the vulva (the ventral commissure), lie the clitoris and the three clitoral sinuses (one medial and two lateral; Fig. 1.5). These sinuses are of importance in the mare as they provide an ideal environment for the harbouring of many venereal disease (VD) bacteria, in particular Taylorella equigenitalis (causal agent for contagious equine metritis (CEM)), but also Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Hence, this area is regularly swabbed in mares prior to covering, and, indeed, in the Thoroughbred industry such swabbing is compulsory (McAllister and Sack, 1990; Ginther, 1992; Horse Race Betting Levy Board, 2014). Within the walls or labia of the vulva lies the constrictor vulva muscle, running along either side of the length of the vulval lips. This muscle acts to maintain the vulval seal and to invert and expose the clitoral area during oestrus, known as winking (Ashdown and Done, 1987; Kainer, 1993). Another muscle, the constrictor vestibule muscle, encircles the vulva but is dorsally incomplete allowing the considerable expansion required at parturition (Easley, 1993; Dascanio, 2011). Lying just inside the ventral part of the labia is the vestibular bulb, an enlarged area of tissue thought to assist in holding the penis in place at copulation.
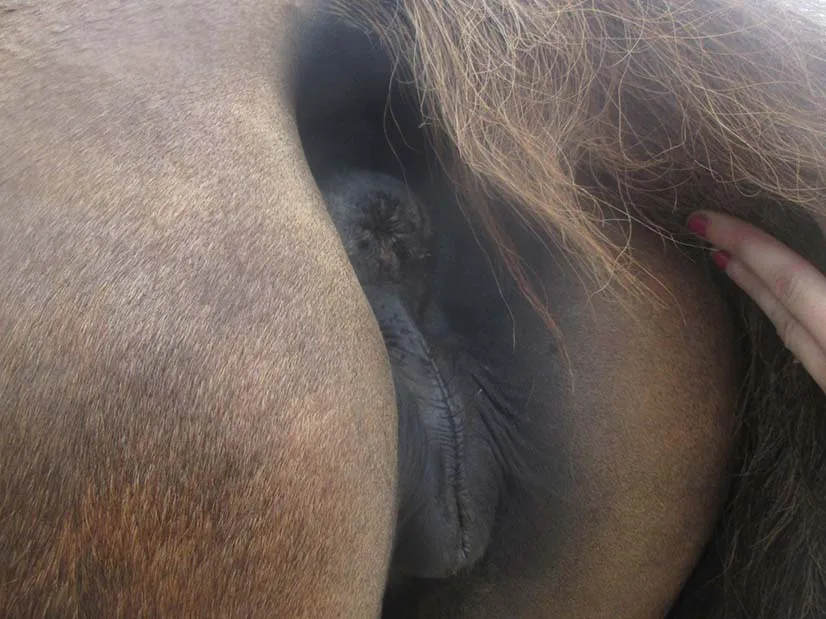
Fig. 1.4 The vulval area of the mare: in this instance, the conformation of the perineal area, is poor with the anus sunken cranially, opening up the vulva to faecal contamination.
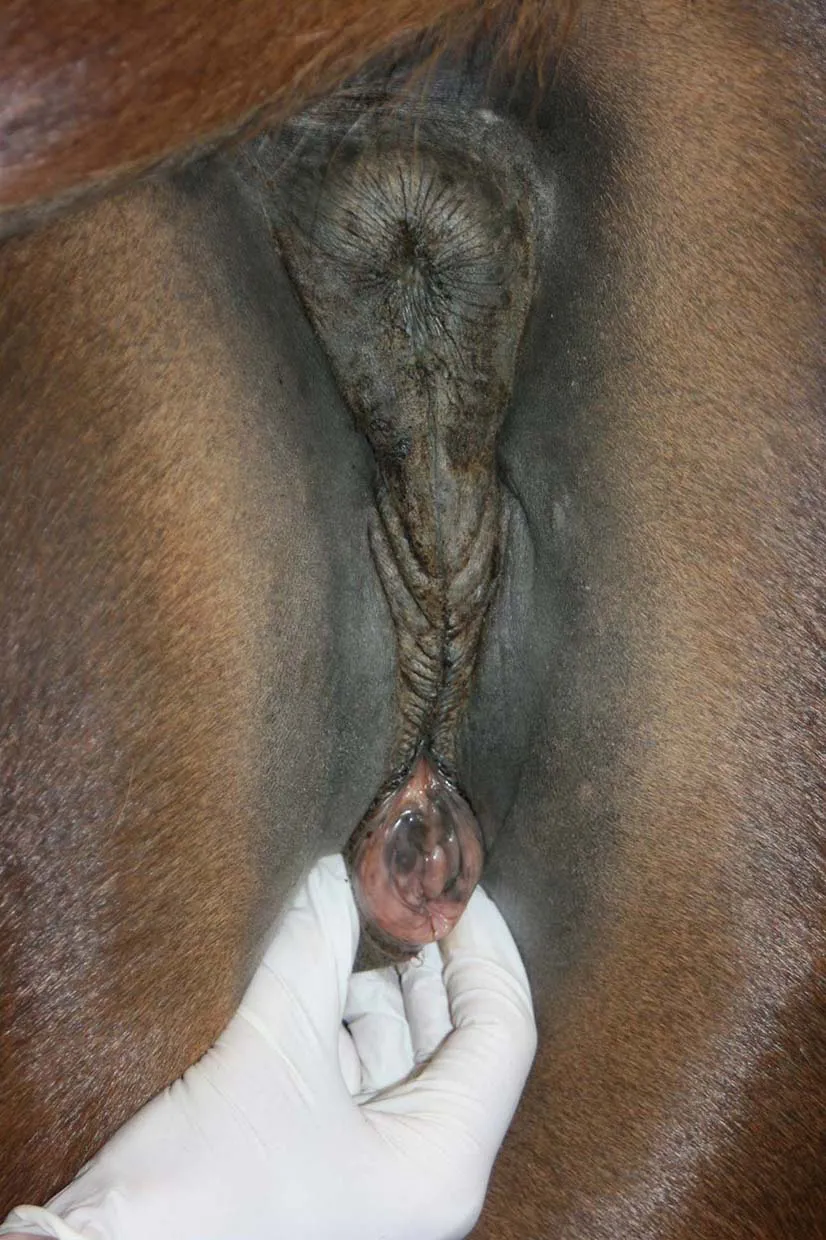
Fig. 1.5 The vulva of the mare showing the ventral commissure within which lie the clitoris and clitoral sinuses on either side.
1.3 The Perineum
The perineum is a rather loosely defined area in the mare, but includes the outer vulva and adjacent skin along with the anus and the surrounding area. In the mare, the conformation of this area is of clinical importance, due to its role in the protection of the genital tract from the entrance of air, solids and bacteria. Mal-conformation in this area predisposes the mare to a condition known as pneumovagina or vaginal wind-sucking, in which air is sucked in and out of the vagina through the open vulva. Along with this passage of air also go bacteria, which bombard the cervix, exposing it to unacceptably high levels of contamination, which it is often unable to cope with, especially during oestrus when it is more relaxed and so less competent. Passage of bacteria into the higher, more susceptible parts of the mare’s tract may result in bacterial infections, leading to endometritis (inflammation/infection of the endometrium lining of the uterus). Additionally, urovagina (collection of urine within the vagina) may also result if the reproductive tract slopes internally, further increasing the chance of bacteria breaching the cervix. Chapter 19 gives further details on the causes of VD infection in the mare, all of which adversely affect fertilization rates (Ginther, 1992; Easley, 1993; Kainer, 1993).
1.3.1 Protection of the genital tract
Adequate protection of the genital tract is essential to prevent the adverse effects of pneumovagina. There are three seals within the tract: the vulval seal, the vestibular or vaginal seal and the cervix; these are illustrated in Fig. 1.6.

Fig. 1.6 The seals of the mare’s reproductive tract during dioestrus.
The perineal area plus the constrictor vulva and constrictor vestibular muscles in the vulval walls form the vulval seal. The vestibular seal is formed by the natural collapsing and apposition of the vagina walls, where it sits above the floor of the upper pelvic bone (ischium), in an area sometimes called the vestibulovaginal fold; plus the hymen, if still present. The tight muscle and collagen ring within the cervix form the cervical seal. On the uterine side of the cervix there are mucocillary (mucous secreting ciliated) cells, equivalent to those in the respiratory tract, that produce a mucopolysaccaride blanket which provides a mucociliary clearance mechanism to clear debris and bacteria from the uterus and back through the cervix (Causey, 2007). Additionally positive abdominal pressure, typical of tight-bellied young horses or ponies, also helps to prevent the entry of air into the reproductive tract. This series of seals is affected by the conformation of an individual (Fig. 1.7) and also by the stage of the oestrous cycle (Fig. 1.8).

Fig. 1.7 The effect of conformation on the competence of the vulval, vestibular and cervical seals in the mare: (A) a low ischium (pelvic floor) results in an incompetent vestibular seal – in this case, the vulval seal is still competent, so infection risk is limited; (B) a low ischium results in an incompetent vestibular seal – in this case, the vulval seal is also incompetent, so infection risk is increased; and (C) an incompetent vestibular and vulval seal plus a sloping perineal area result in a significant infection risk, especially from faecal contamination.
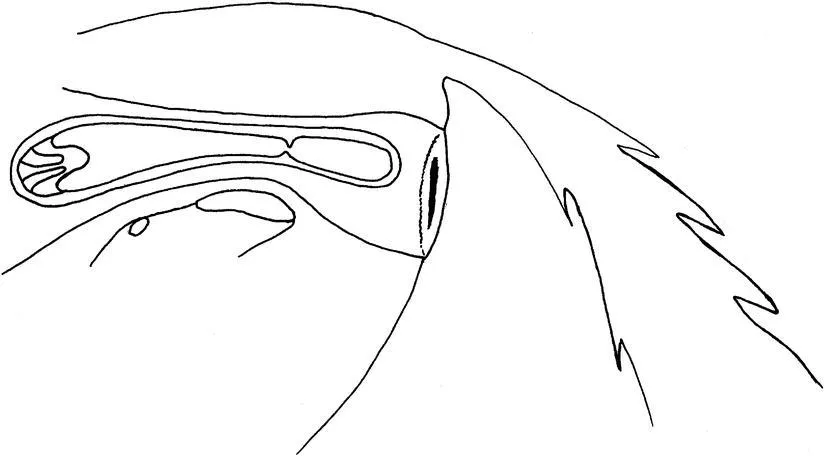

Fig. 1.8 The effect of oestrus on the competence of the vulval, vestibular and cervical seals in the mare: oestrus causes a relaxation of the seals and, therefore, an increase in infection risk.
The ideal conformation is achieved if 80% of the vulva lies below the pelvic floor. A simple test can be performed to assess this. If a sterile plastic tube is inserted through the vulva into the vagina and allowed to rest horizontally on the vagina floor, the amount of vulva lying below this tube should be approximately 80% in well-conformed mares. This technique is illustrated diagrammatically in Fig. 11.5.
If the ischium of the pelvis is too low, the vulva tends to fall towards the horizontal plane as seen in Fig. 1.7. This opens up the vulva to contamination by faeces, increasing the risk of uterine infection due to pneumovagina. Additionally, a low pelvis causes the vagina to slope inwards, preventing the natural drainage of urine at urination leading to urovagina, which further increases the risk of uterine infection. Lastly, negative abdominal pressure, typical of Thoroughbred type, multiparous mares with poor abdominal muscle tone, tends to draw air into the tract especially when the mare is movin...