
Flat Panel Display Manufacturing
Jun Souk, Shinji Morozumi, Fang-Chen Luo, Ion Bita, Jun Souk, Shinji Morozumi, Fang-Chen Luo, Ion Bita
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
Flat Panel Display Manufacturing
Jun Souk, Shinji Morozumi, Fang-Chen Luo, Ion Bita, Jun Souk, Shinji Morozumi, Fang-Chen Luo, Ion Bita
Über dieses Buch
An extensive introduction to the engineering and manufacture of current and next-generation flat panel displays
This book provides a broad overview of the manufacturing of flat panel displays, with a particular emphasis on the display systems at the forefront of the current mobile device revolution. It is structured to cover a broad spectrum of topics within the unifying theme of display systems manufacturing. An important theme of this book is treating displays as systems, which expands the scope beyond the technologies and manufacturing of traditional display panels (LCD and OLED) to also include key components for mobile device applications, such as flexible OLED, thin LCD backlights, as well as the manufacturing of display module assemblies.
Flat Panel Display Manufacturing fills an important gap in the current book literature describing the state of the art in display manufacturing for today's displays, and looks to create a reference the development of next generation displays. The editorial team brings a broad and deep perspective on flat panel display manufacturing, with a global view spanning decades of experience at leading institutions in Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and the USA, and including direct pioneering contributions to the development of displays. The book includes a total of 24 chapters contributed by experts at leading manufacturing institutions from the global FPD industry in Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Germany, Israel, and USA.
- Provides an overview of the evolution of display technologies and manufacturing
- Treats display products as systems with manifold applications, expanding the scope beyond traditional display panel manufacturing to key components for mobile devices and TV applications
- Provides a detailed overview of LCD manufacturing, including panel architectures, process flows, and module manufacturing
- Provides a detailed overview of OLED manufacturing for both mobile and TV applications, including a chapter dedicated to the young field of flexible OLED manufacturing
- Provides a detailed overview of the key unit processes and corresponding manufacturing equipment, including manufacturing test & repair of TFT array panels as well as display module inspection & repair
- Introduces key topics in display manufacturing science and engineering, including productivity & quality, factory architectures, and green manufacturing
Flat Panel Display Manufacturing will appeal to professionals and engineers in R&D departments for display-related technology development, as well as to graduates and Ph.D. students specializing in LCD/OLED/other flat panel displays.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Information
1
Introduction
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Historic Review of TFT‐LCD Manufacturing Technology Progress
1.2.1 Early Stage TFT and TFT‐Based Displays
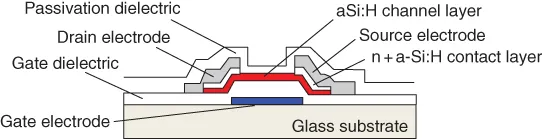
1.2.2 The 1990s: Initiation of TFT‐LCD Manufacturi...
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- List of Contributors
- Series Editor’s Foreword
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: TFT Array Process Architecture and Manufacturing Process Flow
- Chapter 3: Color Filter Architecture, Materials, and Process Flow
- Chapter 4: Liquid Crystal Cell Process
- Chapter 5: TFT‐LCD Module and Package Process
- Chapter 6: LCD Backlights
- Chapter 7: TFT Backplane and Issues for OLED
- Chapter 8A: OLED Manufacturing Process for Mobile Application
- Chapter 8B: OLED Manufacturing Process for TV Application
- Chapter 9: OLED Encapsulation Technology
- Chapter 10: Flexible OLED Manufacturing
- Chapter 11A: Metal Lines and ITO PVD
- Chapter 11B: Thin‐Film PVD: Materials, Processes, and Equipment
- Chapter 11C: Thin‐Film PVD (Rotary Target)
- Chapter 12A: Thin‐Film PECVD (AKT)
- Chapter 12B: Thin‐Film PECVD (Ulvac)
- Chapter 13: Photolithography
- Chapter 14A: Wet Etching Processes and Equipment
- Chapter 14B: Dry Etching Processes and Equipment
- Chapter 15: TFT Array: Inspection, Testing, and Repair
- Chapter 16: LCM Inspection and Repair
- Chapter 17: Productivity and Quality Control Overview
- Chapter 18: Plant Architectures and Supporting Systems
- Chapter 19: Green Manufacturing
- Index
- End User License Agreement