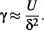![]()
Chapter 1
Fundamentals of Capillarity
1.1 Abstract
In this first chapter, the fundamentals of capillarity are presented. We follow a conventional approach [1], first presenting surface tension of an interface, which is the fundamental notion in capillarity theory; this notion leads naturally to that of wetting, then to Laplace’s law, and to the introduction of Young contact angles and capillary forces. Next, different applications of capillary forces are shown, and the problem of the measurement of surface tensions is presented.
1.2 Interfaces and Surface Tension
1.2.1 The Notion of Interface
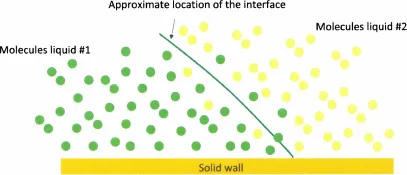
Mathematically speaking, an interface is the geometrical surface that delimits two fluid domains. This definition implies that an interface has no thickness and is smooth (i.e. has no roughness). As practical as it is, this definition is in reality a schematic concept. The reality is more complex, the boundary between two immiscible liquids is somewhat blurred and the separation of the two fluids (water/air, water/oil, etc.) depends on molecular interactions between the molecules of each fluid [2] and on Brownian diffusion (thermal agitation). A microscopic view of the interface between two fluids looks more like the scheme of figure 1.1. However, in engineering applications, it is the macroscopic behavior of the interface that is the focus of attention, and the mathematical concept regains its utility. At a macroscopic size, the picture of figure 1.1 can be replaced by that of figure 1.2, where the interface is a mathematical surface without thickness and the contact angle θ is uniquely defined by the tangent to the surface at the contact line.
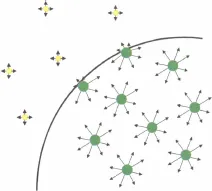
In a condensed state, molecules attract each other. Molecules located in the bulk of a liquid have interactions with neighboring molecules on all sides; these interactions are mostly van der Waals attractive interactions for organic liquids and hydrogen bonds for polar liquids like water [2]. On the other hand, molecules at an interface have interactions in a half space with molecules of the same liquid, and in the other half space interactions with molecules of the other fluid or gas (figure 1.3).
Consider an interface between a liquid and a gas. In the bulk of the liquid, a molecule is in contact with 4 to 12 other molecules depending on the liquid (4 for water and 12 for simple molecules); at the interface this number is divided by two. Of course, a molecule is also in contact with gas molecules, but, due to the low densities of gases, there are fewer interactions and less attraction than on the liquid side. The result is that there is locally a dissymmetry in the interactions, which results in an excess of surface energy. At the macroscopic scale, a physical quantity called “surface tension” has been introduced in order to take into account this molecular effect. The surface tension has the dimensions of energy per unit area, and in the International System it is expressed in J/m2 or N/m (sometimes, it is more practical to use mN/m as a unit for surface tension). An estimate of the surface tension can be found by considering the molecules’ cohesive energy. If U is the total cohesive energy per molecule, a rough estimate of the energy excess of a molecule at the interface is U/2. Surface tension is a direct measure of this energy excess, and if δ is a characteristic molecular dimension and δ2 the associated molecular surface area, then the surface tension is approximately
This relation shows that surface tension is important for liquids with large cohesive energy and small molecular dimension. This is why mercury has a large surface tension whereas oil and organic liquids have small surface tensions. Another consequence of this analysis is the fact that a fluid system will always act to minimize surface area: the larger the surface area, the larger the number of molecules at the interface and the larger the cohesive energy imbalance. Molecules at the interface always look for oth...