INTRODUCTION
Strategic planning facilitates the possibility of thinking about the future, visualizing new opportunities and threats, focusing on the organization's mission, and effectively guiding its course, facilitating direction and leadership. It also allows facing problems such as the allocation of human and financial resources. In relation to classic forms of management, strategic planning introduces a modern methodology.
This modern form of management requires deep knowledge of the organization, greater participation, improving communication and coordination between different levels, and improving management skills, among others.
For the reasons mentioned above, the investigation raises the following question.
How does strategic planning influence employees' job performance?
Nowadays, due to the changes and the new technologies that appear in the market that determine the development of more abilities, skills, and knowledge, organizations find themselves with the need to implement changes in their labor strategy when facing the challenges presented to them.
It is necessary for companies to develop new techniques for production, market, distribution, service, and customer service, for which human capital is needed, and thus assume the organizational challenges.
Within this context, the productivity and management of human capital in organizations will become key elements of survival; therefore, coordination, direction, motivation, and staff satisfaction are increasingly important aspects of the administrative process [1,2].
PLANNING
Planning is the process by which the company's executive bodies continually design the desirable future and select how to make it feasible; It is based on advanced decision-making that, in a systematic and complex way, is oriented to ensure the highest probability of achieving previously designed desired futures.
The planning process works as a global system, considering that all the functions and organizational levels of the company must be planned simultaneously and interdependently, using the methodology of systemic reasoning since the global system works through the joint interaction of its components. Planning is usually classified as strategic and tactical.
Technical planning aims to optimize the allocation of resources to the maximum consequence of compatible company objectives. It is known as programming and is linked to the third stage of budgeting, which refers to the specific time frame in which the accepted programs must be executed. Within the integral perspective of the planning process, budgets are the formalized quantitative and qualitative expression of the partial or global quota of the programs that must be executed in each period.
Three classes are distinguished:
- Optimal, which follows policies of maximization or minimization of the variables.
- Satisfactory, which refers to the level of objectives that, by consensus, satisfy the overall organization of the company.
- Adaptive, which emphasizes the planning process itself, highlighting its value for training and continuous learning.
The plan represents the set of explicit and coherent decisions to allocate resources to pre-established ends.
Planning represents the exercise (the concrete application) of the plan linked to the theoretical instrumentation required to transform the economy or society; for this reason, it is the concept of planning that will be taken during the investigation.
Strategic planning is nothing more than the process of relating the goals of an organization, determining the policies and programs necessary to achieve specific objectives on the way to those goals, and establishing the necessary methods to ensure that the policies and programs are executed, that is, is a formulated long-term planning process that is used to define and achieve organizational goals [3].
Its characteristics are:
- It is conducted or executed by high hierarchical levels.
- Establish a framework for the entire organization.
- It faces higher levels of uncertainty with respect to other types of planning.
- Generally, it covers long periods. The longer the period, the more irreversible the effect of a more strategic plan will be.
- Its parameter is efficiency.
The central objective of strategic planning is to get the most out of internal resources by selecting the environment where they are to be deployed and their deployment strategy. For example, it is about finding a market niche that the company can serve better than potential competitors; therefore, the application of resources is more beneficial than in other circumstances.
It is the antithesis of improvisation and a management style that reacts instead of making decisions based on a plan. Due to its characteristics, it allows the manager to grasp the future of his organization as it commits him to follow previously defined lines of action.
The intensity of planning will depend on different factors such as the anticipation with which a decision must be made, the difficulty of coordination in decision-making, the magnitude of deviations and the consequent changes to be introduced. Available resources cannot be ruled out.
The limits are defined according to the type of organization, the behavior of resources, and the type of activity in question. The short, medium, and long terms can be distinguished.
The long term encompasses items subject to planning such as products, profits, return on investment, cash flow, development, and staff training plans.
The medium term is the period in which the long-term plans are expressed in more detail: the plans for profits, sales, production, inventories, expenses, purchases and financial statements.
In the short term, in terms of planning, maximum detail is reached in everything related to planning: level of installed capacity, fixed costs, variable costs and others.
Problems due to lack of planning can be:
Ignorance of the company's progress, lack of control, only works in the short term, today there are no guidelines for action. There are no clear criteria for decision making and it is not possible to project the future of the organization, and critical situations get out of control.
To define any planning, organizations must first be clear about their mission and vision.
The Mission will be the raison d'être of the company and the Vision is the projection that gives orientation and strategic sense to the decisions, plans, projects, etc.
Another very important point during strategic planning is to carry out an analysis that allows to know those internal and external factors that can help or hinder the organization's operation.
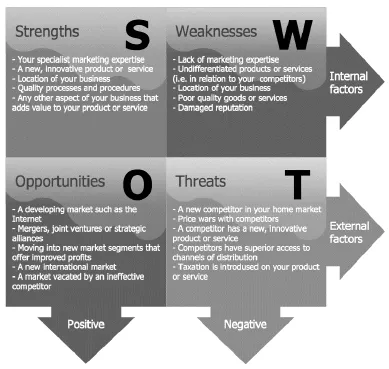
A recommended tool for detecting and classifying the types of opportunities and threats is the “SWOT” analysis (Fig. 1).
Strengths: These are the characteristics of the company that favor the achievement of its objective.
Weaknesses: They are those characteristics that constitute an internal obstacle to achieving the objectives.
Opportunities: These are those situations in the environment that would favor the achievement of the objectives.
Threats: Situations that arise in the company's environment that could negatively affect the possibilities of achieving the objectives.
Strategy selection can have several approaches, according to a traditional approach is the determination of the basic long-term goals and objectives in a company, together with the adoption of action plans and the allocation of resources necessary to achieve these purposes, always considering the boundary conditions or context. The basis of this approach is that a strategy is a means and an objective will be an outcome.
The implementation of the strategy should consider 4 components.
Fig. (1)) SWOT Analysis - created in the 1960s by Albert Humphrey at the Stanford Research Institute.
- Designing an organizational structure: the organization, in order to achieve the functioning of a strategy, needs to adopt the right structure, this implies assigning responsibilities for tasks and authority for decision making, analyzing the best way to do it (dividing the organization into subunits, distributing authority, distributing authority among different hierarchical levels, achieving integration among subunits).
- Design of control systems: the organization must decide on the best way to evaluate performance and control the actions of the sub-units, from market and production controls to bureaucratic and control alternatives through organizational culture, it also implies deciding on the type of compensation and incentive systems to establish for its employees.
- Matching strategy, structure and controls: Because different strategies and environments place different demands on an organization, they require different responses and structural control systems. If the company wants to be successful, it must find a balance between its strategy, structure and controls.
- Managing conflict, politics, and change: Organizational politics plays a key role, is endemic to organizations and different subgroups have their own agendas and conflicts, such as competing for a greater share of the organization's finite resources. organization. These conflicts can be resolved through the relative distribution of power among subunits or through a rational assessment of relative need.
Power struggles and coalition building are the major consequences of these conflicts and are, in fact, part of strategic management.
Strategic change tends to highlight these struggles, since any change causes an alteration in the distribution of power within an organization.
Once the strategy has been implemented, its execution must be monitored to determine the extent to which the strategic objectives are being achieved. This information is fed back to the corporate level through feedback loops, which provide the next phase of strategy implementation and formulation, serving to reaffirm existing corporate objectives and strategies or to suggest changes.
The combination of strengths and opportunities gives rise to potentials, which indicate the most promising lines of action for the organization and make it possible to detect and generate a competitive advantage.
A company is said to have a competitive advantage when its profit ratio is higher than the average for its industry.
The profit rate is usually defined as a given index and the fundamental determinant of a company's profit is its gross profit margin (GPM), which corresponds to the difference between total revenues (TI) and total costs (TC), divided by total costs: GPM = (TI-TC) / TC.
For a gross profit margin to be higher than the industry average, one of the following must occur:
- The company's unit price must be higher than that of the average company and its ...