
Manual of Equine Lameness
Gary M. Baxter
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Manual of Equine Lameness
Gary M. Baxter
Información del libro
MANUAL OF EQUINE LAMENESS
Discover a concise and accessible guide to diagnosing and managing lameness in horses
The revised Second Edition of Manual of Equine Lameness offers a concise and accessible manual of lameness diagnosis and treatment in horses. Perfect for use as a quick reference, this book provides straightforward access to the essentials of equine lameness, including the clinical assessment of the horse and commonly performed diagnostic nerve blocks and the most common conditions of the foot, forelimb, and hindlimb that may be contributing to the lameness. Current therapeutic options to treat lameness are also discussed, as well as guidance on how to manage musculoskeletal emergencies. The content has been distilled from the authoritative Seventh Edition of Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, and this new edition has been re-envisioned to be even quicker and easier to navigate than the previous version.
Color photographs and illustrations support the text, which presents lameness information most relevant to equine general practitioners, mixed animal practitioners, and veterinary students. A companion website offers videos that focus on the clinical examination of the horse and select diagnostic blocks and relevant anatomy. Diagnostic and treatment material has been revised from the previous edition to include the most up-to-date information.
Readers will find:
- A thorough introduction to the assessment of the lame horse, including history, visual exam, palpation, subjective and objective assessments of lameness, perineural anesthesia, and intrasynovial anesthesia
- An exploration of common conditions of the foot, including the navicular region and soft tissue injuries, coffin joint and distal phalanx conditions, and laminitis
- Discussions of the most common conditions of the forelimb, including the pastern, fetlock, metacarpus/metatarsus, carpus, antebrachium, elbow, and humerus, as well as the shoulder and scapula
- Discussions of common conditions of the hindlimb and axial skeleton
- A review of therapeutic options to treat lameness conditions
- How to manage musculoskeletal emergencies in the horse
Ideal for veterinary students, early career equine practitioners, and mixed animal veterinarians, the Second Edition of Manual of Equine Lameness is an indispensable reference for any veterinarian seeking a concise one-stop reference for equine lameness.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
1
Assessment of the Lame Horse
Introduction
- Lameness is an indication of a structural or functional disorder in one or more limbs or the axial skeleton that is evident while the horse is standing or at movement.
- Lameness is a clinical sign, not a disease.
- Lameness can be caused by trauma (single event or repetitive work), congenital or acquired anomalies, developmental defects, infection, metabolic disturbances, circulatory and nervous disorders, or any combination of these.
- It is important to differentiate between lameness resulting from pain and nonpainful alterations in gait, often referred to as “mechanical lameness,” and lameness resulting from neurologic (nervous system) dysfunction.
- Most lameness in horses is due to pain during weight‐bearing, with shifting of load away from the source limb onto the other non‐ or less affected limbs.
- The detection of clinical signs of lameness is primarily the recognition of an asymmetric gait in the horse.
- The primary objectives of a lameness examination are to determine:
- Whether the horse is lame.
- Which limb or limbs are involved?
- The site or sites of the problem.
- The specific cause of the problem.
- The appropriate treatment and/or rehabilitation.
- The prognosis for recovery.
- The steps to perform a routine or traditional lameness examination include
- Complete history including signalment and use.
- Visual exam of the horse at rest.
- Palpation of the musculoskeletal system including hoof tester examination of the feet.
- Observation of the horse in motion (usually at a straight walk and trot/lope followed by circling) with or without objective lameness evaluation tools.
- Observation of the horse under saddle or in work if necessary.
- Manipulative tests such as flexion tests.
- Diagnostic anesthesia, if necessary.
- Diagnostic imaging.
Adaptive Strategies of Lame Horses
- With most lameness conditions, the horse attempts to “unload” the lame limb during weight‐bearing or the stance phase of the stride. As an example, in horses with chronic lameness, the limb with the flatter hoof is thought to exhibit higher vertical loads because it is the non‐lame limb (Figure 1.1).
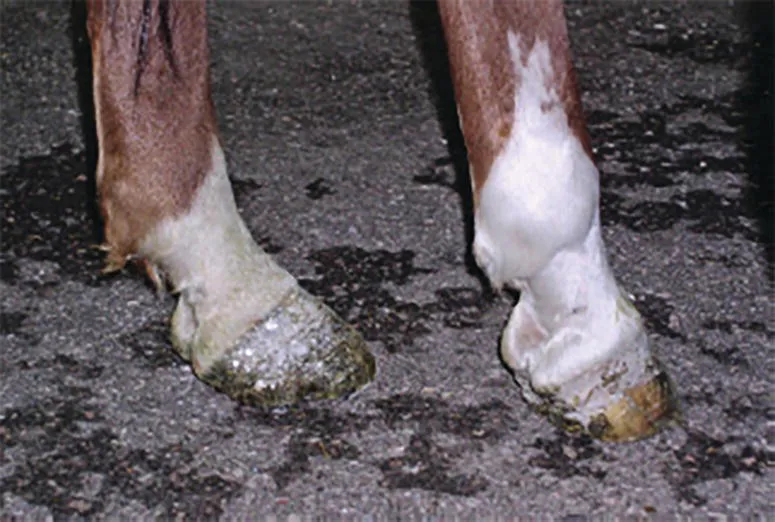 Figure 1.1 Chronic hindlimb lameness that has resulted in a wide flat foot on the sound limb (LH) and a narrow, upright hoof on the lame limb (RH).
Figure 1.1 Chronic hindlimb lameness that has resulted in a wide flat foot on the sound limb (LH) and a narrow, upright hoof on the lame limb (RH). - Horses accomplish this by abnormal movement of a body part (head nod or pelvic hike), weight shifting (to the contralateral or diagonal limb or torso), change in joint angles (lack of fetlock extension), and alterations in foot flight. Detecting these compensatory movements is an integral part of lameness diagnosis.
- The most consistent compensatory movements that are observed in lame horses are the vertical displacement and acceleration of the head in forelimb lameness and of the sacrum and tuber coxae in hindlimb lameness.
- More subtle lameness causes fewer compensatory changes, making lameness diagnosis more difficult. Although these gait changes may be difficult to appreciate during visual examination of a lame horse, it should be remembered that the primary adaptive strategy of the horse is to redistribute load to compensate for pain in a limb without causing an overload situation in other limbs.
Classification of Lameness
- In most cases, there is a primary or baseline lameness that contributes to the most obvious gait abnormalities. Compensatory, secondary, or complementary lameness results from overloading of the other limbs as a result of the primary lameness.
- Lameness may also be classified according to when it occurs (or is best observed) within the stride – i.e. stance, swing, pushoff, etc.
- Visual observation of the gait can usually determine whether the lameness is supporting limb, swinging limb, or mixed. However, because of the many adaptive strategies that occur in lame horses, some clinicians feel that mixed lameness occurs most commonly in horses.
- The different classifications of lameness are:
- Supporting limb lameness: Apparent when the foot first contacts the ground or when the limb is supporting weight (stance phase). This is by far the most common type of lameness identified in the horse.
- Swin...