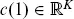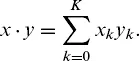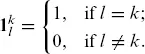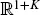Asset Pricing Theory
Costis Skiadas
- 368 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Asset Pricing Theory
Costis Skiadas
Información del libro
Asset Pricing Theory is an advanced textbook for doctoral students and researchers that offers a modern introduction to the theoretical and methodological foundations of competitive asset pricing. Costis Skiadas develops in depth the fundamentals of arbitrage pricing, mean-variance analysis, equilibrium pricing, and optimal consumption/portfolio choice in discrete settings, but with emphasis on geometric and martingale methods that facilitate an effortless transition to the more advanced continuous-time theory.
Among the book's many innovations are its use of recursive utility as the benchmark representation of dynamic preferences, and an associated theory of equilibrium pricing and optimal portfolio choice that goes beyond the existing literature. Asset Pricing Theory is complete with extensive exercises at the end of every chapter and comprehensive mathematical appendixes, making this book a self-contained resource for graduate students and academic researchers, as well as mathematically sophisticated practitioners seeking a deeper understanding of concepts and methods on which practical models are built.
- Covers in depth the modern theoretical foundations of competitive asset pricing and consumption/portfolio choice
- Uses recursive utility as the benchmark preference representation in dynamic settings
- Sets the foundations for advanced modeling using geometric arguments and martingale methodology
- Features self-contained mathematical appendixes
- Includes extensive end-of-chapter exercises
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
PART ONE
SINGLE-PERIOD ANALYSIS
CHAPTER ONE
Financial Market and Arbitrage
1.1 MARKET AND ARBITRAGE