
Introduction to Automotive Engineering
R. Sakthivel, Faisal O. Mahroogi, S. Narayan, S. Abudbaker, M. U. Kaisan, Youssef Alammari
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Introduction to Automotive Engineering
R. Sakthivel, Faisal O. Mahroogi, S. Narayan, S. Abudbaker, M. U. Kaisan, Youssef Alammari
Información del libro
The automotive industry is one of the largest and most important industries in the world. Cars, buses, and other engine-based vehicles abound in every country on the planet, and it is continually evolving, with electric cars, hybrids, self-driving vehicles, and so on. Technologies that were once thought to be decades away are now on our roads right now. Engineers, technicians, and managers are constantly needed in the industry, and, often, they come from other areas of engineering, such as electrical engineering, process engineering, or chemical engineering. Introductory books like this one are very useful for engineers who are new to the industry and need a tutorial.
Also valuable as a textbook for students, this introductory volume not only covers the basics of automotive engineering, but also the latest trends, such as self-driving vehicles, hybrids, and electric cars. Not only useful as an introduction to the science or a textbook, it can also serve as a valuable reference for technicians and engineers alike. The volume also goes into other subjects, such as maintenance and performance. Data has always been used in every company irrespective of its domain to improve the operational efficiency and performance of engines. This work deals with details of various automotive systems with focus on designing various components of these system to suit the working conditions on roads.
Whether a textbook for the student, an introduction to the industry for the newly hired engineer, or a reference for the technician or veteran engineer, this volume is the perfect introduction to the science of automotive engineering.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 Classification of Motor Vehicle
1.1.1 Based on Type of Roads
- Guided and Non-guided vehicles Guided Motor vehicles move along a fixed guide way; that includes railway vehicles. Non-guided motor vehicles move in any direction. The non-guided motor vehicles are the subject of this book.
- Classification according to Running gear – Single Track motor vehicles and Multi-Track motor vehicles
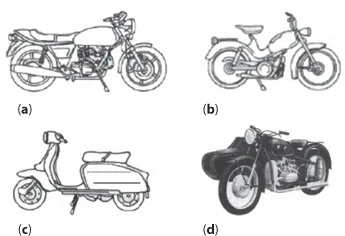
Single Track motor vehicles are motor vehicles with two wheels with or without a sidecar. Examples: Motorcycle – Any two-wheeled vehicle with or without a sidecar.
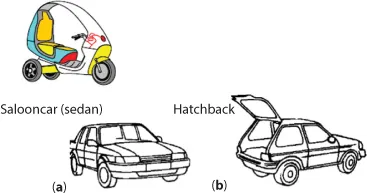
- Salooncar (sedan) –This is a type of motor car in which the space for driver and passengers is cut off from other areas.
- Hatchback car having a large sloping back.
- Pick-up (also pickup) – it is a small truck commonly used by operators.
- Van - covered vehicle, with no side windows, for transporting goods or people.
- Truck (UK Lorry) - large strong motor vehicle for transporting goods, soldiers, etc., by road.
- Tractor fitted with an endless belt passing round the wheels of a tractor enabling it to travel over rough ground.
- Car - Motor vehicle intended for carrying a maximum of 9 passengers with luggage.
1.1.2 Buses
- Microbus: The capacity of microbuses is approximately 25 passengers.
- City buses (Urban buses): are designed and equipped for driving regularly scheduled in-city and suburban routes. Due to short intervals between stops in local traffic, facilitation of rapid passenger turnover by means of low steps, wide doors and as low a vehicle floor as possible, is particularly important.
- Tour buses (Long-distance coach): are designed to provide a comfortable ride over long distances. Tour buses have large luggage compartments from front to rear below the floor.
- General-purpose cargo trucks: with an open drop-sided body used for carrying bulk and packaged goods.
- Special-purpose trucks: with bodies adapted for a certain kind of work, e.g., dump trucks with tiltable bodies used to carry viscous and bulk materials, or with bodies specially adapted for transporting peat, cement, mixed fodder, grain, cotton, cattle, gasoline, milk, etc.
- Extra-light-duty trucks: up to 0.75 Ton, built on the chassis of passenger cars and used for deliveries of light loads in the communication and communal services and in trade.
- Light-duty vehicles: from 0.75 to 2.5 Ton, that work in trade, at industrial enterprises and in agriculture, hauling light loads. They also serve as cargo taxis.