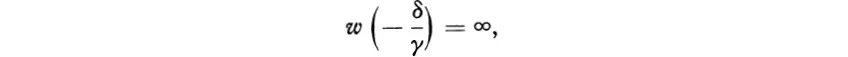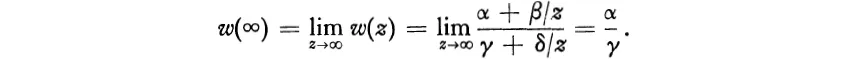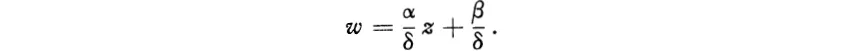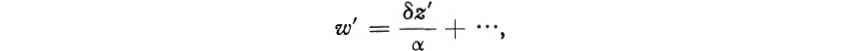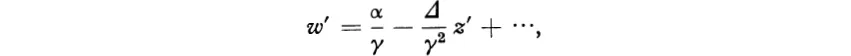![]()
[ I ]
Discontinuous Groups
An analytic function f is called automorphic with respect to a group Γ of transformations of the plane if f takes the same value at points that are equivalent under Γ. That is,
for each V ∈ Γ and each z ∈ D, the domain of f. If we want to have nonconstant functions f, we must assume there are only finitely many equivalents of z lying in any compact part of D. This property of Γ is known as discontinuity.
The most important domain for f from the standpoint of applications is the upper half-plane † H. Now from (1) with f analytic in H we deduce that V is analytic in H and maps H into itself. It is natural to require that V be one-to-one in order that V−1 should be single-valued. Hence F is a linear-fractional transformation. The group Γ will therefore be a group of linear-fractional transformations, or as we shall call them, linear transformations.
The present chapter is devoted to a study of discontinuous groups of linear transformations.
1. Linear Transformations
1A. A linear transformation is a nonconstant rational function of degree 1; that is, a function
where α, β, γ, δ are complex numbers and z is a complex variable. The function w is defined on all of the complex sphere Z except z = −δ/γ and z = ∞. With the usual convention that w/0 = ∞ for u ≠ 0, we have
and we obtain w(∞) by continuity:
In particular, −δ/γ will be ∞ if and only if γ = 0, and in that case α/γ = ∞: the infinite points of the two planes then correspond under the mapping w.
As a rational function, w is regular in Z except for a simple pole at z = −δ/γ. Suppose γ = 0. Then necessarily δ ≠ 0, α ≠ 0 (because of αδ − βγ ≠ 0) and
Hence dw/dz = α/δ ≠ 0 and w is conformal at every finite z. At infinity we must use the uniformizing variables z′ = l/z, w′ = 1/w; then we find that
and w′ is conformal at z′ = 0, which by definition means that w is conformal at z = ∞.
If γ ≠ 0, we have
hence dw/dz ≠ 0 and w is conformal except possibly at z = −δ/γ, z = ∞. At z = − δ/γ we must use the variables z′ = z + δ/γ, w′ = 1/w:
so that (dw′/dz′)z = 0 ≠ 0. At z = ∞ the correct variables are z′ = 1/z, w′ = w and we get
yielding the same conclusion.
Solving (2) for z we get
which is also a linear transformation and so is defined on the extended w-plane. The mapping z → w is therefore onto and hence one-to-one, and we may write z = w−1.
Putting these results together we can assert:
THEOREM. The linear transformation (2) is a one-to-one conformal mapping of all of Zon itself.
For this reason a linear transformation is also called a con...