
eBook - ePub
Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing
Karen Blair
This is a test
- 224 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing
Karen Blair
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
Children?s nurses must develop the crucial skills of correct medicines management and calculations in order to provide safe care to their patients. This book specifically supports pre-registration students in meeting the required competencies for medicines management needed to pass formal assessment and qualify as a children?s nurse. It is clearly structured around the NMC Essential Skills Clusters for medicines management, covering legal aspects, drugs calculations, administration, storage, record keeping, introductory pharmacology, patient communication and contextual issues in medication. The book is written in user-friendly language and uses patient scenarios to explain concepts and apply theory to practice.
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing par Karen Blair en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Medicina et Habilidades de enfermería. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
Chapter 1
Calculating children’s medicines
Chapter aims
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- estimate what a reasonable dose would be;
- demonstrate a sound understanding of the metric system and SI units of mass and volume;
- calculate paediatric drug doses;
- calculate rates for intravenous fluids;
- demonstrate an awareness of professional decision making when administrating medicines.
Case study
Many years ago, as a fairly newly qualified children’s nurse on night duty, I was dealing with a seriously ill baby admitted with meningitis and was supporting a consultant paediatrician and a doctor who was relatively inexperienced in paediatrics. The consultant asked me to prepare the intravenous antibiotics, but the less experienced doctor insisted he would do this himself and did not require my help. The drugs were prepared and administered to the baby by the less experienced doctor swiftly, as the situation warranted, without checking with me or the consultant. As soon as the baby was stabilised, I started tidying up the treatment area, including the drugs used, and picked up an empty gentamicin vial and asked the doctor where it had all gone. He immediately realised his error, as he had mistakenly administered the whole vial to the baby, which was four times the recommended dose. Thankfully the baby recovered, but needed very close monitoring for drug toxicity, which could lead to kidney damage and hearing loss.
Introduction
The above case study highlights the important factors children’s nurses should be aware of when calculating and administering medicines to children. Unlike for most adult patients, children’s doses need to be calculated on an individual basis according to their age, weight or body surface area. A drug miscalculation in a child can have catastrophic effects and all care needs to be taken to avoid this. As a children’s nurse you must have an awareness of what a sensible dose would be for the children in your care, and guide other professionals and parents. You need to be confident and skilled in your ability to calculate doses in all situations.
This chapter will start by reviewing the metric system in order that you are able to understand the basic units of measurement used in the prescribing of drugs and how drug strengths are expressed, including percentages and units. You should feel comfortable about converting from one unit of measurement to another, and understand the terms of expression in medicines. As most drugs are prescribed according to a child’s weight, converting weights from imperial to metric will be covered and vice versa, including methods of estimating a child’s weight in an emergency situation. This will help you always to have in mind what is a sensible estimate of weight at different ages, so you can be confident the recorded weight on the child’s drug chart is correct.
The chapter covers the calculation of tablets and capsules, and the more commonly used liquid medicines and intravenous fluids, and how to work out if the prescribed dose or rate is correct for the child. It is essential that the children’s nurse administering the dose is capable of checking the calculation and has an awareness of what a reasonable dose would be. Throughout the chapter there will be worked examples in order to demonstrate the methods used and activities for you to practise the skills needed to gain competence.
The metric system
In order to calculate medicine dosages safely, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the units of measurements used in the prescribing and dispensing of drugs. The strength of medicines should always be expressed using the standard metric system of weights and measures. The basic units used in clinical practice derive from the Système International (SI). The SI units for weight (mass) are shown in Table 1.1 and those for volume in Table 1.2.
Note that nanograms and picograms are rarely used in clinical practice.
The terms ‘micrograms’, ‘nanograms’ and ‘picograms’ should NOT be abbreviated but always written in full. This is to prevent medication error attributable to abbreviations. Abbreviating micrograms as µg (the official abbreviation for microgram in the SI system) can be mistaken for mg and lead to a one thousandfold dosage error.
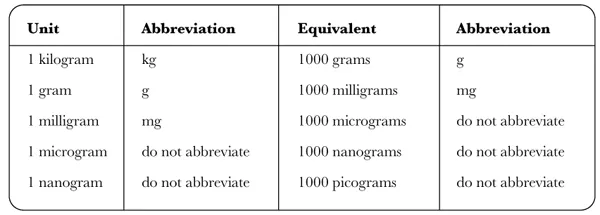
Table 1.1: The SI units for weight (mass)
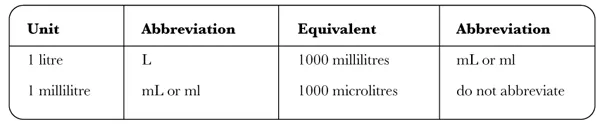
Table 1.2: The SI units for volume
Note that the term ‘millilitre’ (ml or mL) is used in medicine and pharmacy rather than cubic centimetre abbreviated as ‘cc’, as this can be mistaken for ‘u’ (units) when poorly written.
The term ‘litre’ is generally not abbreviated to avoid error. It is safer to express volume in millilitres in order to avoid the unnecessary use of...
Table des matières
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Foreword
- About the author
- Introduction
- 1 Calculating children’s medicines
- 2 Legal and ethical issues in children’s medicines management
- 3 Holistic care and treatment options in children’s nursing
- 4 Knowledge of children’s medicines and their actions
- 5 Storing, ordering and receiving medicines in children’s nursing
- 6 Medicines administration in children’s nursing
- 7 Working in partnership with parents, carers and children in medicines management
- 8 Keeping up to date with evidence-based practice
- Glossary
- References
- Index
Normes de citation pour Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing
APA 6 Citation
Blair, K. (2011). Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing (1st ed.). SAGE Publications. Retrieved from https://www.perlego.com/book/1431496/medicines-management-in-childrens-nursing-pdf (Original work published 2011)
Chicago Citation
Blair, Karen. (2011) 2011. Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing. 1st ed. SAGE Publications. https://www.perlego.com/book/1431496/medicines-management-in-childrens-nursing-pdf.
Harvard Citation
Blair, K. (2011) Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing. 1st edn. SAGE Publications. Available at: https://www.perlego.com/book/1431496/medicines-management-in-childrens-nursing-pdf (Accessed: 14 October 2022).
MLA 7 Citation
Blair, Karen. Medicines Management in Children′s Nursing. 1st ed. SAGE Publications, 2011. Web. 14 Oct. 2022.