
The Paracellular Channel
Biology, Physiology, and Disease
Jianghui Hou
- 248 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
The Paracellular Channel
Biology, Physiology, and Disease
Jianghui Hou
À propos de ce livre
The Paracellular Channel: Biology, Physiology and Disease serves as the first volume to offer a cohesive and unifying picture of the critical functions of paracellular channels (tight junctions) in different tissues. This new class of ion channel utilizes a completely different mechanism to create ion passage pathways across the cell junction. This volume outlines common principles that govern the organization and regulation of these diverse cellular structures, describes the methodology of study, and highlights the pathophysiologic consequence of abnormal structure and functions of the paracellular channels in human diseases.
Coverage includes biochemical, biophysical, structural, physiologic analyses of the paracellular channel, and new technologies for recording and characterization.
- Offers integrated coverage of all key aspects of the paracellular channel, an understudied field that may hold key insights into some of the most mysterious aspects of physiology
- Targets different levels of expertise, spanning from graduate students, interns and clinical fellows, to seasoned researchers that study functions, regulation and dysfunctions of different tissue barriers
- Provides a cohesive and unifying picture that describes the critical functions of paracellular channels (tight junctions) in different tissues
Foire aux questions
Informations
Introduction
Abstract
Keywords
1.1 A new class of ion channel
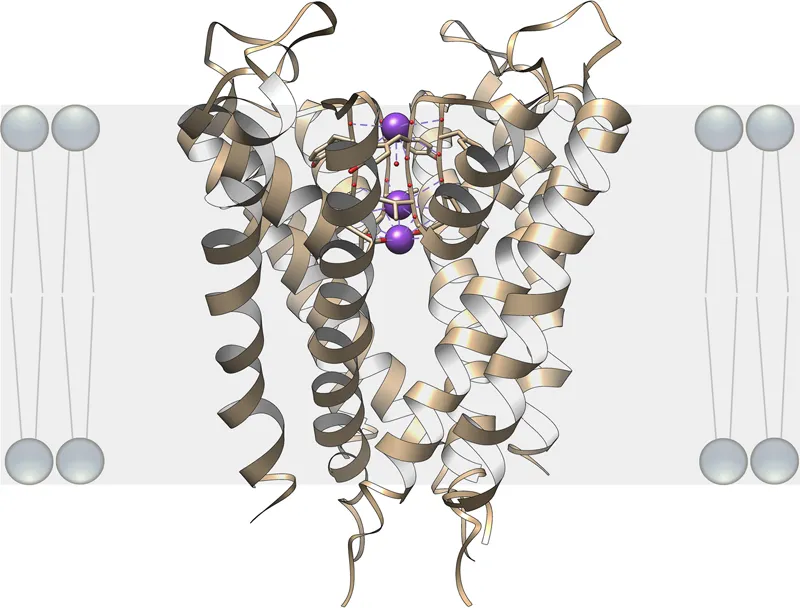
The ion channel in the lipid bilayer permits passage of potassium ions (labeled in violet) but not sodium ions. The oxygen atoms (labeled in red) of the amino acid residues forming the channel pore interact with and stabilize the potassium ions by creating an environment very similar to the aqueous environment outside the lipid bilayer. Cells may open or close the channel by employing additional gating mechanisms. The depicted ion channel structure is based upon the X-ray analysis of the KcsA K+ channel from Streptomyces lividans (MacKinnon, 2004).
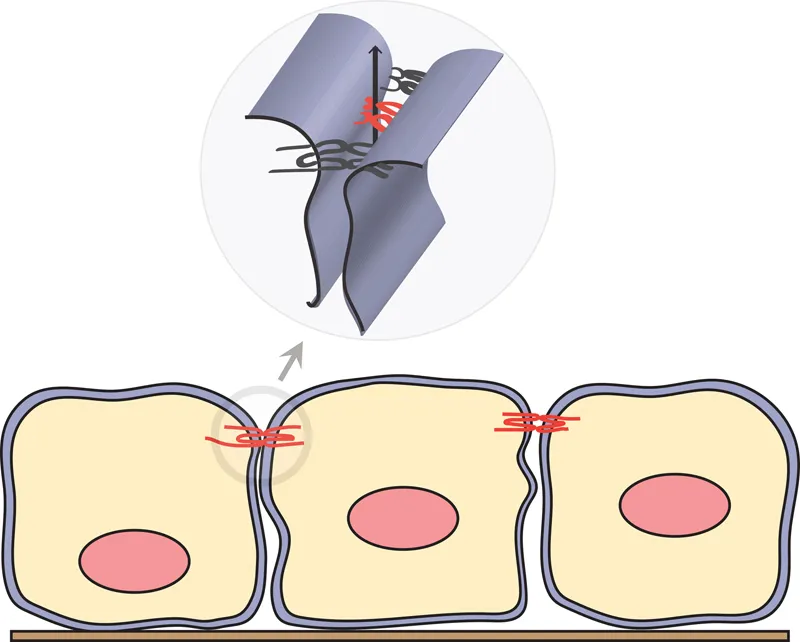
The paracellular channel is found within the TJ structure and is part of the paracellular diffusion barrier between the two plasma membranes. The paracellular channel conducts ions on the basis of size and charge. The paracellular channel is thought ...
Table des matières
- Cover
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Author Biography
- Preface
- Acknowledgment
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Paracellular Channel Formation
- Chapter 3: Paracellular Channel Recording
- Chapter 4: Paracellular Cation Channel
- Chapter 5: Paracellular Anion Channel
- Chapter 6: Paracellular Water Channel
- Chapter 7: Paracellular Channel in Organ System
- Chapter 8: Paracellular Channel in Human Disease
- Chapter 9: Paracellular Channel as Drug Target
- Chapter 10: Paracellular Channel Evolution
- Chapter 11: Perspective
- Index