
eBook - ePub
Energy Storage for Sustainable Microgrid
David Wenzhong Gao
This is a test
Partager le livre
- 152 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Energy Storage for Sustainable Microgrid
David Wenzhong Gao
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
Energy Storage for Sustainable Microgrid addresses theissues related to modelling, operation and control, steady-state and dynamic analysis of microgrids with ESS. This book discusses major electricity storage technologies in depth along with their efficiency, lifetime cycles, environmental benefits and capacity, so that readers can envisage which type of storage technology is best for a particular microgrid application. This book offers solutions to numerous difficulties such as choosing the right ESS for the particular microgrid application, proper sizing of ESS for microgrid, as well as design of ESS control systems for proper interfacing with the microgrid.
- Explanations for major power electronic converters/technology required to achieve the desired interfacing
- Case studies on the major impacts of energy storage on microgrid
- Detailed solutions for choosing the right ESS for particular microgrid applications
- Valuable economics chapter to help evaluate entire systems
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Energy Storage for Sustainable Microgrid est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Energy Storage for Sustainable Microgrid par David Wenzhong Gao en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Technology & Engineering et Power Resources. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
Sous-sujet
Power ResourcesChapter 1
Basic Concepts and Control Architecture of Microgrids
This chapter discusses the basic concepts and control structures of microgrids. Nowadays, distributed generation technology is becoming increasingly mature, and is deployed as active distribution networks working cooperatively with conventional power grids. In addition, the issues of exhaustible natural resources, fluctuating fossil fuel prices and the security of electricity have encouraged governments around the world to hold positive attitudes toward the development of emerging microgrids. Future microgrids will allow high renewable penetration and become building blocks of smart grids thanks to advanced communication and information technology. As the underlying scientific and engineering research questions are being answered, there is no doubt that microgrids will play an extremely important role in future electric power and energy systems.
Keywords
Centralized control; Control architectures; Decentralized control; Energy storage system; Microgrid concepts; Microgrid protection; Renewable energy resources; State estimation
1.1 Introduction
This chapter discusses the basic concepts and control structures of microgrids. Nowadays, distributed generation technology is becoming more and more mature, and is deployed as key elements of active distribution network working cooperatively with conventional power grids. In addition, the issues of exhaustible natural resources, fluctuating fossil fuel prices and security of electricity have encouraged governments around the world to hold positive attitudes toward the development of emerging microgrids. Future microgrids will allow high renewable penetration and become building blocks of smart grids thanks to advanced communication and information technology. As the underlying scientific and engineering research questions are being answered, there is no doubt that microgrids will play an extremely important role in future electric power and energy systems.
1.1.1 Concepts of Microgrids
Power generation in the traditional power grid is highly centralized, with power and energy flowing unidirectionally from large synchronous generators through a transmission/distribution network to end-users. However, the technological issues associated with traditional electric utilities, as well as the environmental problems caused by the combustion of fossil fuels, have stimulated research and development into new power system technologies. With the emergence of distributed energy resource (DER) units, e.g., wind, photovoltaic (PV), battery, biomass, micro-turbine, fuel cell, etc., microgrid technologies have attracted increasing attention as an effective means of integrating such DER units into power systems. However, there is no clear definition of a microgrid, and the concept varies in different countries and regions. Based on the European Technology Platform of Smart Grids [1], a microgrid is a platform that facilitates the integration of distributed generators (DG), energy storage systems (ESS) and loads to ensure that the power grid can supply sustainable, price-competitive and reliable electricity. Figure 1.1 shows a typical microgrid structure, comprising DGs, such as combined heat and power unit (CHP), microturbines, PV systems, wind power systems, fuel cells; a distributed energy storage (DES) facility such as battery banks, super-capacitors, flywheels, electric vehicles; flexible loads and control devices.
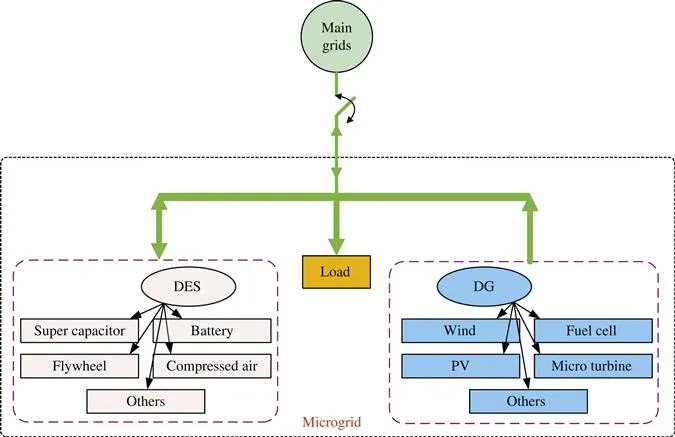
Microgrids can be classified as AC and DC types. AC microgrids can be integrated into existing AC power grid, but they require quite complicated control strategies for the synchronization process in order to preserve the stability of the system. On the other hand, DC microgrids have better short circuit protection and significantly improved efficiency. Furthermore, some synchronous units (e.g., diesel generators) and some non-synchronous units (e.g., micro-turbine machines) are usually connected in the same microgrid system. As the penetration level of more DC loads (especially Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles) increases, hybrid AC/DC synchronous/non-synchronous microgrids via multiple bi-directional converters will become increasingly attractive. Figure 1.2 shows a typical system structure for a hybrid AC/DC microgrid that contains power electronic interfaces and multiple DER units.

Although many types of DG units are more sustainable, a high level penetration of renewable energy resources (e.g., wind, PV) in microgrids can make maintaining grid stability and delivering reliable power challenging due to intermittency and fluctuation issues. In such cases, a DES can play an essential role in improving stability, strengthening reliability, and ensuring security. Not only can DES units be used for smoothing the fluctuations from the output of DG units, but they ...