
Math in Economics
Susheng Wang
- 272 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Math in Economics
Susheng Wang
À propos de ce livre
This textbook concisely covers math knowledge and tools useful for business and economics studies, including matrix analysis, basic math concepts, general optimization, dynamic optimization, and ordinary differential equations. Basic math tools, particularly optimization tools, are essential for students in a business school, especially for students in economics, accounting, finance, management, and marketing. It is a standard practice nowadays that a graduate program in a business school requires a short and intense course in math just before or immediately after the students enter the program. Math in Economics aims to be the main textbook for such a crash course.
The 1st edition was published by People's University Publisher, China. This new edition contains an added chapter on Probability Theory along with changes and improvements throughout.
Request Inspection Copy
This textbook concisely covers math knowledge and tools useful for business and economics studies, including matrix analysis, basic math concepts, general optimization, dynamic optimization, and ordinary differential equations. Basic math tools, particularly optimization tools, are essential for students in a business school, especially for students in economics, accounting, finance, management, and marketing. It is a standard practice nowadays that a graduate program in a business school requires a short and intense course in math just before or immediately after the students enter the program. Math in Economics aims to be the main textbook for such a crash course.
The 1st edition was published by People's University Publisher, China. This new edition contains an added chapter on Probability Theory along with changes and improvements throughout.
Request Inspection Copy
Readership: Students ranging from final undergraduate year, to master's and PhD level in economics, accounting, finance, management, and marketing courses.
Key Features:
- It concisely covers main math knowledge and tools useful for business and economics studies, which includes matrix analysis, basic math concepts, general optimization, dynamic optimization, ordinary differential equations, and probability theory
- Basic math tools, particularly optimization tools, are essential for students in business schools, and especially for students in economics, accounting, finance, management, and marketing
Foire aux questions
Informations
1. Vector

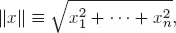
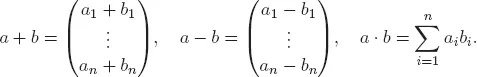
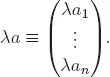
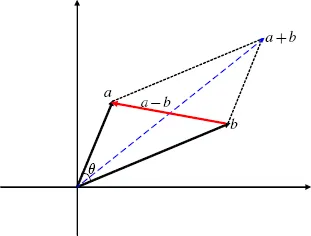
Table des matières
- Cover Page
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Chapter 1. Linear Algebra
- Chapter 2. Basic Real Analysis
- Chapter 3. General Optimization
- Chapter 4. Dynamic Optimization
- Chapter 5. Ordinary Differential Equations
- Chapter 6. Difference Equations
- Chapter 7. Probability Theory
- References
- Index