
Introduction to Numerical Methods for Time Dependent Differential Equations
Heinz-Otto Kreiss, Omar Eduardo Ortiz
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Introduction to Numerical Methods for Time Dependent Differential Equations
Heinz-Otto Kreiss, Omar Eduardo Ortiz
À propos de ce livre
Introduces both the fundamentals of time dependent differential equations and their numerical solutions
Introduction to Numerical Methods for Time Dependent Differential Equations delves into the underlying mathematical theory needed to solve time dependent differential equations numerically. Written as a self-contained introduction, the book is divided into two parts to emphasize both ordinary differential equations (ODEs) and partial differential equations (PDEs).
Beginning with ODEs and their approximations, the authors provide a crucial presentation of fundamental notions, such as the theory of scalar equations, finite difference approximations, and the Explicit Euler method. Next, a discussion on higher order approximations, implicit methods, multistep methods, Fourier interpolation, PDEs in one space dimension as well as their related systems is provided.
Introduction to Numerical Methods for Time Dependent Differential Equations features:
- A step-by-step discussion of the procedures needed to prove the stability of difference approximations
- Multiple exercises throughout with select answers, providing readers with a practical guide to understanding the approximations of differential equations
- A simplified approach in a one space dimension
- Analytical theory for difference approximations that is particularly useful to clarify procedures
Introduction to Numerical Methods for Time Dependent Differential Equations is an excellent textbook for upper-undergraduate courses in applied mathematics, engineering, and physics as well as a useful reference for physical scientists, engineers, numerical analysts, and mathematical modelers who use numerical experiments to test designs or predict and investigate phenomena from many disciplines.
Foire aux questions
Informations
PART I
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS AND THEIR APPROXIMATIONS
CHAPTER 1
FIRST-ORDER SCALAR EQUATIONS
1.1 Constant coefficient linear equations
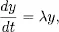
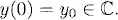
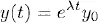
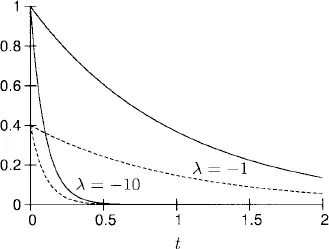
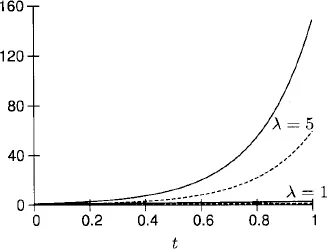
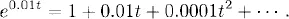
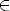
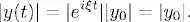
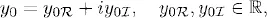
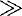
Table des matières
- Cover
- Half Title page
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Dedication
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Part I: Ordinary Differential Equations and Their Approximations
- Part II: Partial Differential Equations and Their Approximations