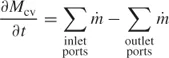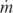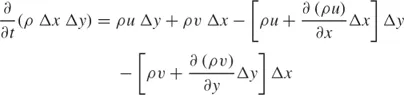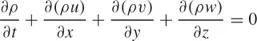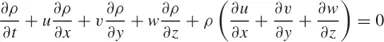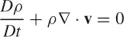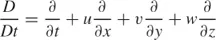![]()
Chapter 1
Fundamental Principles
Convective heat transfer, or simply,
convection, is the study of heat transport processes effected by the flow of fluids. The very word
convection has its roots in the Latin verbs
convecto-are and
convho-vhre [1],
1 which mean to bring together or to carry into one place. Convective heat transfer has grown to the status of a contemporary science because of our need to understand and predict how a fluid flow acts as a “carrier” or “conveyor belt” for energy and matter.
Convective heat transfer is clearly a field at the interface between two older fields: heat transfer and fluid mechanics. To study the interdisciplinary is valuable, but it must come after one possesses the disciplines, not the other way around. For this reason, the study of any convective heat transfer problem must rest on a solid understanding of basic heat transfer and fluid mechanics principles. The objective in this chapter is to review these principles in order to establish a common language for the more specific issues addressed in later chapters.
Before reviewing the foundation of convective heat transfer methodology, it is worth reexamining the historic relationship between fluid mechanics and heat transfer. Especially during the past 100 years, heat transfer and fluid mechanics have enjoyed a symbiotic relationship in their development, a relationship where one field was stimulated by the curiosity and advance in the other field. Examples of this symbiosis abound in the history of boundary layer theory and natural convection. The field of convection grew out of this symbiosis, and if we are to learn anything from history, important advances in convection will continue to result from this symbiosis. Thus, the student and the future researcher would be well advised to devote equal attention to fluid mechanics and heat transfer literature.
1.1 Mass Conservation
The first principle to review is undoubtedly the oldest: It is the conservation of mass in a closed system or the “continuity” of mass through a flow (open) system. From engineering thermodynamics, we recall the mass conservation statement for a control volume [2]:
where
Mcv is the mass that is trapped instantaneously inside the control volume (cv), while the
's are the mass flow rates associated with flow into and out of the control volume. In convective heat transfer, we are usually interested in the velocity and temperature distribution in a flow region near a solid wall; hence, the control volume to consider is the infinitesimally small Δ
x Δ
y box drawn around a fixed location (
x, y) in a flow field. In
Fig. 1.1, as in most of the problems analyzed in this book, the flow field is two-dimensional (i.e., the same in any plane parallel to the plane of
Fig. 1.1). In a three-dimensional flow field, the control volume would be the parallelepiped Δ
x Δ
y Δ
z. Taking
u and
as the local velocity components at point (
x, y), the mass conservation equation (
1.1) requires that
or, dividing through by the constant size of the control volume (Δx Δy),
In a three-dimensional flow, an analogous argument yields
where w is the velocity component in the z direction. The local mass conservation statement (1.4) can also be written as
or
In expression (
1.6),
v is the velocity vector (
u,
,
w), and
D/Dt represents the “material derivative” operator,
Of particular interest to classroom and fundamental treatment of the convection problem is the wide class of flows in which temporal and spatial variations in density are negligible relative to the local variations in velocity. For this class, the mass co...