
Incident Response Techniques for Ransomware Attacks
Oleg Skulkin
- 228 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Incident Response Techniques for Ransomware Attacks
Oleg Skulkin
Informazioni sul libro
Explore the world of modern human-operated ransomware attacks, along with covering steps to properly investigate them and collecting and analyzing cyber threat intelligence using cutting-edge methods and toolsKey Features• Understand modern human-operated cyber attacks, focusing on threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures• Collect and analyze ransomware-related cyber threat intelligence from various sources• Use forensic methods and tools to reconstruct ransomware attacks and prevent them in the early stagesBook DescriptionRansomware attacks have become the strongest and most persistent threat for many companies around the globe. Building an effective incident response plan to prevent a ransomware attack is crucial and may help you avoid heavy losses. Incident Response Techniques for Ransomware Attacks is designed to help you do just that.This book starts by discussing the history of ransomware, showing you how the threat landscape has changed over the years, while also covering the process of incident response in detail. You'll then learn how to collect and produce ransomware-related cyber threat intelligence and look at threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures. Next, the book focuses on various forensic artifacts in order to reconstruct each stage of a human-operated ransomware attack life cycle. In the concluding chapters, you'll get to grips with various kill chains and discover a new one: the Unified Ransomware Kill Chain.By the end of this ransomware book, you'll be equipped with the skills you need to build an incident response strategy for all ransomware attacks.What you will learn• Understand the modern ransomware threat landscape• Explore the incident response process in the context of ransomware• Discover how to collect and produce ransomware-related cyber threat intelligence• Use forensic methods to collect relevant artifacts during incident response• Interpret collected data to understand threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures• Understand how to reconstruct the ransomware attack kill chainWho this book is forThis book is for security researchers, security analysts, or anyone in the incident response landscape who is responsible for building an incident response model for ransomware attacks. A basic understanding of cyber threats will be helpful to get the most out of this book.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Section 1: Getting Started with a Modern Ransomware Attack
- Chapter 1, The History of Human-Operated Ransomware Attacks
- Chapter 2, The Life Cycle of a Human-Operated Ransomware Attack
- Chapter 3, The Incident Response Process
Chapter 1: The History of Human-Operated Ransomware Attacks
- 2016 – SamSam ransomware
- 2017 – BitPaymer ransomware
- 2018 – Ryuk ransomware
- 2019-present – ransomware-as-a-service programs
2016 – SamSam ransomware

Who was behind the SamSam ransomware

2017 – BitPaymer ransomware
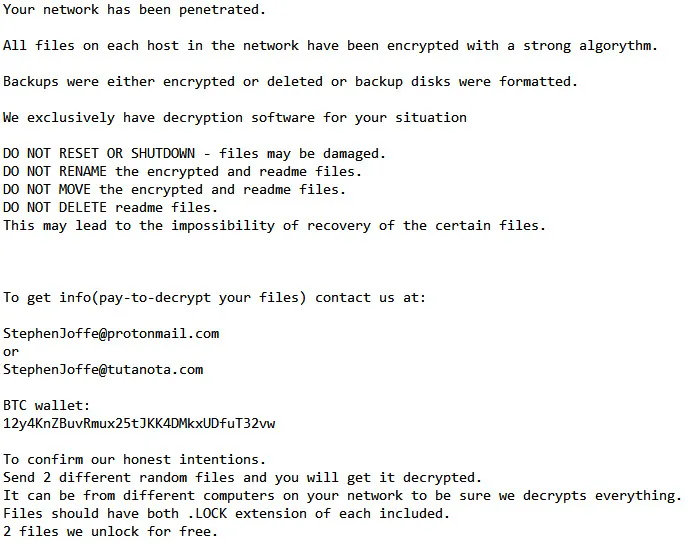
The mastermind behind the BitPaymer ransomware

2018 – Ryuk ransomware
Indice dei contenuti
- Incident Response Techniques for Ransomware Attacks
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1: Getting Started with a Modern Ransomware Attack
- Chapter 1: The History of Human-Operated Ransomware Attacks
- Chapter 2: The Life Cycle of a Human-Operated Ransomware Attack
- Chapter 3: The Incident Response Process
- Section 2: Know Your Adversary: How Ransomware Gangs Operate
- Chapter 4: Cyber Threat Intelligence and Ransomware
- Chapter 5: Understanding Ransomware Affiliates' Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures
- Chapter 6: Collecting Ransomware-Related Cyber Threat Intelligence
- Section 3: Practical Incident Response
- Chapter 7: Digital Forensic Artifacts and Their Main Sources
- Chapter 8: Investigating Initial Access Techniques
- Chapter 9: Investigating Post-Exploitation Techniques
- Chapter 10: Investigating Data Exfiltration Techniques
- Chapter 11: Investigating Ransomware Deployment Techniques
- Chapter 12: The Unified Ransomware Kill Chain
- Other Books You May Enjoy