Arithmetic Circuits for DSP Applications
Pramod Kumar Meher, Thanos Stouraitis, Pramod Kumar Meher, Thanos Stouraitis
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Arithmetic Circuits for DSP Applications
Pramod Kumar Meher, Thanos Stouraitis, Pramod Kumar Meher, Thanos Stouraitis
Informazioni sul libro
A comprehensive guide to the fundamental concepts, designs, and implementation schemes, performance considerations, and applications of arithmetic circuits for DSP
Arithmetic Circuits for DSP Applications is a complete resource on arithmetic circuits for digital signal processing (DSP). It covers the key concepts, designs and developments of different types of arithmetic circuits, which can be used for improving the efficiency of implementation of a multitude of DSP applications. Each chapter includes various applications of the respective class of arithmetic circuits along with information on the future scope of research. Written for students, engineers, and researchers in electrical and computer engineering, this comprehensive text offers a clear understanding of different types of arithmetic circuits used for digital signal processing applications.
The text includes contributions from noted researchers on a wide range of topics, including a review of circuits used in implementing basic operations like additions and multiplications; distributed arithmetic as a technique for the multiplier-less implementation of inner products for DSP applications; discussions on look up table-based techniques and their key applications; CORDIC circuits for calculation of trigonometric, hyperbolic and logarithmic functions; real and complex multiplications, division, and square-root; solution of linear systems; eigenvalue estimation; singular value decomposition; QR factorization and many other functions through the use of simple shift-add operations; and much more. This book serves as a comprehensive resource, which describes the arithmetic circuits as fundamental building blocks for state-of-the-art DSP and reviews in - depth the scope of their applications.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
1
Basic Arithmetic Circuits
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Addition and Subtraction
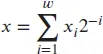
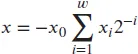

1.2.1 Ripple-Carry Addition