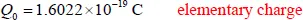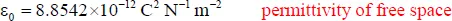Electrochemical Science and Technology
Fundamentals and Applications
Keith Oldham, Jan Myland, Alan Bond
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Electrochemical Science and Technology
Fundamentals and Applications
Keith Oldham, Jan Myland, Alan Bond
Informazioni sul libro
Electrochemistry is a discipline of wide scientific and technological interest. Scientifically, it explores the electrical properties of materials and especially the interfaces between different kinds of matter. Technologically, electrochemistry touches our lives in many ways that few fully appreciate; for example, materials as diverse as aluminum, nylon, and bleach are manufactured electrochemically, while the batteries that power all manner of appliances, vehicles, and devices are the products of electrochemical research. Other realms in which electrochemical science plays a crucial role include corrosion, the disinfection of water, neurophysiology, sensors, energy storage, semiconductors, the physics of thunderstorms, biomedical analysis, and so on.
This book treats electrochemistry as a science in its own right, albeit resting firmly on foundations provided by chemistry, physics, and mathematics. Early chapters discuss the electrical and chemical properties of materials from which electrochemical cells are constructed. The behavior of such cells is addressed in later chapters, with emphasis on the electrodes and the reactions that occur on their surfaces. The role of transport to and from electrodes is a topic that commands attention, because it crucially determines cell efficiency. Final chapters deal with voltammetry, the methodology used to investigate electrode behavior. Interspersed among the more fundamental chapters are chapters devoted to applications of electrochemistry: electrosynthesis, power sources, "green electrochemistry", and corrosion.
Electrochemical Science and Technology is addressed to all who have a need to come to grips with the fundamentals of electrochemistry and to learn about some of its applications. It will constitute a text for a senior undergraduate or graduate course in electrochemistry. It also serves as a source of material of interest to scientists and technologists in various fields throughout academia, industry, and government – chemists, physicists, engineers, environmentalists, materials scientists, biologists, and those in related endeavors.
This book:
- Provides a background to electrochemistry, as well as treating the topic itself.
- Is accessible to all with a foundation in physical science, not solely to chemists.
- Is addressed both to students and those later in their careers.
- Features web links (through www.wiley.com/go/EST ) to extensive material that is of a more tangential, specialized, or mathematical nature.
- Includes questions as footnotes to support the reader's evolving comprehension of the material, with fully worked answers provided on the web.
- Provides web access to Excel ® spreadsheets which allow the reader to model electrochemical events.
- Has a copious Appendix of relevant data.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni