
eBook - ePub
International Business
Radha Jethu-Ramsoedh, Maud Hendrickx
This is a test
Share book
- 324 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
International Business
Radha Jethu-Ramsoedh, Maud Hendrickx
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
The open character of the global economy combined with the internationalization of business means that business students are increasingly required to understand the complexities of international business. This introductory textbook provides students with a comprehensive overview of this vital topic.
Subjects discussed withing the text include: the political and economic environment; culture; management and organization; international marketing strategies; intercultural communication; international law; international finance; and logistics / international transport.
Frequently asked questions
How do I cancel my subscription?
Can/how do I download books?
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
What is the difference between the pricing plans?
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
What is Perlego?
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Do you support text-to-speech?
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Is International Business an online PDF/ePUB?
Yes, you can access International Business by Radha Jethu-Ramsoedh, Maud Hendrickx in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & International Business. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
1
Introduction to international business

International business
Low-wage countries
Globalisation
Gross National Product
BRIC countries
Sustainable international business
Stakeholder
People
Planet
Profit
International trade
Import
Export
Foreign Direct Investment
Proactive motives
Reactive motives
Active trade balance
Trade surplus
Trade deficit
Passive trade balance
In this introductory chapter, we discuss the essence of international business and its context. Furthermore, we look at what motivates companies to cross borders. A number of terms that will repeatedly occur in this book, such as import and export, are discussed here. Finally, we zoom in on the performance of the European Union member states concerning international business.
Amazon seeks to expand globally
Amazon says it plans to revamp its international e-commerce platform to make it easier for the company to reach customers in new markets.
The online retailer, the world’s largest by number of visitors, operates online businesses in six countries outside the US. It says it has set up a new team that will create “the architectural underpinnings to greatly simplify country expansions”, by translating content into different languages and adjusting taxes, prices and delivery options to better suit customers’ locations. The move underlines the increasing globalisation of online retailing, as companies such as Gap, the US clothing retailer, and Walmart, the world’s largest retailer by sales, seek to use e-commerce sites and cross-border shipping to reach a wider audience.
Walmart, one of Amazon’s main online rivals in the US, has invested heavily in a global e-commerce platform over the past two years, which it says it plans to use to reach customers both in existing markets and in countries where it has no physical stores.

Japan’s largest online retailer, Rakuten, has also recently acquired or launched sites in the US, Europe and China for its Ebay-style online marketplaces.
Amazon operates websites in Canada, China, Japan, the UK, Germany and France, and offers customers ordering from other countries the ability to pay for purchases in their own currencies. But it has not entered a new country since 2004, when it acquired Joyo.com, its Chinese site. Instead, it has focused on steadily expanding the new product categories on its range of global sites. The retailer is now seeking to recruit senior software engineers for what it says is “a new team that is gearing up to make a substantial impact on how Amazon does business around the world”.
A job posting says the team is “tackling interesting problems like rendering content in multiple languages and calculating tax, price and shipping variations on the fly based on the customer’s preferred shipping destination”.
Gap has recently launched a UK-based e-commerce site aimed both at the UK and other western European countries, although customers can only pay in sterling, not Euros. Gap has recently launched its first e-commerce sites in Canada and China, while Walmart has said it will shortly open an e-commerce site for its Sam’s Club discount warehouse stores in China. Marks and Spencer, the UK general retailer, has said it hopes to use e-commerce to expand its international sales, once its current agreement to rely on a site run by Amazon expires in 2013. Tesco, the UK supermarket group, also said this month that it planned to open e-commerce sites in China, Poland and the Czech Republic.
Edited source: www.ft.com, 23 December 2010
1.1 What is international business?
If European consumers consider the origin of their products, they rapidly become aware that few products are manufactured in Europe. ‘Made in China’ is a common label in or on various products. The market for products and services is not limited to European borders, but extends across the whole world. Furthermore, there are many foreign companies that operate worldwide. These companies are called multinationals. They include Daimler, Suez, BP en Metro. But even small and medium-size companies are not limited to doing business in their own country any longer. Gradually small companies are venturing across their national borders: for example, through web shops that are set up abroad.
● www.bndestem.nl
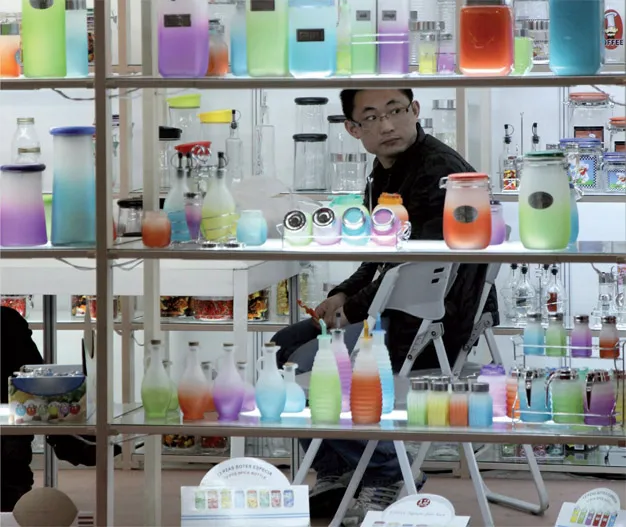

Source: Qilai Shen/EPA
Made in China
SHANGHAI – A man waits for the opening of the 20th East China Fair in Shanghai among an array of colourful storage jars.
With around 6,000 exhibitors, this is China’s largest trade show for consumer articles and is primarily focused on export. Last year, around 50,000 buyers from more than 100 countries came to the show.
4 March 2010
International business
Low-wage countries
International business is a broad definition. It covers more than marketing and selling goods and services abroad. It is also related to the development of international commerce or the actions that are necessary to do business on an international level. Companies increasingly seek collaborations with partners abroad. They outsource activities to low-wage countries to increase their productivity or reduce their labour costs. They share knowledge with foreign partners to obtain a stronger competitive position, or they work with others to realise economies of scale. Since international business is much more complicated than national business, we wish to focus with as many aspects as possible which differ from domestic business practice.
1.1.1 Globalisation
Globalisation
Why has international business expanded so enormously? Due to the opening of borders, it has become increasingly easy to buy products or services from, or sell them to, other countries. The advent of the internet has made a significant contribution to this. It has become easier and cheaper to be connected worldwide. Due to the industrialisation process of low-wage countries such as China, India and Bangladesh, manufacturing can be done more cheaply. Globalisation does refer to goods and services but also to capital, knowledge and labour which find their way around the globe. Due to the abolition of frontiers, people travel more than ever. Because of this, political systems, economies and cultures influence each other. This can be seen in metropolises: more and more cities are starting to look alike. Look, for example, at McDonald’s, which has an outlet in every metropolis.
Gross National Product
BRIC countries
The last ten years often referred to as ‘the age of globalisation’. However, globalisation is not a phenomenon of recent decades. Nevertheless, its development has changed in the last decade. Considering the growth of the Gross National Product (GNP) of countries together, we notice that more than half of this growth comes from the new industrial countries (emerging markets). These countries play an increasingly important role in globalisation – the BRIC countries (Brazil, Russia, India and China) in particular, where enormous growth in GNP is expected in the coming years. This is in contrast to Western countries, whose economies have stagnated, due to the effects of the current credit crisis.
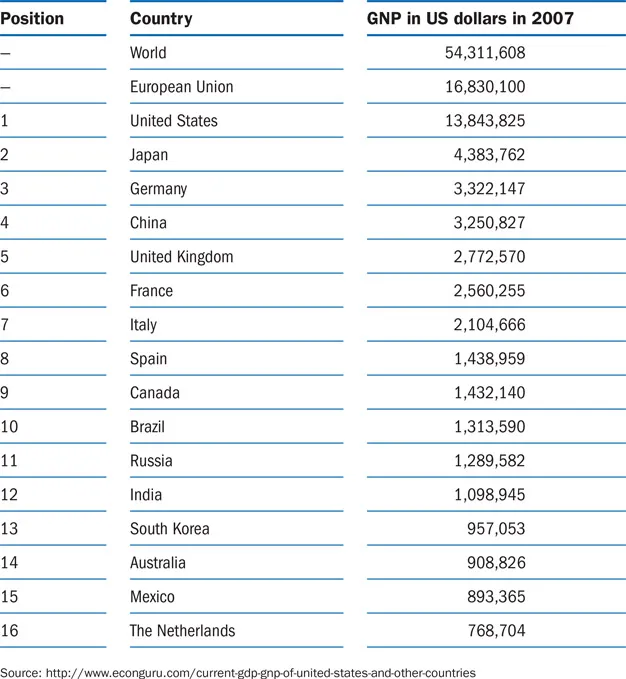
Gross National Product (GNP)
The extent to which a country participates in international trade depends primarily on its GNP. The Gross National Product of a country is the total of what is produced in that country in terms of goods and services by firms that are nationally owned, plus the income derived from nationally-owned firms abroad, which is received as a reward for making production facilities available. GNP is an important measure of the economic performance of a country. Table 1.1 lists several countries and their GNP.
TABLE 1.1 Different countries and their GNP
Just like all phenomena, globalisatio...