![]()
1 Introduction
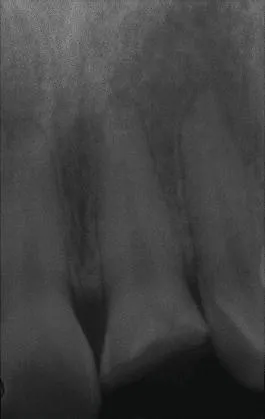
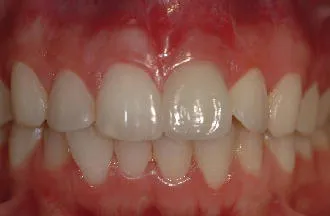
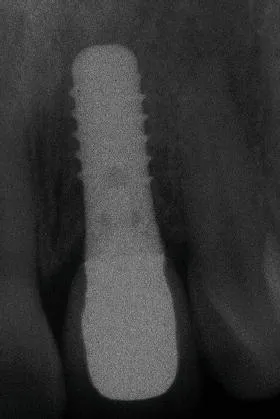
The initial report in the literature regarding the placement of an implant immediately following tooth extraction was published by Schulte in 1976 (Schulte and Heimke 1976). It was not until the early 1990s that the concept was reintroduced in the English-language literature by Lazzara, who illustrated this method of treatment with three case reports (Lazzara 1989). Lazarra’s landmark paper provided insight into the future of surgical implant dentistry, with technical aspects that remain critical today. The immediate placement treatment protocol was validated in the literature several years later by Gelb, who reported on a series of fifty consecutive cases followed over a 3-year period, providing a survival rate of 98% (Gelb 1993). Since then, numerous animal studies, human case reports, and several randomized controlled studies have furthered the science of this treatment modality (Figures 1.1–1.3) (Chen, Wilson, et al. 2004; Chen, Beagle, et al. 2009).
An understanding of the clinical and histologic realities of bone resorption that naturally occur following tooth extraction originally led to the concept of placing implants into sockets immediately following tooth extraction. This concept attempted, and still attempts today, to take advantage of the pre-treatment alveolar ridge contours (Chen, Wilson, et al. 2004). Many have noted additional advantages of this technique including reduced treatment visits and costs, simplified restorative care, and improved patient psychological outlook for treatment (Lazzara 1989; Parel and Triplett 1990; Shanaman 1992; Werbitt and Goldberg 1992; Denissen, Kalk, et al. 1993; Schultz 1993; Watzek, Haider, et al. 1995; Missika, Abbou, et al. 1997).
Numerous published works now indicate that outcomes of immediate placement procedures can be equally successful as a delayed approach when initial primary stability is achieved (Barzilay 1993; Schwartz-Arad and Chaushu 1997; Mayfield 1999; Chen, Wilson, et al. 2004; Chen, Beagle, et al. 2009).
The intent of this book is to provide clinicians with essential evidence-based information necessary to incorporate immediate implant placement into their modality of patient care. Certainly not exhaustive in terms of literature, this text references the classic and contemporary scientific articles that provide the foundation for the art and science of this important clinical topic. For some, these pages will begin their journey into a fascinating area of implant dentistry, while for others these written words will serve to reinforce and challenge their clinical expertise.
References
Barzilay, I. (1993). “Immediate implants: Their current status.” Int J Prosthodont 6(2): 169–175.
Chen, S. T., J. Beagle, et al. (2009). “Consensus statements and recommended clinical procedures regarding surgical techniques.” Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 24 Suppl: 272–278.
Chen, S. T., T. G. Wilson, Jr., et al. (2004). “Immediate or early placement of implants following tooth extraction: Review of biologic basis, clinical procedures, and outcomes.” Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 19 Suppl: 12–25.
Denissen, H. W., W. Kalk, et al. (1993). “Anatomic consideration for preventive implantation.” Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 8(2): 191–196.
Gelb, D. A. (1993). “Immediate implant surgery: Three-year retrospective evaluation of 50 consecutive cases.” Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 8(4): 388–399.
Lazzara, R. J. (1989). “Immediate implant placement into extraction sites: Surgical and restorative advantages.” Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 9(5): 332–343.
Mayfield, L., ed. (1999). Immediate, Delayed, and Late Submerged and Transmucosal Implants. Berlin: Quintessence.
Missika, P., M. Abbou, et al. (1997). “Osseous regeneration in immediate postextraction implant placement: A literature review and clinical evaluation.” Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 9(2): 165–175; quiz 176.
Parel, S. M., and R. G. Triplett (1990). “Immediate fixture placement: A treatment planning alternative.” Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 5(4): 337–345.
Schulte, W., and G. Heimke (1976). “[The Tubinger immediate implant].” Quintessenz 27(6): 17–23.
Schultz, A. J. (1993). “Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) of nonsubmerged implants in immediate extraction sites.” Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 5(2): 59–65; quiz 66.
Schwartz-Arad, D., and G. Chaushu (1997). “Placement of implants into fresh extraction sites: 4 to 7 years retrospective evaluation of 95 immediate implants.” J Periodontol 68(11): 1110–1116.
Shanaman, R. H. (1992). “The use of guided tissue regeneration to facilitate ideal prosthetic placement of implants.” Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 12(4): 256–265.
Watzek, G., R. Haider, et al. (1995). “Immediate and delayed implantation for complete restoration of the jaw following extraction of all residual teeth: A retrospective study comparing different types of serial immediate implantation.” Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 10(5): 561–567.
Werbitt, M. J., and P. V. Goldberg (1992). “The immediate implant: Bone preservation and bone regeneration.” Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 12(3): 206–217.
![]()
2 Risk Assessment
Implant dentistry requires the execution of a thorough treatment plan to obtain an ideal result for the patient. Although a proposed implant site may initially appear straightforward, the clinician should be aware that there is nothing “simple” about outcomes with dental implants. This is certainly true regarding treatment plans in the esthetic zone and especially valid with regards to immediate implant placement. The clinician’s primary goal should be to provide the patient with the highest level of outcome possible with the least degree of risk or complications (Dawson, Chen, et al. 2009). With this as the endpoint, several primary factors should be evaluated. These include the judgment and experience of the dentist, the local and systemic factors of the patient, and the biomechanics of the chosen implant system and grafting materials (Figure 2.1). Together, comprehensive evaluation of these factors will empower the dental team toward obtaining an ideal outcome.
SURGEON
It is clear that implant dentistry is not “easy.” Not only is the dental team responsible for achieving a perfect esthetic, functional, and phonetic outcome, but it is also often responsible for the reconstruction of the alveolar bone and peri-implant soft tissues. This is often the case with immediate placement procedures (Figures 2.2–2.5).
As a mechanism to assist dental te...