
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Rotating Electrical Machines
About this book
In this book a general matrix-based approach to modeling electrical machines is promulgated. The model uses instantaneous quantities for key variables and enables the user to easily take into account associations between rotating machines and static converters (such as in variable speed drives). General equations of electromechanical energy conversion are established early in the treatment of the topic and then applied to synchronous, induction and DC machines. The primary characteristics of these machines are established for steady state behavior as well as for variable speed scenarios.
Important new applications for this technology (such as wind turbines, electric propulsion systems for large ships, etc.) are addressed and the book is illustrated with a large number of informative and detailed photographs, provided by various companies at the leading edge of research and applications in the field.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Main Requirements
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Sinusoidal variables
1.2.1. Single-phase variables
1.2.1.1. Timed expressions
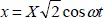
1.2.1.2. Vector representation
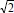
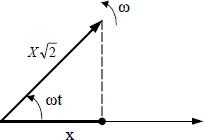
1.2.1.3. Single-phase currents and voltages
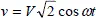
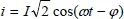
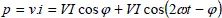
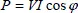
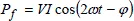
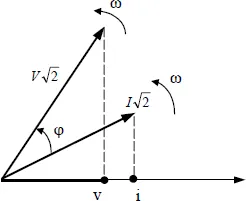
1.2.1.4. Complex representation


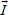
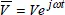
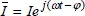

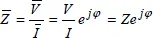
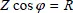
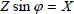
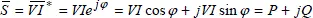
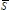
1.2.2. 2-phase voltages and currents
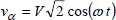
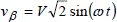
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Main Requirements
- Chapter 2: Introduction to Rotating Electrical Machines
- Chapter 3: Synchronous Machines
- Chapter 4: Induction Machines
- Chapter 5: Direct Current Machines
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app