
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
The AST Handbook of Transplant Infections
About This Book
Whether you need to manage a post-transplant infection or reduce the possibility of infection, you will find effective guidance in this handbook. The work of the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice, this reference exclusively uses tables and flowcharts to speed up decision making.
This distinguished group of investigators and teachers provide point of care information on optimum management of infection in adult and pediatric organ and stem cell transplant patients. The unique tables and flowcharts are devised by the authors, backed up with extensive references, making the book a fully researched yet easy to use guide.
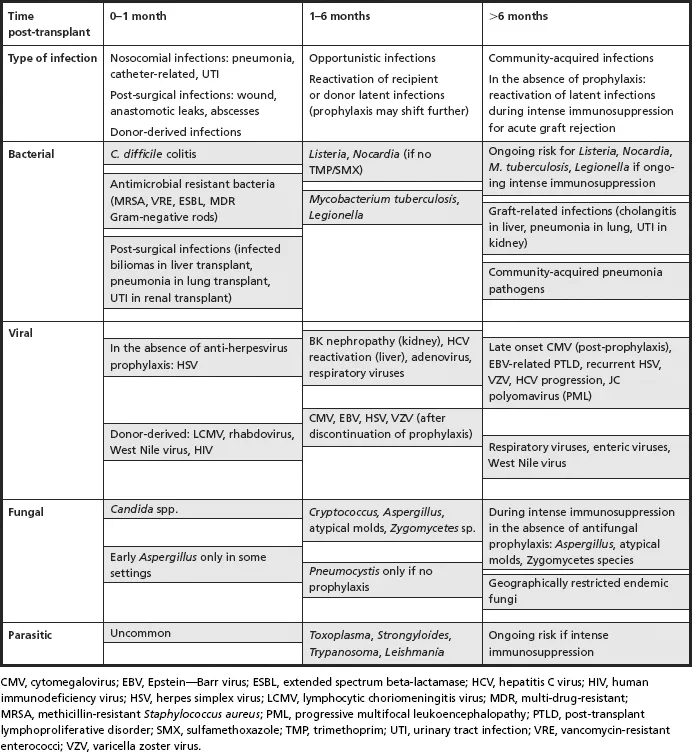
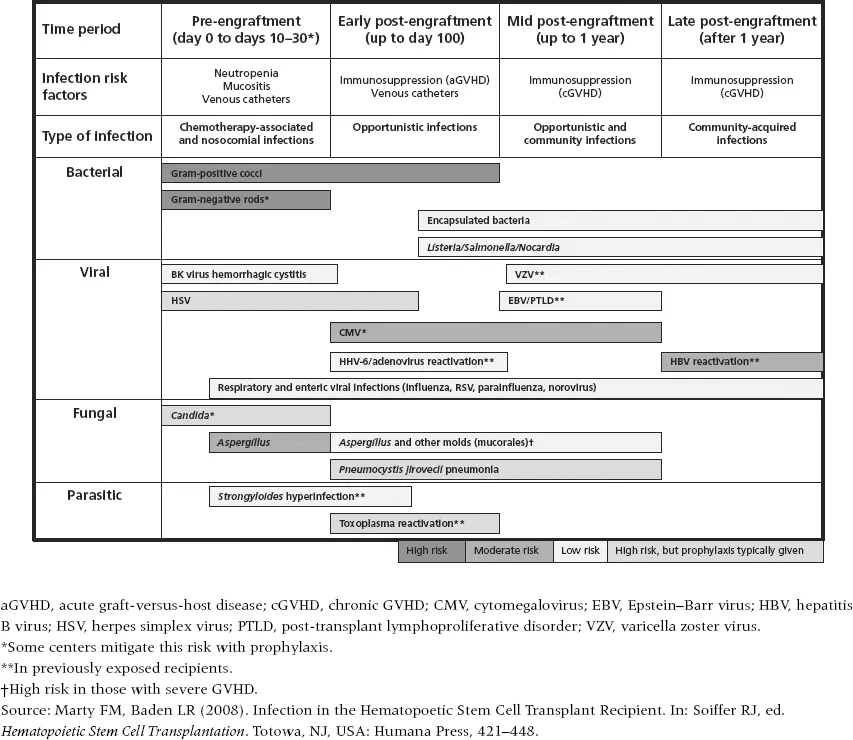
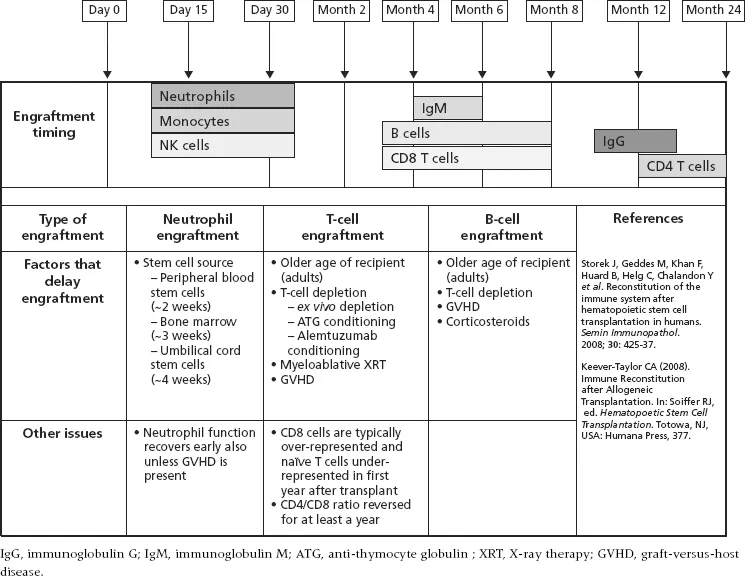
The fast growing specialty of transplantation will be well served by this book as increasing numbers of successful procedures mean transplant teams have to be ever more alert to the possibility of and need for action in the event of ensuing infection.
Frequently asked questions
Information
| Routine screening | Optional testing (if clinically indicated only) | Organ-specific considerations |
|
| Patients with end-stage organ disease are susceptible to certain infections which should be diagnosed and treated prior to transplantation if at all possible. Specific considerations include the following:
|
| Routine screening of all recipients | Optional testing (if clinically indicated only) | Comments |
|
|
Table of contents
- Cover
- Contents
- Title
- Copyright
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Part I: General Issues and Infectious Syndromes
- Part II: Specific Pathogens
- Part III: Donor Issues
- Part IV: Prevention of Infections after Transplantation
- Part V: Post-transplant Medications and Drug Interactions
- Index