
eBook - ePub
Design for Flooding
Architecture, Landscape, and Urban Design for Resilience to Climate Change
Donald Watson, Michele Adams
This is a test
Share book
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Design for Flooding
Architecture, Landscape, and Urban Design for Resilience to Climate Change
Donald Watson, Michele Adams
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
" Design for Flooding contains considerable useful information for practitioners and students. Watson and Adams fill the void for new thinking…and they advance our ability to create more sustainable, regenerative, and resilient places." —Landscape Architecture Magazine
Frequently asked questions
How do I cancel my subscription?
Can/how do I download books?
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
What is the difference between the pricing plans?
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
What is Perlego?
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Do you support text-to-speech?
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Is Design for Flooding an online PDF/ePUB?
Yes, you can access Design for Flooding by Donald Watson, Michele Adams in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Architecture & Architecture Design. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
PART I
NATURE OF WATER
Watershed design and floodplain management are based on the physics of water at all scales of the hydrologic cycle.
We are tied to the ocean … and when we go back to the sea, whether it is to sail or to watch, we are going back from whence we came.
—John F. Kennedy, 1962
Figure 1.1 Self-regulating climate: Clouds form as moisture in thermals updrafts condenses upon meeting cooler air aloft, shading the land and limiting further warming. Gulf of Carpentaria, Northern Australia.
(PHOTO: © Reg Morrison)
Source: Reg Morrison, The Climate Debate, 2009, <homepage.mac.com/gregalchin/rm/pdfs/climate%20debate.pdf> .

CHAPTER 1
WEATHER
1.1 SUN AND EARTH
The thin line of life that surrounds the globe is defined by the precise juxtaposition of Earth’s orbit around the Sun, its orientation in its orbital eccentricity, and Moon’s gravitational balance. Earth’s geological history, atmosphere of oxygen and water, and magnetic field contribute to the conditions that created and sustain our biological life. Earth’s axial tilt and annual rotation around the Sun define our climates and seasons. The Sun’s radiant energy and thermal flux of lands and oceans drive the daily progression of water within the atmosphere and regions of the globe.
Earth has just the right mass, chemical composition, and distance from the Sun to permit water to exist as a liquid, solid, or gas, freely changing its state as it is transported through our atmosphere. Not a drop of liquid water has been found elsewhere in the solar system. This was not always so. Channels on Mars suggest that early in its history, its climate was warmer and it too had free-flowing water.
To understand flooding, one must understand water. To understand water, one must understand climate and weather. Variations that we experience on Earth in climate, weather, and water begin with Sun-Earth geometry. Viewed from a hypothetical position above the North Pole, the Earth orbits the Sun counterclockwise in an elliptical orbit, close to a perfect circle. The average distance to the Sun is 93 million miles (150 million km). This distance is called 1 astronomical unit of length (AU), defined by the International Astronomical Union as the mean distance between the Earth and Sun over 1 orbit of the Earth. (Figure 1.2.)
Earth’s axis is tilted 23.4° with respect to its orbital plane, defined by the line between the Sun and Earth. The angle of incidence is the angle formed between the Sun’s parallel rays and earth’s surface. This angle is known to designers familiar with requirements for window shading and solar control: For any building at any latitude, the range of solar altitude in degree angles is 23.4° + 23.4° = 46.8°.
Due to the Earth’s axial tilt, the amount of sunlight reaching the surface of Earth varies over the course of the year, and heat imbalance is created between the poles, generating conditions for global thermal flows in atmosphere and oceans. By convention, the seasons of the calendar are determined by the summer and winter solstice—when the tilt of Earth’s axis is most inclined toward or away from the Sun—and the vernal and autumnal equinox, when the angle of the tilt is perpendicular to the Sun-Earth line and the Sun directly overhead along the equator.
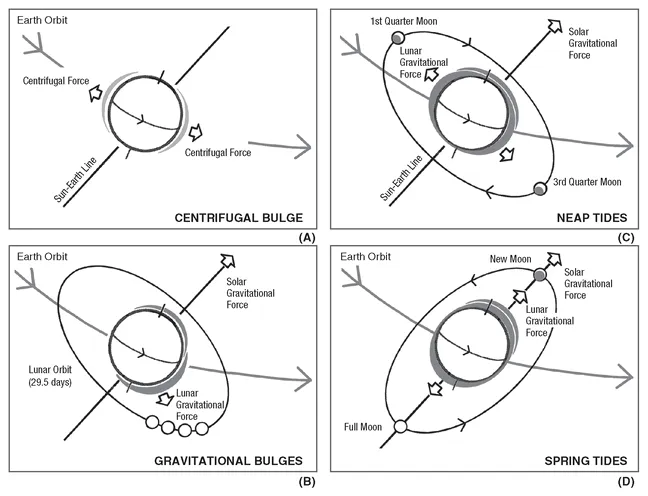
The average distance between Earth and Moon is approximately 240,000 miles (386,000 km) or, for purposes of visualization, approximately 30 times Earth’s diameter. Earth is held in orbit by the gravitational force of the Sun. Earth and Moon are influenced by mutual gravitation that counteracts their centrifugal forces. The world’s ocean mass is pulled by lunar gravity that influences tides more than the Sun’s gravitation field. (Figures 1.3 and 1.4.)
Figure 1.2 Earth, Moon, and Sun shown in scale of size and distance.
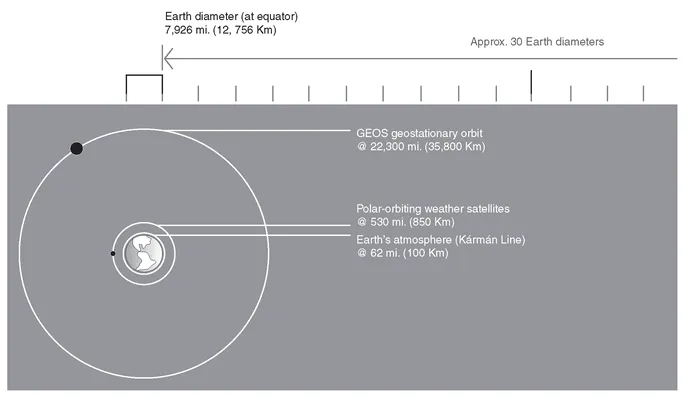
Figure 1.3a Solar geometry: Earth’s fixed angle of tilt as it orbits the Sun accounts for seasonal climate and weather.
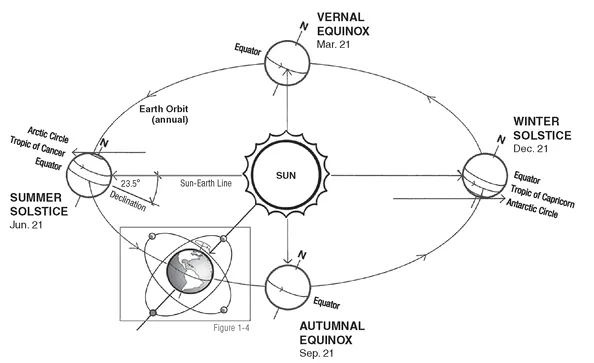
Figure 1.3b Midnight Sun: Time lapse of the Sun tracing a line just above the horizon, defining the Arctic Circle, Summer Solstice.
(PHOTO: © J. Farley)

Figure 1.4 Tides and time: The ebb and flow of tides result from the 19-year metonic cycle of solar and lunar gravitational forces.
1.2 THE ATMOSPHERE
Earth is enveloped by an atmosphere comprised of gases, water, and fine dust retained by gravity and characterized by different layers of distinct temperature and composition. The atmosphere is captured by the gravitational force of its mass and density. The chemical composition of our atmosphere has been created over geologic time by compounds outgassed from Earth’s crust, or possibly from impacts of volatile compounds from comets. The atmosphere is composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and small amounts of carbon dioxide, argon, and other gases and an average of 1% water vapor. The oxygen is the product of organic plant growth. (Table 1.1.)
The atmosphere expands and contracts as a function of season and magnetic and solar fluxes. It constantly loses molecules of lighter gases, such as helium and hydrogen. The outer limit has no clear boundary because the layer becomes increasingly thinner with altitude until it merges with outer space. (Figure 1.5 and Table 1.2.)
TABLE 1.1 EARTH ATMOSPHERE AIR COMPOSITION BY VOLUME
| Nitrogen | 78.08% |
| Oxygen | 20.95% |
| Argon | 0.93% |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.03% |
| Traces: neon: 0.0012%; krypton: 0.00005%; xenon: 0.000006%; helium: 0.0003%; also nitrous oxide, methane, and carbon monoxide. | |
Figure 1.5 Dimensions of the atmosphere.
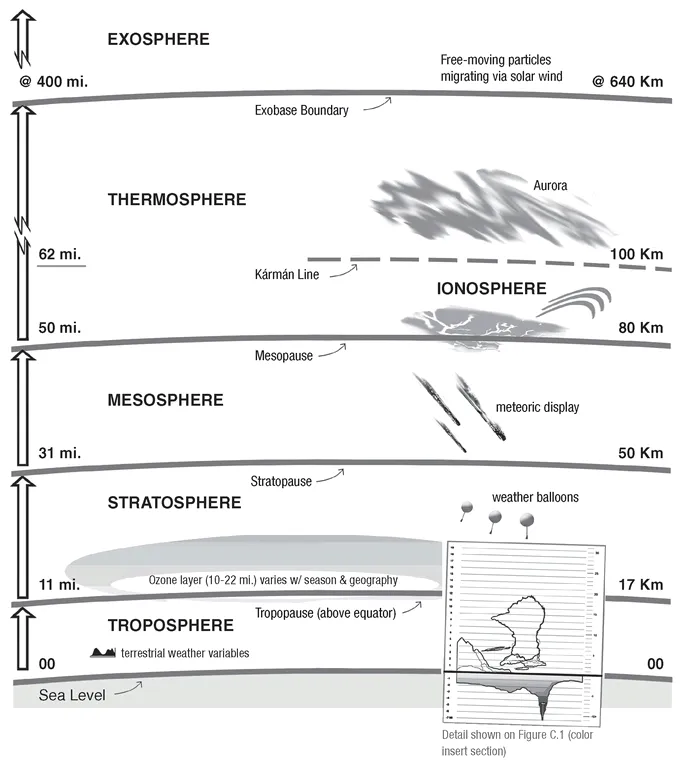
TABLE 1.2 EARTH’S ATMOSPHERIC LAYERS
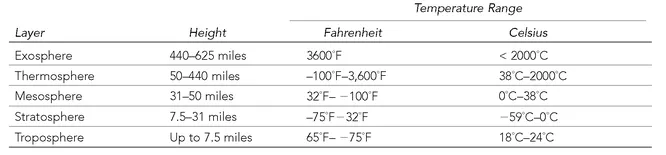
Exosphere. The outermost layer of the atmosphere in which gases get thinner and thinner and drift off into space.
Thermosphere. Temperatures generally increase with altitude, influenced by solar radiation. The gases of the thermosphere are thin but sufficient to absorb ultraviolet light from the Sun. Within the thermosphere, the ionosphere contains gas particles that are electrically charged by the Sun’s ultraviolet rays and bounce radio signals transmitted from Earth.
Mesosphere. Temperatures generally decrease with height because thinning gases do not absorb much of the Sun’s heat. The air density is sufficient to slow down meteorites hurtling into the atmosphere.
Stratosphere. Freezing temperatures gradually increase with height to about 32°F (0°C). The stratosphere contains 19% of the atmosphere’s gases, which move slowly and contain little moisture, so that clouds rarely form. Within the stratosphere is the ozone layer, a band of ozone gas that absorbs the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays.
Troposphere. Lowest major atmospheric layer, containing 75% of the atmospheric mass and 99% of water vapor and aerosols. Named after the Greek tropos, meaning “mixing,” it is turbulent and influenced by the surface of the Earth. The height of the troposphere varies with latitude, ranging between 5 miles (8 km) at the poles to 10.5 miles (17 km) at the equator.
The Kármán line is the adopted reference for the boundary between atmosphere and space, defined by the International Federation of Aeronautics as the “edge of space” at an altitude of 62 miles (100 km) above Earth’s surface.
All of Earth’s weather occurs in the troposphere. Energy from the Sun heats this layer and the land and oceans below, causing expansion of the air. This lower-density air then rises and is replaced by cooler, higher-density air. The resulting atmospheric circulation drives the weather through redistribution of heat energy and water in all its forms.
Earth’s surface has alter...