![]()
CHAPTER I
PREHISTORIC DRESS. FEMALE.
THE woman’s attire would have been chiefly a shortish skirt or wrap of coarse linen, wool, or leather, gathered in front or folded at one hip; grass cloth may also have been in use in most primitive tribes. Probably the upper part of the body was kept bare, except for many ornaments and necklaces, but a bodice or jacket cut in the same simple form as the male shirt, with a heavy belt or girdle, would have been used, and certainly a large shawl, which could be wrapped over the head and round the figure during inclement hours, Dyed or painted patterns on the cloths might well have been also in use, their chief designs being stripes, circles or dots, zigzag lines, diamonds and plaid squares, rope patterns and plaited patterns. The hair would have been loose, plaited, or coiled on top, held by bone pins or circlets of bronze.
PREHISTORIC DRESS. MALE.
We have little description or illustration to certify the actual dress of the early inhabitants of Britain, but we can draw conclusions with pretty certain assurance, from the knowledge of their mode of living. From their attainments in artistic design and handiwork, it is clear they had arrived at a very high state of savage culture before the Roman invasion; and we have only to study the better types of savage life still in progress, to picture how our own primitive race would be likely to dress under the conditions of climate. The thousands of “finds,” which accumulate evidence every year, give us a closer acquaintance with their customs and work. The rest we must imagine from our general knowledge of what they had to contend with in climate, forest, cave, and floods.
These early people, it is presumed from certain discoveries, had long known the art of coarsely weaving flax and wool, which must soon have been in general use, from its being healthier and cleaner than the garments of skin. And very probably a coarse linen, with simple dyes of red, blue, yellow, and brown, was in use here when the Romans came.
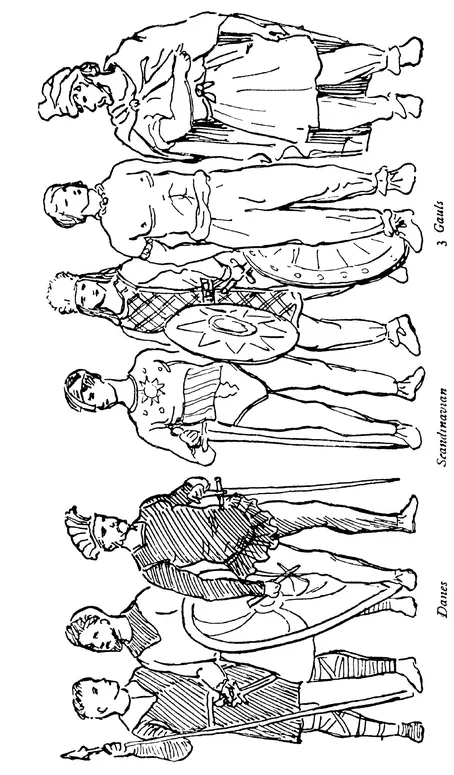
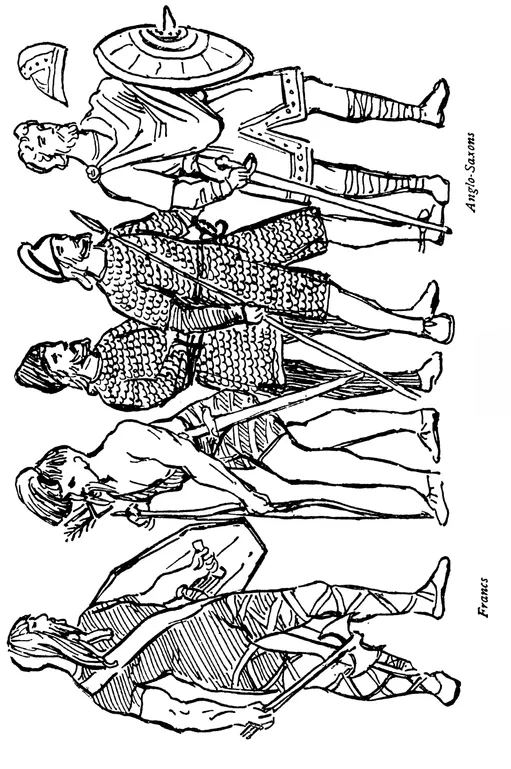
The head-dress consisted of a cap of fur or wool, probably decorated with a feather, over loose and most likely very unkempt hair falling to the shoulders. The Gauls cut their locks from the back of the head, often tying up the remainder in a tuft on the top; no doubt the hair was sometimes plaited or pinned up with wood, bone, or bronze ornaments. Bone pins, teeth, and boar tusks were carried in the ears, as well as studs of bone or stone in the underlip, and even the cheek may have been so decorated, as it was amongst the Esquimaux. The face and body were painted with red and white ochre and a blue stain. The neck was adorned with strings of teeth, stones, amber, jet, bronze, and probably beads of glass or baked clay coloured. Amulets and tokens, armlets and bracelets were all in use. Also the torque, a twisted rod of gold flattened or curled together at the ends, was a mark of dignity. A wristlet of wood, bone, or leather was worn when the bow and arrows were used. The arms were a spear of flint or bronze and a dagger of the same, a hatchet or heavy club, a mace studded with flint or bronze spikes, and the sling, which would have necessitated a leather wallet to carry the stones; fish spears and snags. Also the bolas for felling cattle seems to have been known; in fact nearly all the usual implements appertaining to savage life were in use.
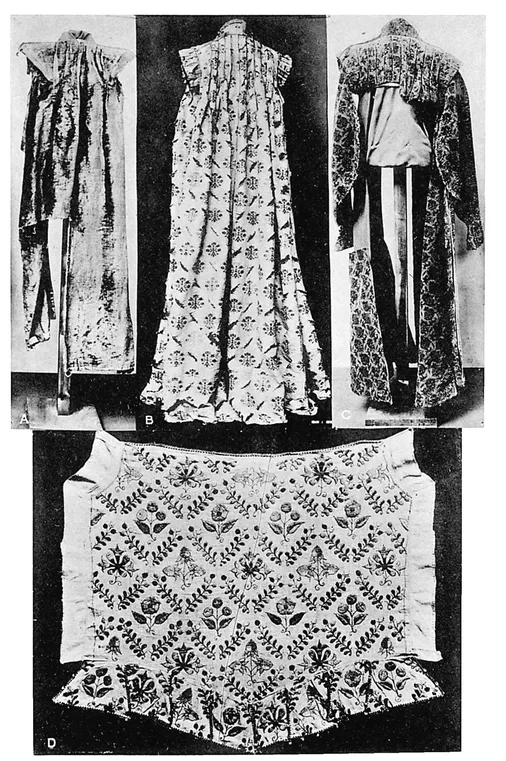
Plate II.—(a) Elizabethan Robe in Plush. 1585-1605.
(b) Elizabethan Robe in Silk Brocade. 1565-85.
(c) Elizabethan Male Robe in Velvet Brocade. 1580-1615.
(d) Back-piece of Elizabethan Doublet in Embroidered Linen. 1580-1605.
The first item of male attire was of two skins fastened at the shoulders, and from this we get the early chasuble form (which may be so beautifully treated, even to the present time), girt with a leather thong or strap at the waist. One skin lapped the other, and hardly needed sewing together at the sides, while thus it was easier to throw off; it may also have been tied up between the legs. The fur was worn both inside and out, according to the weather; this large skin wrap would also be worn crossways with the right shoulder free, and the simple cloak of various lengths with a hole for the head to pass through was no doubt one of the first discoveries in costume.
A loin cloth or skin may have been worn alone, caught up through the legs and fastened at the back of the waist with a heavy belt, and set well down the hips. This would hold a number of personal necessities, in the shape of a wallet and dagger. The legs would be wrapped with skins, tied up or crossed by leather or sinew thongs, or with hemp or grass rope. Skins may have been also used on the feet, gathered and tied above the instep and round the ankle.
The enumeration of these items will give a pretty definite idea of how the early race would appear in their more or less attired form. In fighting, they cleared for action (as it were) and discarded all clothing, their only protection being a shield of wicker or wood covered with leather; it may have been studded with bronze plates or painted with grotesque characters, as were their own bodies, in true savage style, to strike fear into their enemies; it is even possible feather decorations formed part of their “get up.”
![]()
CHAPTER II
THE DEVELOPMENT OF COSTUME TO THE TENTH CENTURY. FEMALE.
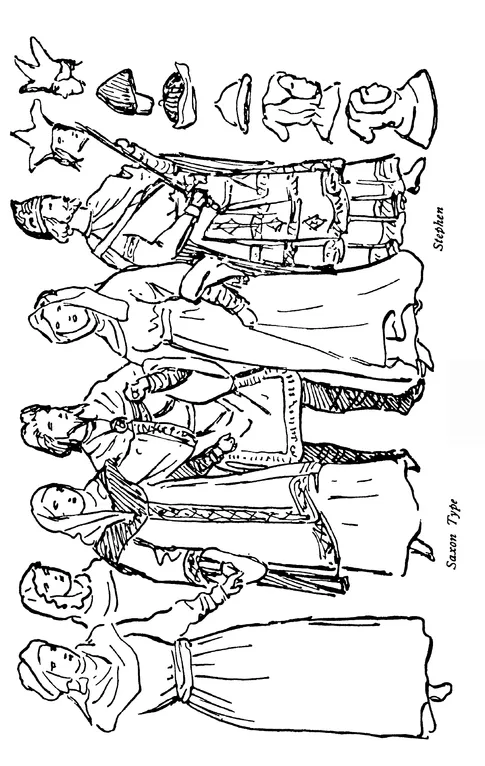
THE female head-dress consisted chiefly of flowing hair banded with a circlet of various shapes, but a development of braiding plaits is found very early, and the hair was probably arranged so before the Roman era. These plaits were generally brought over the shoulder to the front, the hair being parted in the centre, thus making an oval forehead. Various caps began to show originality, and jewels were set in the centre of the forehead on the little crown-like hat, which must have been most becoming. Squares of coloured stuffs were draped over the head and shoulders, sometimes upon white linen squares, and many ladies began to bind the face and head, shutting out the hair, in the 8th century. The kerchief draping is very important to study, because it was the general mode amongst the people.
Heavy collars of ornament and strings of beads, hanging even to the waist, are noticeable features of these centuries, also large ear-rings.
A full cloak, with a large clasp or brooch, opened in front, or was turned to free one shoulder; there was also a long “drape” thrown round over the opposite shoulder or brought picturesquely over the head.
The ecclesiastical form of cloak as described in the male attire was also formed about the 6th century; its graceful line was frequently bordered completely with a band of ornament, and it was clasped just across the breasts.
The complete circular cloak, with a hole for the head, is seen very early, decorated with a pinked edge, which may also be noted on some of the short dresses of the middle classes. Aprons are no doubt of the earliest origin. A loose tunic falling to the hips was girded rather high up the body, as in the classic dress, and bands passing both outside or crossing between the breasts and going over the shoulder came from the same source; these were with, or without, short sleeves to the elbow. A long loose robe was the chief attire to the 6th century, belted rather high in the waist, and caught up with a girdle at the hips; these girdles gave a great interest to the early centuries, with the art of arranging the fullness of skirt into its hold.
From the 6th century the dress became closer fitting, and a short bodice is seen; the neck was cut very low, either square or round in shape, and this style had short tight sleeves or tight sleeves to the wrist. The later tunic of the 9th century marked the beginning of the slit-open upper sleeve, and a greater length of the neck opening, which came to be fastened down the front to the waist.
The early skirts (to the 6th century) were hung from the hips, and were often attached to a heavy girdle band, the fullness was gathered mostly at the back and front; other skirts hung from a higher belt and were again caught up in the girdle. A V-shaped neck setting was worn by the Franks, from which probably came the shaped front piece that will interest us in the 13th century. The shoes were similar to the male shapes described later, and the same mode of binding the stockings was sometimes imitated.
THE DEVELOPMENT OF COSTUME TO THE TENTH CENTURY. MALE.
In taking the long period from the Roman occupation to the 10th century, we can discover a real development of style in costume, as with the system of vassalage a distinction of class arose. No doubt the Romans introduced a finer tuition of weaving, needlecraft, decoration, and dyeing; and later the various peoples coming from the Continent, when settled under Alfred in the 9th century, produced a solid style of barbaric splendour.
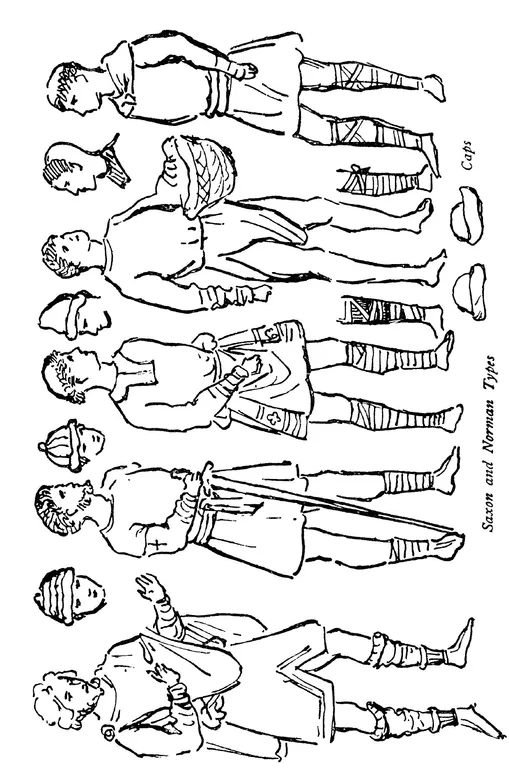
The male hair dressing, from the rugged mass of hair, soon became well combed and trimmed square across the neck: ear-rings may still have been in use by some nobles till the 11th century, and chaplets were worn upon the hair. The Saxon beard was divided into two points. Small round tight caps of wool, fur, or velvet, and rush or straw hats of a definite shape were in use to the 10th century. Tight caps, with lappets tied under the chin, and hoods appear on the short capes about the 8th century, or probably earlier. The garment was of the simplest form, cut like a plain square loose shirt to the middle of the thigh, and this was put on over the head. The opening to pass the head through was the first part to receive a band of decoration. The sides were sometimes opened to the hips and the front caught between the legs and held at the waist. A garment opened down the front, and another wrapped across to either shoulder is also seen. A belt girt the waist, and the tunic was pulled loosely over it. This also carried the essential requirements in the shape of a pouch, dagger, knife, comb, sword, &c. The neck was ornamented with chains of bronze, gold, beads, and charms, and up to the 8th century a bronze ornamental armlet was worn, besides a wristlet.
The men of the ruling class from the 8th century were clothed in a long garment of simple shape, falling to the ankle, richly bordered at the hem and neck. This generally had long tight sleeves, and often over this a shorter tunic, reaching just below the knee, sometimes sleeveless, or with rather full sleeves tightening to the wrist.
A plain square chasuble shape was in fashion from the 8th century, reaching to the bottom of the calf of the leg, and richer materials began to be used; no belt was passed round this, as it was allowed to fall straight.
Loose breeches were worn from very early times, and a loose trouser to the ankle, being tied there or bound crosswise from the boot right up the thigh. The same binding was done even with the bare legs, and later tights, close-fitting short breeches and woollen tights, became a feature in the 10th century, and with the latter an ornamental knee-piece or garter below the knee ...