
eBook - ePub
Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics
This is a test
- 656 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
This best-selling dictionary is now in its 4th edition. Specifically written for students of language teaching and applied linguistics, it has become an indispensible resource for those engaged in courses in TEFL, TESOL, applied linguistics and introductory courses in general linguistics.
Fully revised, this new edition includes over 350 new entries. Previous definitions have been revised or replaced in order to make this the most up-to-date and comprehensive dictionary available.
Providing straightforward and accessible explanations of difficult terms and ideas in applied linguistics, this dictionary offers:
- Nearly 3000 detailed entries, from subject areas such as teaching methodology, curriculum development, sociolinguistics, syntax and phonetics.
- Clear and accurate definitions which assume no prior knowledge of the subject matter
- helpful diagrams and tables
- cross references throughout, linking related subject areas for ease of reference, and helping to broaden students' knowledge
The Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics is the definitive resource for students.
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics by Jack C. Richards, Richard W. Schmidt in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Languages & Linguistics & Linguistics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
C
CA n
an abbreviation for CONTRASTIVE ANALYSIS. Also an abbreviation for CONVERSATION ANALYSIS
CACD n
an abbreviation for computer-assisted classroom discussion
CAH n
an abbreviation for the contrastive analysis hypothesis
CAI n
an abbreviation for COMPUTER-ASSISTED INSTRUCTION
CAL n
an abbreviation for COMPUTER-ASSISTED LEARNING
CAL n
also an abbreviation for the Center for Applied Linguistics, located in Washington, DC.
CALICO n
an abbreviation for Computer Assisted Language Instruction Consortium
CALL n
an abbreviation for COMPUTER-ASSISTED LANGUAGE LEARNING
CALP n
an abbreviation for COGNITIVE ACADEMIC LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY.
calque n
see LOAN TRANSLATION
call-word n
see DRILL
Cambridge Exams
a set of examinations developed by Cambridge ESOL (also known as UCLES) which place students according to 5 levels of proficiency from basic (1) to advanced (5):
1 Key English Test (KET)(1)
2 Preliminary English Test (PET)
3 First Certificate in English (FCE)
4 Certificate of Advanced English (CAE)
5 Certificate of Proficiency in English (CPE).
candidate n
another term for TEST TAKER
can-do statements n
an approach to describing learning outcomes associated with the COMMON EUROPEAN FRAMEWORK, which describes the learner’s performance or some aspect of it in terms of what the learner is able to do. For example:
The learner can express simple opinions on familiar topics in a familiar context.
The “can-do” statements of learning outcomes are linked to different levels on a proficiency band or scale.
canonical n
typical or usual. For example, the canonical word order of English is SVO (subject-verb-object), although other orders are possible.
canonical form n
the form of a linguistic item which is usually shown as the standard form. For example, the plural morpheme in English is usually shown as -s, even though it may appear as -s, -es, -en, etc., -s is the canonical form.
canonical order n
also canonical word order
the basic order of the constituents subject (S), object (O) and verb (V) in a particular language. For example, the canonical order of English is SVO, while in Japanese the canonical order is SOV.
captioned video n
see SUBTITLES
captioning n
see SUBTITLES
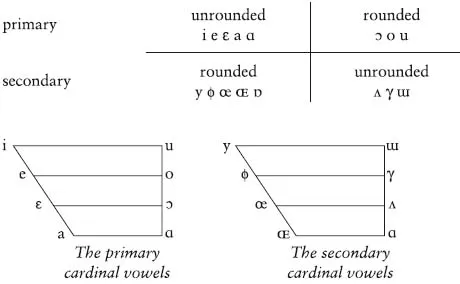
cardinal vowel n
any of the VOWELS in the cardinal vowel system. The cardinal vowel system was invented by Daniel Jones as a means of describing the vowels in any language. The cardinal vowels themselves do not belong to any particular language, but are possible vowels to be used as reference points.
The cardinal vowel [i] is made with the front of the tongue as high as possible in the mouth without touching the roof of the mouth. It is a front vowel. By gradually lowering the tongue, three more front vowels were established: [e], [ε] and [a]. The difference in tongue position for [i] and [e], for [e] and [ε] and for [ε] and [a] is approximately equal and the difference in sound between each vowel and the next one is also similar. All these front vowels are made with fairly spread lips.
Cardinal vowel [ɑ] is made with the back of the tongue as low as possible in the mouth. It is a back vowel. By gradually raising the back of the tongue from the [ɑ] position, three other cardinal vowels were established: [ɔ], [o] and [u]. These three are made with the lips gradually more rounded.
These eight vowels are known as the primary cardinal vowels. The five vowels: [i], [e], [ε], [a] and [ɑ] are unrounded vowels and [ɔ], [o] and [u] are rounded vowels.
With the tongue in these eight positions, a secondary series of cardinal vowels was established. Where the primary cardinal vowels are unrounded, the secondary cardinal vowels are rounded. Where the primary cardinal vowels are rounded, the secondary cardinal vowels are unrounded.
caretaker speech n
also motherese, mother talk, baby talk
the simple speech used by mothers, fathers, babysitters, etc., when they talk to young children who are learning to talk.
Caretaker speech usually has:
| a | shorter utterances than speech to other adults |
| b | grammatically simple utterances |
| c | few abstract or difficult words, with a lot of repetition |
| d | clearer pronunciation, sometimes with exaggerated INTONATION patterns |
Caretaker speech is easier for children to understand, and many people believe that it helps children to learn language.
see also FOREIGNER TALK
carrel n
in a LANGUAGE LABORATORY or multimedia centre, an installation containing individual recording decks and headphones, or a computer, video and TV monitor for student use. Carrels may be arranged in rows or other layouts. In a language laboratory, a carrel is also known as an audio booth.
cascade model n
an approach to teacher training and curriculum innovation in which one group receives training in the innovation (e.g. a new teaching method) and goes on to train other groups, who continue the process. In this way the innovation is said to “cascade” downwards. This model of dissemination allows new ideas and practices to reach large numbers of teachers relatively quickly.
see MULTIPLIER EFFECT
case1 n
(in some languages) a grammatical category that shows the function of the noun or noun phrase in a sentence. The form of the noun or noun phrase changes (by INFLECTION) to show the different functions or cases. For example, German has four cases, NOMINATIVE, ACCUSATIVE, DATIVE, GENITIVE. Endings on the article change to show the case (the function) of the noun, e.g.:
Nominative case (table is the subject of the sentence)
Der Tisch ist gross.
The table is big.
Accusative case (table is the object of the sentence)
Karin kaufte den Tisch.
Karin bought the table.
Some languages, e.g. Russian, have more than four cases, others have fewer, and some have none at all. In these languages the functions shown by case marking may be shown by WORD ORDER or by PREPOSITIONS.
English marks case only on pronouns. Three cases are recognized:
Nominative: I, we, you, he, she, it, they, who
Objective: me, us, you, him, her, it, them, who(m)
Genitive: my, our, your, his, her, its, their, whose.
case2
see CASE GRAMMAR
case assigner n
(in CASE THEORY) an element that assigns a particular function, a case (see CASE1), to a noun phrase in a sentence. Case assigners are often verbs or prepositions.
case grammar n
an approach to grammar developed in the 1970s which stresses the semantic relationships in a sentence. Parts of case grammar have been incorporated into more recent versions of GENERATIVE GRAMMAR.
see also AGENTIVE CASE, BENEFACTIVE CASE, DATIVE CASE2, FACTITIVE CASE, INSTRUMENTAL CASE, LOCATIVE CASE, OBJECTIVE CASE
case methods n
in language teaching and teacher education, the use of cases as a form of peda...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- GUIDE TO THE DICTIONARY
- INTRODUCTION
- Table of Contents
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z