![]()
1 |
Introduction |
|
J.-G. Wittneben, H. P. Weber |
The use of dental implants in the esthetic zone is well documented in the literature. Numerous controlled clinical trials have shown that the overall implant survival and success rates involved are similar to those reported for other indications. However, few studies have been published in which the actual success of the treatment was measured. This would have to include a critical and systematic assessment of short-term and long-term outcomes with implant-supported prostheses in the esthetic zone, including esthetic parameters.
Implant therapy in the esthetic zone is considered an advanced or complex procedure that requires comprehensive preoperative planning and precise surgical execution based on a restoration-driven approach. The esthetic zone is generally defined as any dentoalveolar segment that is visible in full smile. For the purposes of this text, the esthetic zone has been defined as the portion of the dentition that is predominantly visible when facing an individual, encompassing the maxillary anterior teeth from the right to the left canine.
There is convincing evidence that replacement of single teeth with implant-supported restorations in the esthetic zone will yield esthetically and functionally successful treatment outcomes if the hard and soft tissues surrounding the adjacent natural teeth are intact and if guidelines for correct three-dimensional implant placement and restoration, as appropriate for the respective indications, are properly followed.
By contrast, esthetically ideal outcomes are less predictably achieved when replacing multiple adjacent missing teeth in the anterior maxilla with fixed implantsupported restorations, the main problem being that the bone and soft-tissue volume is often deficient both vertically and horizontally in multi-tooth edentulous areas. Deficiencies of this type will require appropriate procedures to augment the hard or soft tissues affected. But the efficacy and predictability of these procedures are limited when it comes to vertical augmentation and, for that matter, biologic ways of replacing any missing soft tissue between implants.
The present volume within the ITI Treatment Guide series summarizes the results and consensus statements of the 3rd and 4th ITI Consensus Conferences. It also contains a review of current evidence regarding the treatment of extended edentulous spaces in the esthetic zone with implant-supported restorations. Clinical recommendations for treatment alternatives and procedures are based, as much as possible, on existing scientific and clinical evidence, including the experiences and suggestions of many seasoned clinicians within the ITI and outside. Special emphasis is given to the preoperative evaluation, treatment planning, and assessment of risk factors for these—often complex—indications. Surgical and prosthodontic procedures are presented with detailed descriptions and illustrations followed by a number of step-by-step clinical case presentations. Complications of various etiologies are highlighted and suggestions are made on how to avoid them. A number of clinical cases documenting various complications and their treatment complete this volume of the ITI Treatment Guide.
In summary, the purpose of this sixth volume of the ITI Treatment Guide series is to provide clinical recommendations for implant-supported prosthodontic treatments in patients with multiple missing adjacent teeth in the esthetic zone. The authors hope that they have created a valuable resource for clinicians who perform implant treatment on patients with indications of this type and that they can enhance the ability of clinicians to achieve successful long-term outcomes in these situations despite their often complex esthetic nature.
![]()
2 | Proceedings of the 3rd and 4th ITI Consensus Conferences and Literature Review: Extended Edentulous Spaces in the Esthetic Zone |
The International Team for Implantology (ITI) is an independent academic organization that brings together professionals from various fields in implant dentistry and tissue regeneration. The ITI regularly publishes treatment guidelines based on evidence from systematic reviews or clinical studies with long-term clinical results. Information of this type is also included in the ITI Treatment Guides, which have become a valuable resource for clinicians engaging in patient care involving implant dentistry of various degrees of difficulty.
The ITI regularly organizes Consensus Conferences to review the current literature in the field with the aim of evaluating and updating the scientific evidence supporting the entire variety of clinical materials and techniques. The resulting consensus statements and clinical recommendations are agreed upon by invited panels of experts, and the results are published in peer-reviewed journals.
In keeping with the topic of Volume 6 of the ITI Treatment Guide, “Extended Edentulous Spaces in the Esthetic Zone,” Consensus Statements and Clinical Recommendations from the 3rd ITI Consensus Conference in 2003 in Gstaad, Switzerland and the 4th ITI Consensus Conference in 2008 in Stuttgart, Germany have been extracted from the original Consensus Proceedings. The following paragraphs will list the Consensus Statements with direct relevance to the main objectives of this text, namely considerations of treatment planning, risk assessment, and prosthodontic concepts to successfully replace multiple missing teeth in the maxillary anterior region with implant-supported restorations.
2.1.1Proceedings of the 3rd ITI Consensus Conference 2003
International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 2004, Vol. 19 (Supplement)
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Esthetics in Implant Dentistry (Belser and coworkers 2004)
Long-term results
•The use of dental implants in the esthetic zone is well documented in the literature. Numerous controlled clinical trials show that the respective overall implant survival and success rates are similar to those reported for other segments of the jaws. However, most of these studies do not include well-defined esthetic parameters or criteria of patient satisfaction.
•The replacement of multiple adjacent missing teeth in the anterior maxilla with fixed implant restorations is poorly documented. Esthetic reconstructions, particularly regarding the contours of the interimplant soft tissue, are not predictable in this situation.
Surgical considerations
•Planning and execution. Implant therapy in the anterior maxilla is considered an advanced or complex procedure that requires comprehensive preoperative planning and precise surgical execution based on a prosthetically driven approach.
•Patient selection. Appropriate patient selection is essential to achieving esthetic treatment outcomes. Treatment of high-risk patients identified through site analysis and a general risk assessment (medical status, periodontal susceptibility, smoking, and other risks) should be undertaken with caution, since esthetic results are less consistent in these cases.
•Implant selection. Implant type and dimensions should be selected based on site anatomy and on the planned restoration. Inappropriate dimensions of the implant body and shoulder may result in hard- or soft-tissue complications.
•Implant positioning. Correct three-dimensional implant placement is essential to an esthetic outcome of treatment. If the comfort zones are respected in all three dimensions, the implant shoulder will be located in an ideal position, allowing for an esthetic implant restoration with long-term stability of the peri-implant tissue support.
•Soft-tissue stability. For long-term stability of esthetic soft tissue, an adequate horizontal and vertical bone volume is essential. Where deficiencies exist, appropriate grafting or procedures to augment hard or soft tissue are required. Correcting deficiencies in bone height remains a challenge, often resulting in esthetic shortcomings.
Prosthodontic considerations
•Esthetic fixed implant-supported restorations. An esthetic implant-supported restoration was defined as one that is in harmony with the perioral facial structures of the patient. The esthetic peri-implant tissues must be in harmony with the healthy surrounding dentition—including health, height, volume, color, and contours. The restoration should imitate the natural appearance of the missing dental unit(s) in color, form, texture, size, and optical properties.
•Esthetic zone. Objectively, the esthetic zone can be defined as any dentoalveolar segment that is visible in full smile. Subjectively, the esthetic zone can be defined as any dentoalveolar area of esthetic importance to the patient. (Note: For purposes of the present volume, the esthetic zone is defined as being limited to the anterior maxilla, from right to left canine.)
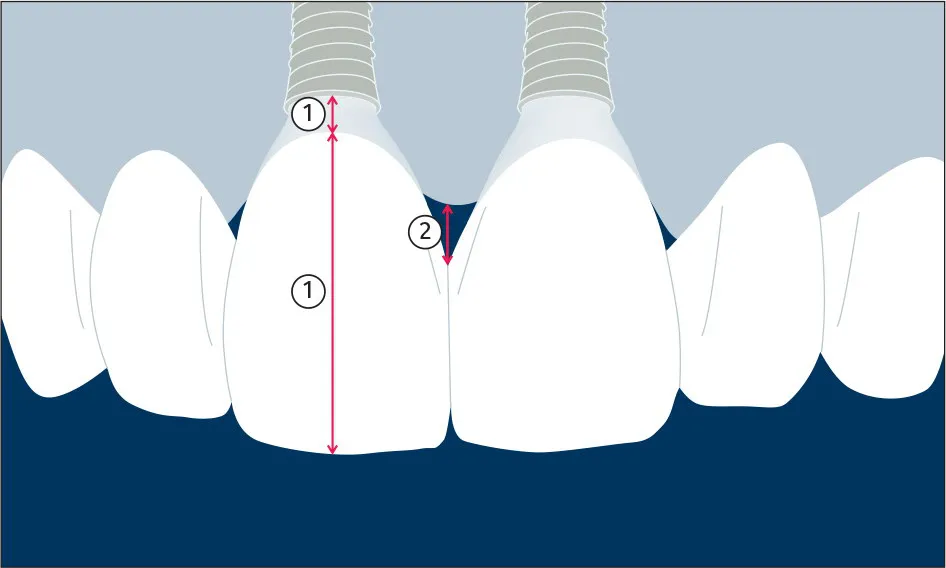
Fig 1Illustration of esthetic soft-tissue parameters: (1) location of the mid-facial soft-tissue margin adjacent to an implant-supported restoration in relation to the incisal edge or implant shoulder; (2) distance between the tip of the papilla and the most apical interproximal contact.
•Esthetic outcomes. The following soft-tissue parameters were considered esthetically relevant and proposed for use in clinical studies:
–Location of the mid-facial soft-tissue margin adjacent to an implant-supported restoration in relation to the incisal edge or implant shoulder (Fig 1).
–Distance between the tip of the papilla and the most apical interproximal contact (Fig 1).
–Width of the facial keratinized mucosa.
–Assessment of mucosal conditions (modified gingival index, bleeding on probing).
–Subjective (patient-centered) measures of esthetic outcomes, such as visual analog scales.
•Provisional restorations. To optimize esthetic treatment outcomes, the use of provisional restorations with adequate emergence profiles is recommended to guide and shape the peri-implant tissue prior to definitive restoration.
•Implant shoulder. In most esthetic areas, the implant shoulder is located subgingivally, resulting in a deep interproximal margin. This shoulder location makes it difficult to seat the restoration and to remove cement. A screw-retained restoration (or a cemented restoration over a screw-retained custom abutment) is recommended to minimize these potential problems resulting from cementation errors.
2.1.2Proceedings of the 4th ITI Consensus Conference 2008
International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 2009, Vol. 24 (Supplement)
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols (Weber and coworkers 2009)
Principal consensus
In agreement with the 2007 Cochrane Report (Esposito and coworkers 2007), the ITI proposes the following definitions for the loading of dental implants (Weber and coworkers 2009):
•Conventional loading of dental implants is defined as later than 2 months following implant placement.
•Early loading of dental implants is defined as between 1 week and 2 months following implant placement.
•Immediate loading of dental implants is defined as earlier than 1 week following implant placement.
•A separate definition for delayed loading is no longer required.
Consensus statements relative to loading protocols for the esthetic zone (Grütter and Belser 2009)
While implant survival in partially edentulous areas of the esthetic zone does not appear to be affected by loading protocols, success criteria and patient-centered outcomes may be. As no data evaluating these aspects are available, clinical trials are recommended.
•Early loading of microrough implants between 6 and 8 weeks following implant placement can be considered routine in partially edentulous areas of the esthetic zone.
•Immediate loading of microrough dental implants can be considered a viable treatment option for partially edentulous areas in the esthetic zone. Treatment within this time frame is, however, complex and can be considered a valid treatment option for clinicians with an appropriate level of education, experience, and skills.
•Conventional loading (later than 2 months following implant placement) remains the procedure of choice in partially edentulous areas of the esthetic zone in the following situations:
–Stability is considered inadequate for early or immediate loading
–Specific clinical conditions such as compromised host or implant site
–Presence of parafunction or other dental complications
–Need for extensive or simultaneous augmentation procedures or sinus floor elevation
2.2 | Literature Review |
| H. P. Weber, J.-G. Wittneben |
2.2.1General Aspects and Biological Considerations
The use of dental implants in the esthetic zone is well documented in the literature. Numerous controlled clinical trials have shown that the overall implant survival and success rates are similar to those reported for other indications. However, most of these studies did not include well-defined esthetic parameters (Belser and coworkers 2004a; Belser and coworkers 2004b; Grütter and Belser 2009).
Implant therapy in the esthetic zone is considered an advanced or complex procedure that requires comprehensive preoperative planning and precise surgical execution based on a prosthetically driven approach (Buser and coworkers 2004). In general, the esthetic zone is defined as any dentoalveolar segment that is visible in full smile. Subjectively, the esthetic zone can be defined as any dentoalveolar area of esthetic importance to the patient (Higginbottom and coworkers 2004). (Note: For the purpose of this text, the esthetic zone has been defined as the portion of the dentition that is predominantly visible when facing an individual, encompassing the maxillary anterior teeth from right to left canine.)
There is convincing evidence that the replacement of single teeth with implant-supported restorations in the esthetic zone will be successful both esthetically and functionally if the hard and soft tissues at the adjacent natural teeth are intact and if the guidelines for correct three-dimensional implant placement for the respective indication are properly followed (Garber and Belser 1995; Buser and coworkers 2004).
Conversely, the esthetic result when replacing multiple adjacent missing teeth in the anterior maxilla with fixed implant-supported restorations is not as predictable (Kan and Rungcharassaeng 2003; Mitrani and coworkers 2005). The main problem is that vertical as well as horizontal bone and soft-tissue volumes in the a...