
Surgical Complications in Oral Implantology
Etiology, Prevention, and Management
Louie Al-Faraje
- 248 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Surgical Complications in Oral Implantology
Etiology, Prevention, and Management
Louie Al-Faraje
About This Book
This exceptional new book is designed as a self-instruction guide to the diagnosis, management, and prevention of surgery-related complications in implant dentistry. It functions in two ways: First, it is a valuable resource for the implant surgeon seeking practical and succinct information about how to manage a complication in an emergency setting; and second, it can be read from cover to cover as a primer on implant surgery, from the initial consultation and treatment planning through the restorative phase of treatment. Besides addressing pre-, intra-, and postoperative implant surgery complications, the book also includes a comprehensive treatment-planning protocol that allows for the early detection of potential surgical complications and how to avoid them. Early detection of complications that are amenable to rescue therapies may reverse the fate of a failing implant or a bone-grafting procedure. Invaluable for the novice and experienced implant surgeon alike.
Frequently asked questions
Information
PART 1
Identifying Preoperative Conditions That Could Lead to Complications
- 1 Inadequate or Excessive Vertical Restorative Space
- 2 Inadequate Horizontal Restorative Space
- 3 Limited Jaw Opening and Interarch Distance
- 4 Inadequate Alveolar Width for Optimal Buccolingual Positioning
- 5 Maxillary and Mandibular Tori
COMPLICATION 1
Inadequate or Excessive Vertical Restorative Space
Vertical space requirement for fixed restorations
Single-unit fixed restoration
Multi-unit fixed prosthesis
Vertical cantilever
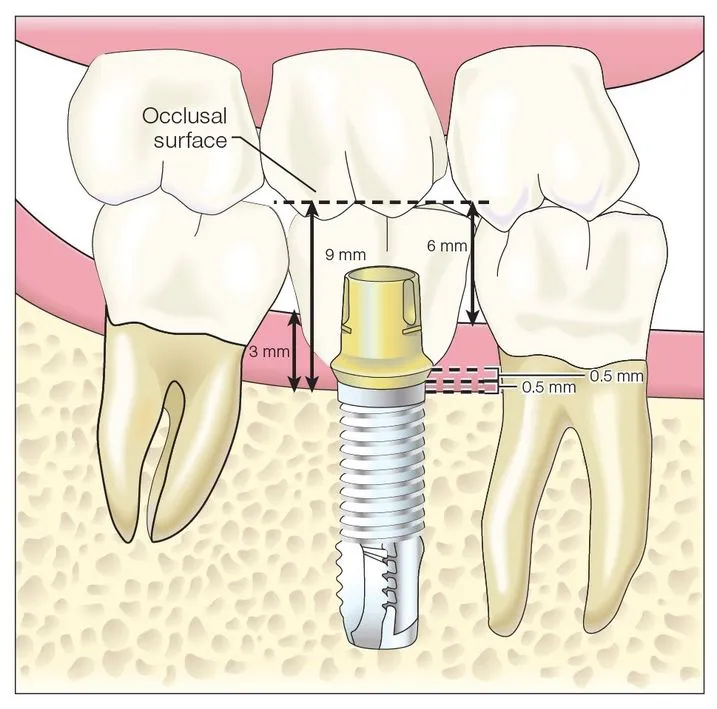
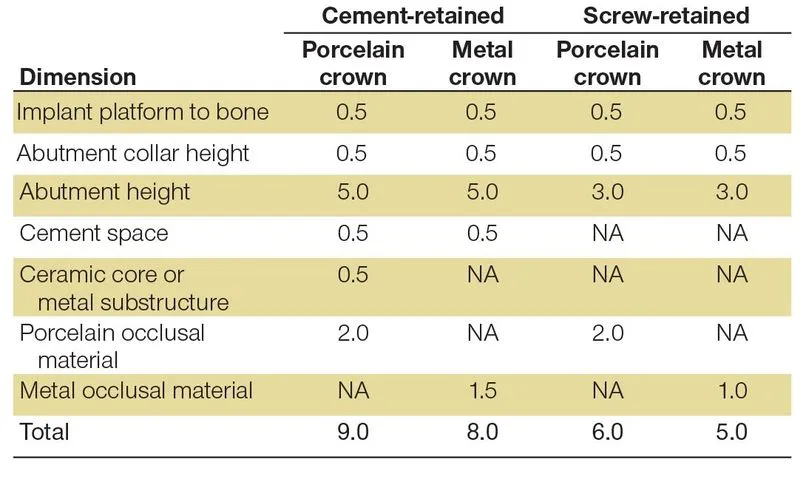
Vertical space requirement for removable restorations
Bar-retained overdenture
Ball- or Locator-retained overdenture


