
- 576 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Dictionary and Handbook of Nuclear Medicine and Clinical Imaging
About This Book
This impressive dictionary/handbook presents the nomenclature characteristic of nuclear medicine, explaining the meaning and current usage of a large variety of terms. It is designed as a ready-to-use and simple guide, arranged in alphabetical order with additional basic information assembled in the appendices. The single volume offers a look into the multidisciplinary world of this specialty. The field of nuclear medicine has emerged as an integrated medical discipline. It is an example of the convergence of many scientific disciplines with those of medicine emphasizing the use of radionuclides in research, diagnosis and therapy. The dictionary/handbook will be of importance to individuals in nuclear medicine and the following fields: physics, instrumentation, techniques, computers, radiopharmacology and radiopharmacy, radioimmunoassay, radiobiology and radiation protection, quality control, math and statistics, nuclear science and technology, radiology, ultrasound, and nuclear magnetic resonance.
Frequently asked questions
Dictionary
Fundamentals of English Medical Etymology
English, the Lingua Franca of Medicine
Analytical and Etymological Word List of Greek and Latin Combined forms, Prefixes and Suffixes












- Borland’s Illustrated Medical Dictionary, 26th Edition, W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1981.
- Illustrated Stedman’s Medical Dictionary, 24th Edition, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1962.
- International Dictionary of Medicine and Biology, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1986.
Common Prefixes, Suffixes, and Roots



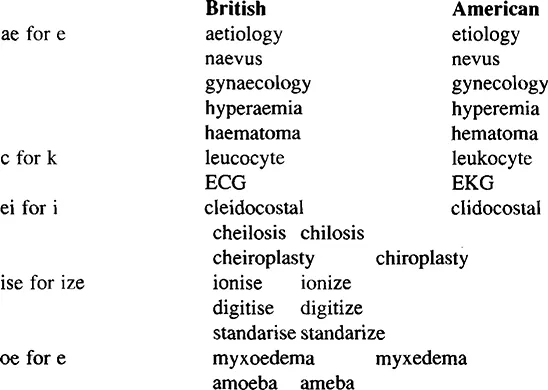
British and American Spellings

Terms Used to Describe Anatomical Positions and Planes



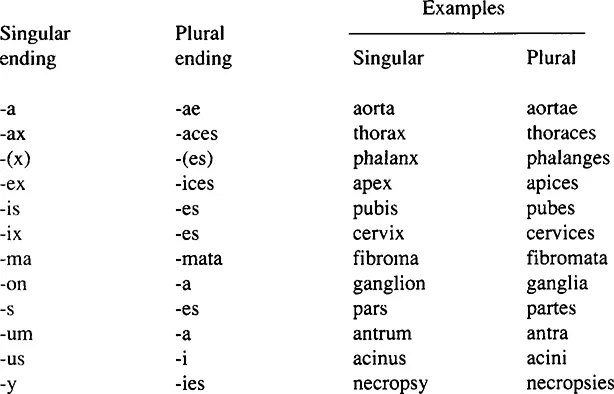
Plural Endings for Medical Terms
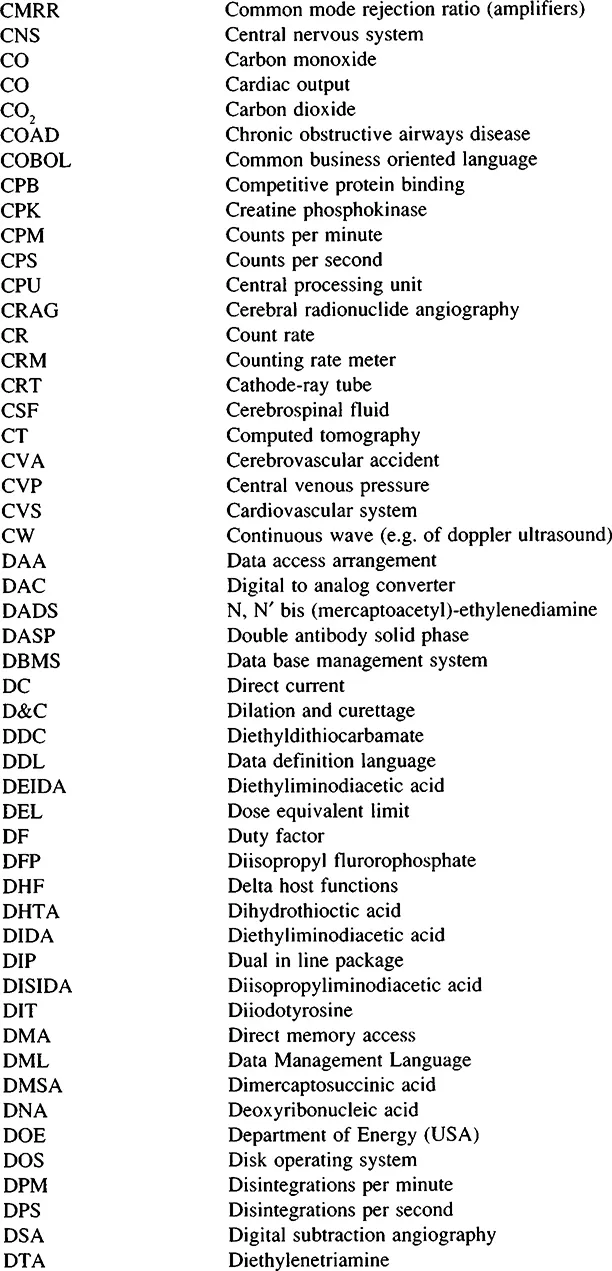
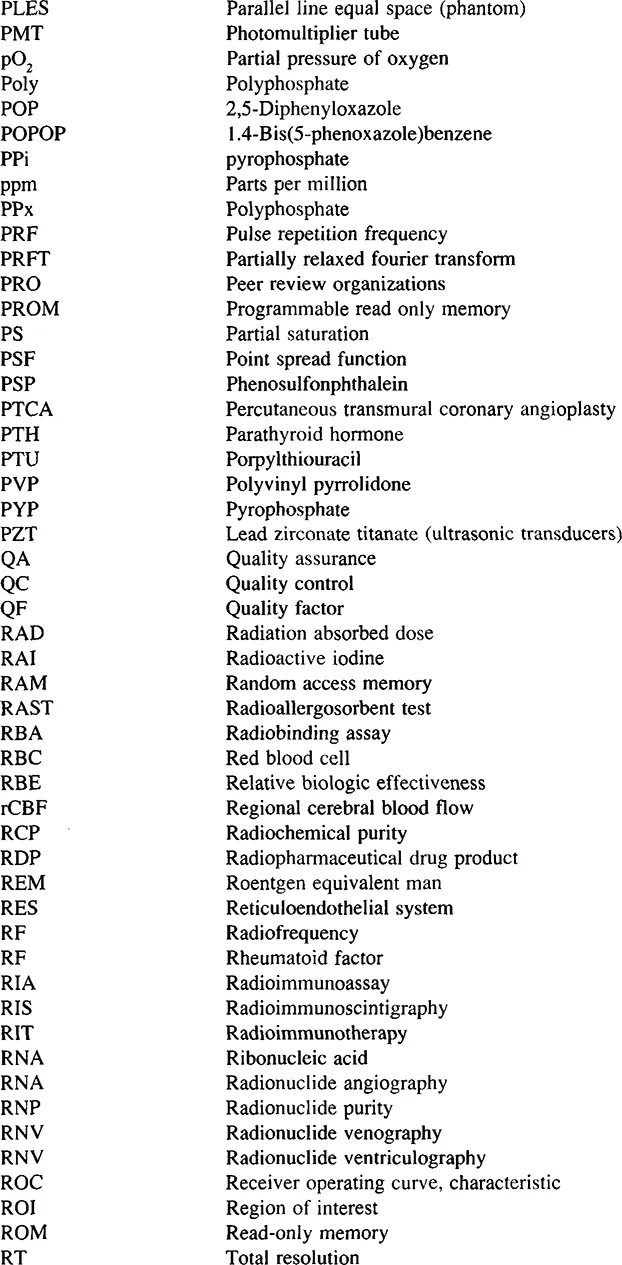
Abbreviations, Acronyms, Symbols, Denotations, and Signs Commonly Used or Defined in the Dictionary
Abbreviations and Acronyms






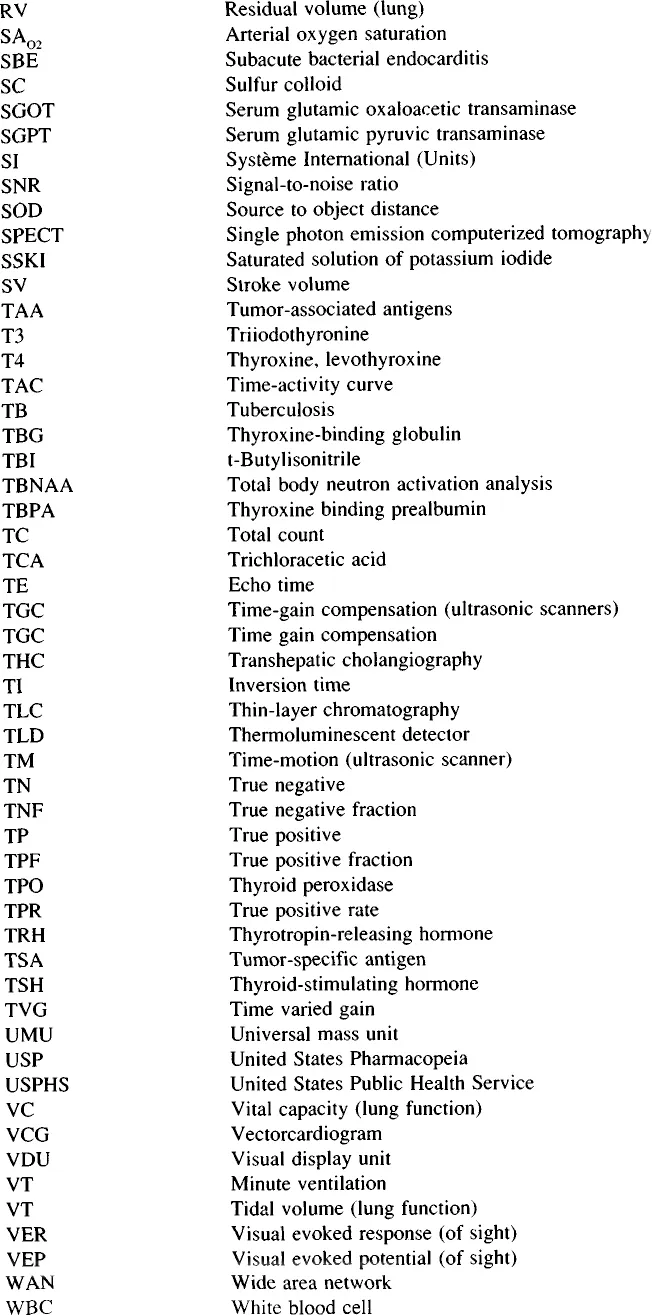






COMMON BASIC SIGNS


Other Useful Information
PHONETIC ALPHABET
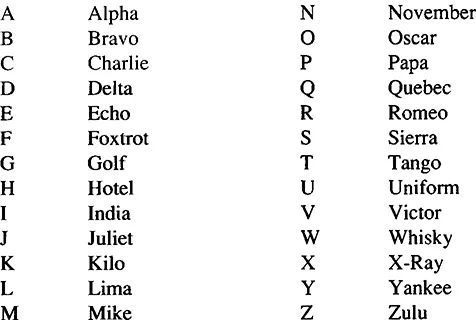
GREEK ALPHABET
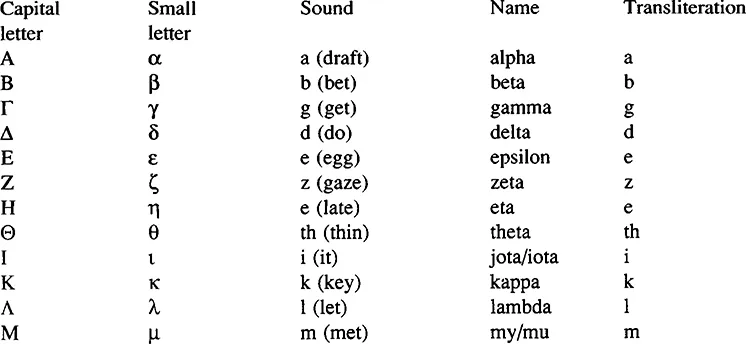

EUROPEAN AND AMERICAN NOTATIONS FOR LARGE NUMBERS
Bibliography
Books
- Amersham Nuclear Medicine Catalogue. Amersham International, Plc., Amersham. 1986.
- Basic and Clinical Immunology. 3rd Edition. H. Hugh Fundenberg, Daniel P. Sites, Joseph L. Cladwell, J. Vivian Wells. Lange Medical Publications. Los Altos, California. 1980.
- Basic Clinical Ultrasound. Hylton B. Meire, Pat Farrant. Bir Teaching Series.
- Basic Medical Statistics. Anita K. Bahn. Grune and Stratton, New York. 1972.
- Basics of Radiopharmacy. Buck A. Rhodes and Barbara Y. Croft. The C. V. Mosby Company, Saint Louis. 1978.
- Biomedical Instrumentation and Measurements. 2nd Edition. Leslie Cromwell, Fred J. Weibell, and Erich A. Pfeiffer. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey. 1980.
- Computer-Assisted Medical Decision Making. Homer R. Warner. Academic Press, New York. 1979.
- Computers and The General Practitioner. Alastair Malcolm and John Poyser. Pergamon Press, New York. 1982.
- Computers in Radiology. George B. Greenfield and Lincoln B. Hubbard. Churchill Livingstone, New York. 1984.
- Computers in the Practice of Medicine. Vol 1. Introduction to Computing Concepts. H. Dominic Covvey and Neil Harding McAlister. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company. Menlo Park, CA. 1980.
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 67th Edition (Definitions. Robert C. Weast, Editor-in-Chief. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. 1986–1987.
- CRC Handbook of Management of Radiation Protection Programs. K. L. Miller, and W. A. Weidner, Editors. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. 1986.
- CRC Handbook Series in Clinical Laboratory Science. Section A: Nuclear Medicine, Volume II. David Selingson, Editor-in-Chief, Richard P. Spencer, Section Editor. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. 1982.
- CRC Handbook of Medical Physics. Vol III. Robert G. Waggener, James G. Kereiakes and Robert J. Shalek. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
- Diagnostic Ultrasound. Text and Cases. Dennis A. Sarti and W. Frederick Sample. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. The Hague. 1980.
- Dictionary of Medical Equipment. Malcolm Brown, Paul Hammond, and Tony Johnson. Chapman and Hall. London. 1986.
- Dictionary of Radiation Protection, Radiobiology and Nuclear Medicine (in four languages). Compiled by Rald Sube. Elsevier, Amsterdam. 1986.
- Fundamentals of Immunology. 2nd Edition. Quentin N. Myrvik and Russell S. Weiser. Lae and Febiger, Philadelphia. 1984.
- Fundamentals of Nuclear Medicine. Naomi P. Alazraki and Fred S. Mishkin. The Society of Nuclear Medicine, New York. 1984.
- Fundamentals of Nuclear Pharmacy. 2nd Edition. Copal B. Saha. Springer-Verlag, New York. 1984.
- Glossary of Atomic Terms. Public Relations Branch, Atomic Energy Authority United Kingdom. London. 1974.
- Glossary of NMR Terms. Leon Axel, Alexander R. Margulis, Thomas F. Meaney American College of Radiology, Chicago, IL, 1983.
- Glossary of Terms in Nuclear Medicine and Technology. American Nuclear Society Standard Subcommittee on Nuclear Terminology and Units. La Grange Park, IL, 1976.
- Golden’s Diagnostic Radiology. Section 17: Tomography: Physical Principles and Clinical Applications. J. T. Littleton, M. L. Durizch, E. H. Crosby, and J. C. Geary. The Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore.
- Health Physics Handbook. General Dynamics. Fort Worth, Texas. 1963.
- Introduction to Radiological Physics and Radiation Dosimetry. Frank Herbert Attix. John Wiley & Sons, New York. 1986.
- MR Imaging Compendium. W. Koops. Philips Medical Systems. W. Koops, Rotterdam. 1986.
- NEMA Standards for Performance Measurements of Scintillation Cameras. The NEMA Standards Publication No. NU 1-1980, Washington, D. C. 1980.
- Newnes Concise Encyclopaedia of Nuclear Energy. D. E. Barnes, R. Batchelor, A. G. Maddock, J. A. Smedley, and Denis Taylor. George Newnes, London. 1962.
- NMR Data Handbook for Biomedical Applications. Paula T. Beal, Sharad R. Amtey, and Sitapati R. Kasturi. Pergamon Press, New York. 1984.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, NMR Imaging. C. Leon Parrain, A. Everette James, F. David Rollo, and Ronald R. Price. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia. 1983.
- Nuclear Medicine Technology and Techniques. Donal R. Bernier, James K. Langan, and L. David Wells. The C. V. Mosby Company. St. Louis. 1981.
- Physics in Medicine and Biology Encyclopedia. T. F. McAinsh. Pergamon Press, New York. 1986.
- Physics in Nuclear Medicine. 2nd Edition. James A. Sorenson, Michael E. Phelps. Grune and Stratton. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Orlando, 1987.
- Practical Abdominal Ultrasound. Constantine Metreweli. William Heinemann Medical Books, London. 1978.
- Principles and Practice of Nuclear Medicine. Paul J. Early, D. Bruce Sodee. The C. V. Mosby Company, St. Louis. 1985.
- Principles of Radioisotope Methodology. Grafton D. Chase, Joseph L. Rabinowitz. Burgess Publishing, Minneapolis, MN 1963.
- Positron Emission Tomography. Martin Reivich and Abass Alavi, Editors. Alan R. Liss, Inc. New York. 1985.
- Quality Assurance in Nuclear Medicine. World Health Organization, Geneva. 1982.
- Quality Assurance of Radiopharmaceuticals. M. Frier and S. R. Hesslewood, Editors. Special Issue of Nuclear Medicine Communications. The British Nuclear Medicine Society. Chapman and Hall, London. 1980.
- Radiation Protection. Carl B. Braestrup, and Harold O. Wyckoff, Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, IL. 1958.
- Radiation Protection. Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 3. Pergamon Press, Oxford. 1960.
- Radiological Health Handbook. Division of Radiological Health. U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare. Bureau of State Services. Washington. 1960.
- Scientific Table. 7th Edition. K. Diem and C. Leintner. Ciba-Geigy, Basle, Switzerland. 1970.
- Siemens. Computer Terms and Definitions. Siemens Gassasonics, B. V. Uithoorn, The Netherlands. 1986.
- South African Bureau of Standards. South African Standard Code of Practice for the Industrial Use of Ionising Radiation. SABS 0203. Part 1. Pretoria. 1985.
- The Radiochemical Manual. 2nd Edition. The Radiochemical Centre, Amersham. 1966.
- Ultrasound. Environmental Health Criteria 22. World Health Organization, Geneva. 1982.
Periodicals
- American Journal of Cardiology
- American Journal of Physiologic Imaging
- British Journal of Radiology
- European Journal of Nuclear Medicine
- International Journal of Cancer
- Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography
- Journal of Nuclear Medicine
- Journal of Ultrasound and Medical Biology
- Nuclear Medicine Communications
- Radiology
- Seminars in Nuclear Medicine
Recognition of Copyrights
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- Dictionary
- Data Handbook
- Index to Handbook