Cognitive radio (CR) and opportunistic spectrum sharing are promising ideas for boosting the proficiency of spectrum usage, which is otherwise vacant for most of the time. Both of them require an alternate level of discernment about the encompassing condition and an alternate level of refinement, which prompts distinctive difficulties. CR is a hopeful technology that is anticipated as an impending candidate that can assuage the problem of spectrum crux. This is promising in a scenario where unlicensed (secondary) users concur with the incumbent (primary) user in licensed spectrum bands without inducing any intrusion to the incumbent communication. One of the essential mechanisms to achieve this is spectrum (range) sensing. To alleviate the problem of scarcity of spectrum the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has allowed the use of spectrum bands by the unlicensed users as far as they do not cause any interference to the primary users. Also, the secondary users have to vacate the spectrum as soon as they detect any incumbent user communication. This opportunistic use of spectrum increases the efficiency of the spectrum utilization and is referred to as opportunistic spectrum access (OSS) [2].
A cognitive radio (CR) is a radio that can change its transmission parameters in light of the apparent accessibility of the range groups in its working condition. CRs support dynamic spectrum access and encourage an auxiliary unlicensed client to productively use the accessible underutilized spectrum designated to the essential authorized clients.
A cognitive radio system (CRN) is made out of both the optional clients with CR-empowered radios and the incumbent users. A CR is characterized as a radio that can change its transmitter parameters according to the requirements and is cognizant about the environment in which it works. A CR has the capacity (intellectual ability) to detect and assemble data (e.g. the transmission recurrence, transfer speed, control, balance, etc.) from the encompassing condition and has the capacity (reconfigurability) to quickly adjust the operational parameters, for ideal execution, as per the data detected. With the above highlights, the CR innovation is being seen as the key empowering innovation for the cutting edge dynamic spectrum access systems that can proficiently use the accessible underutilized spectrum allotted by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to authorized holders, known as essential clients. CRs encourage a more adaptable and extensive utilization of the constrained and underutilized range for the optional clients, who have no range licenses.
CRs empower the utilization of transiently unused range, alluded to as range gap or blank area, and if an essential client means to utilize this band, at that point the optional client ought to consistently move to another range opening or remain in a similar band, adjusting its transmission control level or balance plan to abstain from meddling with the essential client. Customary range assignment plans and range get to conventions may never again be relevant when optional unlicensed clients exist together with essential authorized clients. In the event that auxiliary clients are permitted to transmit information alongside essential clients, the transmissions ought not to meddle with each other past an edge. If optional clients can transmit just without essential clients, at that point, auxiliary client transmitting information without an essential client ought to have the capacity to distinguish the return of the essential client and clear the band. At present, there is a lot of research being conducted and more should be performed to grow new range of administration approaches identified with CR for both range detection and dynamic range sharing.
Intellectual radio system engineering incorporates segments relating to both the auxiliary clients (optional system) and the essential clients (essential system). The auxiliary system is made out of an arrangement of optional clients with or without an optional base station, which are all furnished with CR capacities. An auxiliary system with a base station is alluded to as the framework-based CR. The base station goes about as a center point gathering the perceptions and consequences of spectrum investigation performed by every optional client and settling on the most proficient method to maintain a strategic distance from intrusion with the essential systems. According to this choice, every auxiliary client reconfigures the correspondence parameters. An auxiliary system without a base station is alluded to as the foundation less subjective radio specially appointed system or cognitive radio ad-hoc network (CRAHN). In a CRAHN, the CR auxiliary clients utilize collaboration plans to trade privately watched data among the gadgets to expand their insight into the whole system and choose their activities in light of this apparent worldwide information. An essential system involves essential clients and at least one essential base station, which are all as a rule not furnished with CR capacities. Consequently, if an auxiliary system shares an authorized range band with an essential system, the optional system is required to be capable to recognize the nearness of an essential client and direct the optional transmission to another accessible band that would not meddle with the essential transmission.
In numerous groups, spectrum access is a more major issue than physical shortage of spectrum. Because of heritage summon and control direction, the capacity of potential range clients to get such access is restricted. By checking the parts of the radio range, we find that:
1. Some recurrence groups in the range are very empty more often than not.
2. Some different groups of recurrence are incompletely possessed.
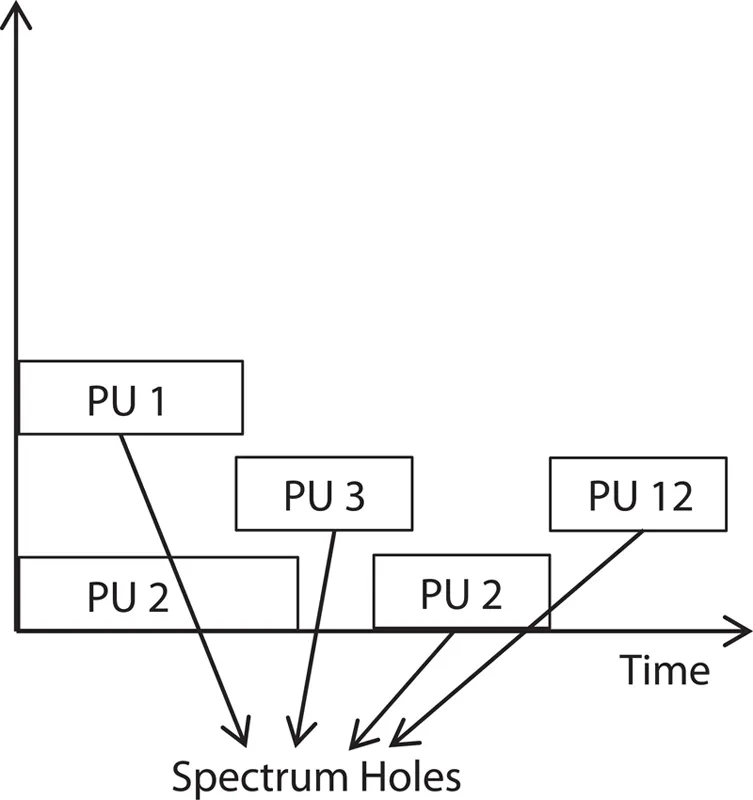
3. The rest of the groups of recurrence are to a great extent utilized. Spectrum hole is that in which a specific group of frequencies are relegated to a specific client at some particular land locale for some particular time, and this band is not utilized by another client around them. The CR empowers the utilization of unused range, which is known as void area or range opening. When the primary user is not utilizing the particular band, then the secondary user can utilize that band and enhance the spectrum usage resulting in the effective utilization of spectrum. The unused spectrum band is referred to as the spectrum hole. Figure 1.1 shows the illustration of spectrum hole.
1.3 Characteristics of CR
The main features of CR are:
1. It can decide its geographic area.
2. It can recognize and approve its clients.
3. It can perform encryption and decryption.
4. It can detect adjacent radios.
5. It can adapt to the environment in which it operates.
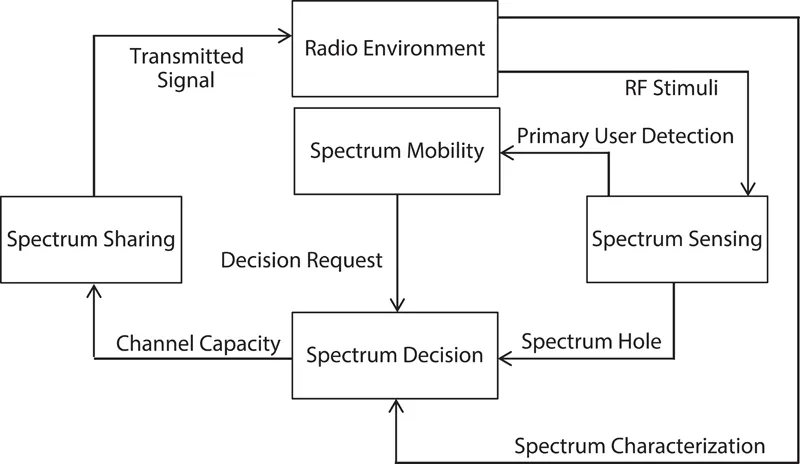
Figure 1.2 shows the cognition cycle on which the cognitive radio works [1]
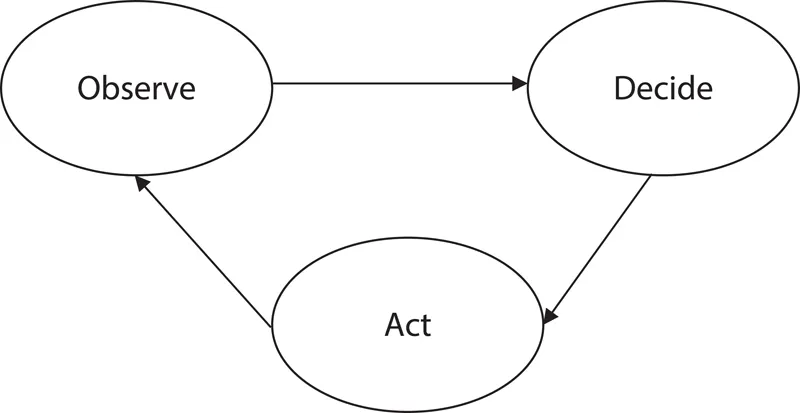
Figure 1.3 shows a simplified version of the cognitive cycle.
Observe: A CR is a gadget that has four wide inputs; to be specific, a comprehension of the environment in which it works, a comprehension of the correspondence prerequisites of the client, a comprehension of the system, and the administrative arrangements that are applied to it, and its very own comprehension abilities. In the end, a CR knows about the setting in which it is working.
Decide: A CR gathers data about the spectrum usage from different sources and reconfigures itself and decides the best way for the correspondence jobs that needs to be done. In choosing how to arrange itself, the radio is cognizant about the imperatives or clashes (physical, administrative, etc.) that may exist.
Act: A CR is produced using programming and hardware parts that can encourage the wide range of designs it needs to impart.
A CR is based on what is called a software defined radio (SDR) [3]. The software allows the radio to tune to different frequencies, power levels, and modulation depending upon its learning and the environment in which it operates. The CR is expected to perform the following four functions:
1. Spectrum Sensing: detection of “white spaces” or the portion of spectrum vacant for use. This must also ensure that no primary user (licensed user) is operating at the same time.
2. Spectrum Management: selection of the best spectrum hole for transmission.
3. Spectrum Sharing: sharing of spectrum with other potential users.
4. Spectrum Mobility: vacate the band when a licensed user is detected (spectrum handoff).
The functions mentioned above form a cognition cycle that forms the basis on which the CR operates. The cognitive cycle consists of five states, namely, Observe, Orient, Plan, Decide, and Act.
It is the capacity of the radio innovation to detect the data from its radio condition. There are some modern procedures that are required to catch the fleeting and spatial variety in the radio condition rather than basically be acknowledged by observing the power and maintain a strategic distance from different clients. By this ability, the unused range can be distinguished at a particular time and area. However, the best range and suitable working parameters can be chosen. The subjective capacity empowers ongoing collaboration with its climate to decide appropriate correspondence parameters and change in accordance with the dynamic radio environment. The three stages of cognitive cycle under this classification are:
Spectrum detection: An intellectual radio recognizes the accessible range groups, takes their data, and then identifies the range gaps.
Spectrum examination: The spectrum gaps that are distinguished by the spectrum detection are evaluated.
Spectrum choice: A subjective (cognitive) radio breaks down the information rate, the data-transfer capacity of the transmission mode. At that point, the appropriate spectrum band is selected as indicated by the range qualities and client necessities. Once the spectrum band is identified, the correspondence can be started by this band.
Range mindfulness is chosen by the cognitive ability; then again, reconfigurability advises the radio on how to program the radio condition powerfully. The radio can transmit and tune to various frequencies to utilize distinguishing transmission parameters. Reconfigurability is the abili...