
Telecommuting
Modelling the Employer's and the Employee's Decision-Making Process
- 182 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About This Book
Telecommuting has been regarded as a powerful tool to reduce traffic congestion, pollution and energy consumption. It also supposed to improve lifestyle quality and job satisfaction by providing employees with flexible schedules with which to address their work load and personal requirements whilst also enhancing recruitment capability and productivity and significantly reducing costs. Nevertheless, a strong resistance to the adoption of telecommuting still persists.
In this book, first published in 1996, state of the art demand modelling techniques are used to delve into critical issues raised by the question of telecommuting. The benefits and costs of telecommuting are investigated in an effort to provide concrete evidence to inform the private sector's adoption decision process and the public sector's policy design. This title will be of interest to students of business studies and human resource management.
Frequently asked questions
V
Model System Estimation Results
MODEL SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
The Employer’s Model
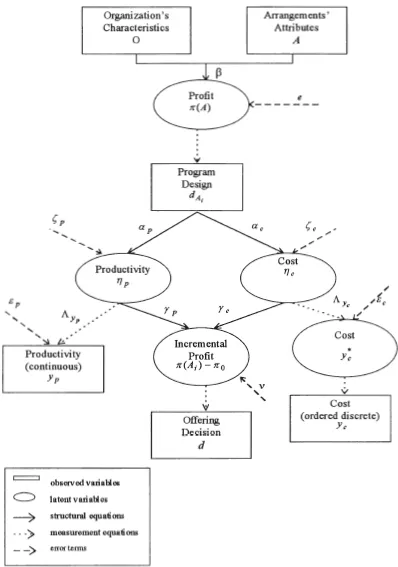
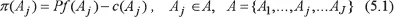
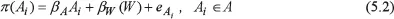
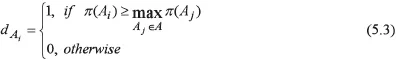
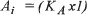
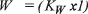
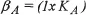
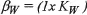
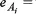

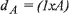
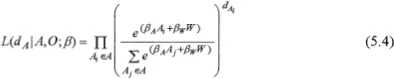
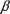
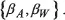
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- I Introduction
- II The State-of-the-Art
- III Analytical Framework
- IV A Survey of Telecommuting Preferences
- V Model System Estimation Results
- VI Analysis of the Results
- VII Conclusion
- A The Employer’s Survey
- B The Employee’s Survey
- References
- Index