
Applied Biostatistical Principles and Concepts
Clinicians' Guide to Data Analysis and Interpretation
- 288 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Applied Biostatistical Principles and Concepts
Clinicians' Guide to Data Analysis and Interpretation
About This Book
The past three decades have witnessed modern advances in statistical modeling and evidence discovery in biomedical, clinical, and population-based research. With these advances come the challenges in accurate model stipulation and application of models in scientific evidence discovery
Applied Biostatistical Principles and Concepts provides practical knowledge using biological and biochemical specimen/samples in order to understand health and disease processes at cellular, clinical, and population levels. Concepts and techniques provided will help researchers design and conduct studies, then translate data from bench to clinics in attempt to improve the health of patients and populations.
This book is suitable for both clinicians and health or biological sciences students. It presents the reality in statistical modelling of health research data in a concise manner that will address the issue of "big data" type I error tolerance and probability value, effect size and confidence interval for precision, effect measure modification and interaction as well as confounders, thus allowing for more valid inferences and yielding results that are more reliable, valid and accurate.
Frequently asked questions
Information
IIBiostatistical modeling
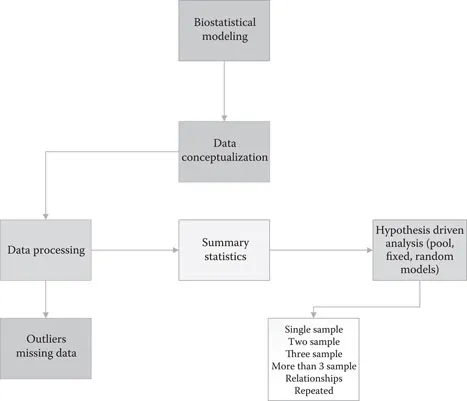
4Statistical considerations in clinical research
4.1Introduction
- Statistics is a highly developed information science.
- It is involved with the study of inferential processes, especially the planning and analysis of experiments, surveys or observational studies.a
- The study of how information should be employed to reflect on, and give guidance for action in a practical situation involving uncertainty.b
- A way of thinking or an approach to everyday problems that relies heavily on designed data production. It is essential in that its proper usability minimizes the chance of drawing incorrect conclusions from data.c
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Foreword
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Author
- Introduction
- References
- Section I Design process
- Section II Biostatistical modeling
- Appendix
- Index