
- 396 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Dynamic Linear Economic Models
About this book
Originally published in 1974. This book provides a rigorous and detailed introductory treatment of the theory of difference equations and their applications in the construction and analysis of dynamic economic models. It explains the theory of linear difference equations and various types of dynamic economic models are then analysed. Including plenty of examples of application throughout the text, it will be of use to those working in macroeconomics and econometrics.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Mathematical Preliminaries
1.1 Complex Numbers
In our analysis of difference equations we shall have to deal with various types of equations whose solutions cannot be found if we restrict our solutions to the set of real numbers. In order to avoid this problem we extend the number system to include complex numbers.
First we outline a list which comprises what is called the real number system. The natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, … are the same as the set of positive integers. To the set of natural numbers, we add the set of negative integers and zero (-1, -2, -3, …) and 0. The set of rational numbers or fractions is the set of numbers which can be written as a/b where b ≠ 0 and where a and b are positive or negative integers or a is zero. The set of irrational numbers is the set of numbers such as
which are expressible in terms of an infinite number of decimals but which cannot be expressed in the form a/b where a and b are integers. The set of rational and irrational numbers is called the set of real numbers. It is assumed that the student is already familiar with these ideas and with the various operations which can be performed on real numbers. For a more detailed treatment he should consult any text on real analysis.
Any real number can be represented by a point on a line called a real axis, as indicated below in Figure 1. The choice of origin and the unit length are completely arbitrary.
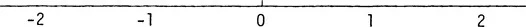
Figure 1
Once we have chosen an origin and a unit length, then to each real number there is one and only one point on the real axis and to each point on the real axis there corresponds one and only one real number. The absolute value of a real number a, d...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- CHAPTER 1 MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES
- CHAPTER 2 INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS
- CHAPTER 3 GENERAL THEORY OF LINEAR DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS
- CHAPTER 4 LINEAR HOMOGENEOUS DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH CONSTANT COEFFICIENTS
- CHAPTER 5 PARTICULAR SOLUTIONS
- CHAPTER 6 SOLVING LINEAR DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS USING OPERATORS
- CHAPTER 7 EQUILIBRIUM AND STABILITY
- CHAPTER 8 SYSTEMS OF DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS
- CHAPTER 9 DISTRIBUTED LAGS
- CHAPTER 10 ANALYSIS OF ACCELERATOR MODELS
- CHAPTER 11 LINEAR DYNAMIC ECONOMIC MODELS
- CHAPTER 12 THE CYCLIC PROPERTIES OF THE LINEAR MODEL
- CHAPTER 13 INTRODUCTION TO OPTIMAL CONTROL
- CHAPTER 14 FORECASTING WITH AUTOREGRESSIVE MODELS
- BIBLIOGRAPHY
- INDEX
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Dynamic Linear Economic Models by James L. Kenkel in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Business General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.