
eBook - ePub
Green and Smart Technologies for Smart Cities
- 361 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Green and Smart Technologies for Smart Cities
About this book
The book starts with an overview of the role of cities in climate change and environmental pollution worldwide, followed by the concept description of smart cities and their expected features, focusing on green technology innovation.
This book explores the energy management strategies required to minimize the need for huge investments in high-capacity transmission lines from distant power plants. A new range of renewable energy technologies modified for installation in cities like small wind turbines, micro-CHP and heat pumps are described. The overall objective of this book is to explore all the green and smart technologies for designing green smart cities.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Green Smart Cities
Akanksha Srivastava, Mani Shekhar Gupta and Gurjit Kaur
Contents
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Meaning of Smart Cities
1.2.1 Secure and Safe Society
1.2.2 Mobility in Green Communication
1.2.3 Attain Excellent Education and Health
1.2.4 Real Estate and Building
1.2.5 Technology and Transportation Amplification
1.3 A Roadmap of Using Communication for Smart City Development
1.3.1 Green Communication-Enabled Knowledge and Information Sharing
1.3.2 Green Communication-Enabled Forecasts
1.3.3 Green Infrastructure
1.3.4 A Cloud Computing Platform
1.4 Potential Communications Technologies to Make Cities Smart
1.4.1 Wireless Technologies
1.4.2 Wired Technologies
1.5 Features of Smart Cities
1.5.1 Sensor-Equipped City and Cloud Computing
1.5.2 Future Research Directions
1.6 Conclusion
Acknowledgment
References
1.1 Introduction
There has been a remarkable growth in the percentage of the world’s population living in urban areas. Presently, almost 55% of the world’s population lives in urban areas and it is expected that the urban population will account for 66% of the world’s population by 2050 (United Nations 2018). Significant advancements in society and a deficiency of resources in rural areas have led to a continous migration of the rural population to urban areas. Table 1.1 presents the projected growth rate of the world’s population from 2020 to 2050, including the urban population percentage. Figure 1.1 shows the percentage of the urban population in the ten most populated countries. This expansion into urban areas requires the optimization of available resources (such as electricity, water, housing and transportation) to meet the needs of citizens. Therefore, emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, cognitive technology, Internet of Things, machine learning and cloud computing are now being used in a significant manner to convert cities into “smart cities”. Energy-efficient green communication and seamless networking are very important pillars of smart city construction, and connect the different essential elements of smart cities. This chapter aims to provide a brief definition of smart cities and to summarize the various emerging technologies which play a vital role in smart cities.
Table 1.1
Projected World Population From 2020 To 2050
Projected World Population From 2020 To 2050
| Year | World Population | Increase in Population (Yearly) | Change in Yearly Population (%) | Rate of Fertility | Urban Population (%) |
| 2020 | 7,794,798,739 | 83,000,320 | 1.10% | 2.47 | 56.2% |
| 2025 | 8,184,437,460 | 77,927,744 | 0.98% | 2.54 | 58.3% |
| 2030 | 8,548,487,400 | 72,809,988 | 0.87% | 2.62 | 60.4% |
| 2035 | 8,887,524,213 | 67,807,363 | 0.78% | 2.70 | 62.5% |
| 2040 | 9,198,847,240 | 62,264,605 | 0.69% | 2.77 | 64.6% |
| 2045 | 9,481,803,274 | 56,591,207 | 0.61% | 2.85 | 66.6% |
| 2050 | 9,735,033,990 | 50,646,143 | 0.53% | 2.95 | 68.6% |
(Mensah et al. 2019)

Figure 1.1
Urban population percentage of the most populated countries (2017)
Urban population percentage of the most populated countries (2017)
(Shahidehpour et al. 2018).
Over the past 50 years, the average growth rate of the world’s population has been almost 1.2% per year (Roser et al. 2013). The urban area population has continuously surpassed the rural area population and it is expected that this will continue, with the urban population accounting for 68.5% of the total population by 2050 (Mensah et al. 2019). Therefore, the present scenario is one of greater urbanization. There are many benefits of urbanization but it also brings many challenges. Increased urbanization means increased demand for various resources such as electricity, water, transportation, sanitation and infrastructure, as well as healthcare, public services and education. The urbanization process also plays a key role in environmental degradation on a local, regional and global level.
At the present time, the conversion of digital cities into smart cities is a major issue of concern for many countries. Intelligent and digital cities are those which are technology-oriented but a city becomes “smart” when it is organized, interconnected, self-repairing, self-decision-taking and healthy. In the literature, various models and explanations have been put forward for smart city description (Wenge et al. 2014). Figure 1.2 presents a layered architecture model for a smart city. This model consists of seven layers of a smart city, in which each layer plays a very important role. A central role is performed by the third layer (i.e. the communication and networking layer). The first layer is infrastructure, which consists of roads, buildings, the electricity grid and parking.
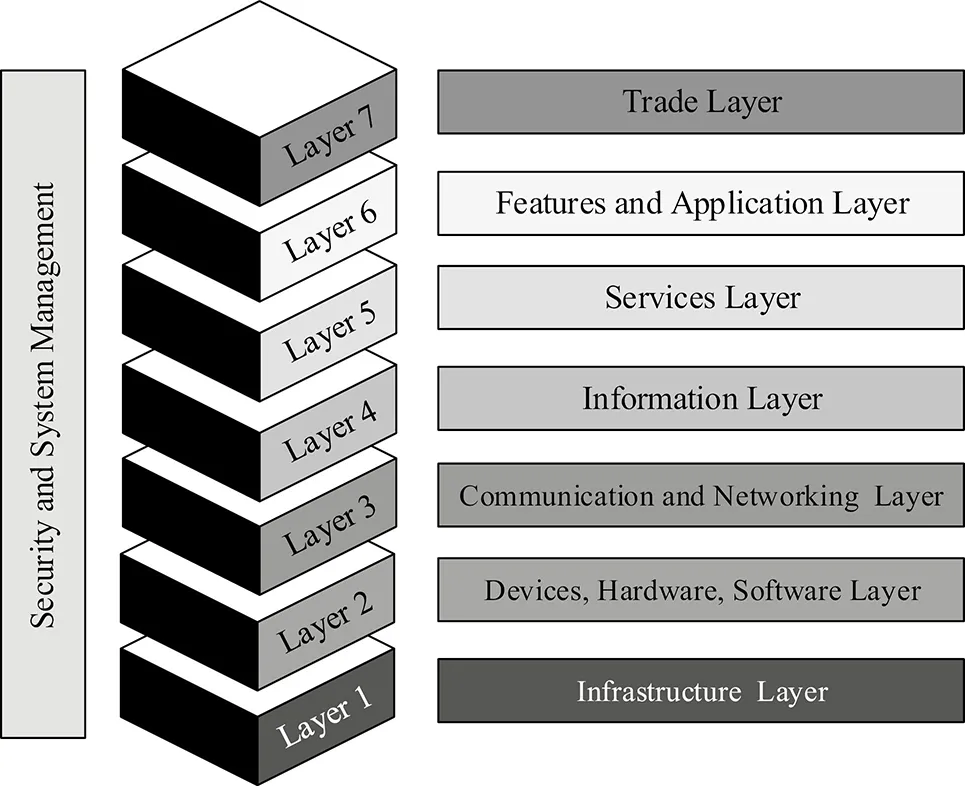
Figure 1.2
Layered architecture model for a smart city.
Layered architecture model for a smart city.
The communication and networking layer facilitates and supports the different forms of communication such as voice, text, data, video, multimedia and real-time services from a personal area network (PAN) to a wide area network (WAN). A question that emerges is how communication and networking provid...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- Abbreviations
- 1 Green Smart Cities
- 2 Green Smart Town Planning
- 3 Green Smart Buildings for Smart Cities
- 4 Green Smart Environment for Smart Cities
- 5 Green Healthcare for Smart Cities
- 6 Green Smart Education System
- 7 Green Smart Agriculture System
- 8 Green Smart Security System
- 9 Green Smart Transport Systems
- 10 Green Smart Energy Management System
- 11 Green Smart Waste Management System
- 12 Green Smart Water and Sanitation System
- 13 Innovation Opportunities through Internet of Things (IoT) for Smart Cities
- 14 Application of Smart City Concept to the Leading Destination: Evidence from Istanbul ‒ A Case Study
- 15 Green Roof Garden Concept for Smart Cities ‒ A Case Study
- 16 School Bus Routing Problems and Solutions for Smart Cities ‒ A Case Study
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Green and Smart Technologies for Smart Cities by Pradeep Tomar, Gurjit Kaur, Pradeep Tomar,Gurjit Kaur in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Matemáticas & Gestión medioambiental. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.