![]()
PART I
M-COMMERCE: MEANING, EVOLUTION, TRENDS, AND HINDRANCES
![]()
CHAPTER 1
M-COMMERCE: MEANING, EVOLUTION, AND GROWTH
MITHUN SHRIVASTAVA1*, DEVIKA PRAKASH1, and VIR VED RATNA2
1Department of Management, Waljat College of Applied Sciences, BIT International Centre Muscat, Oman
2Strategy and General Management Area, Jaipuria Institute of Management, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
ABSTRACT
The term “m-commerce” comes from the union of two words “mobile” and “commerce,” and refers to any transaction of monetary value occurring over a wireless communication network through the use of wireless handheld devices. M-commerce was initially hampered by issues such as slow Internet speeds, lack of standards in hardware and software, and limited capabilities of handheld devices. However, rapid technological development in various domains such as Internet, wireless communication, handheld devices, mobile payment systems, and mobile applications has ensured growing use and adoption of m-commerce today. Widespread acceptance of m-commerce is attributed to its various features such as ubiquity, convenience, localization, personalization, and identifiability. Nevertheless, m-commerce suffers from disadvantages such as the cost of setting up wireless infrastructure and restricted functionality of handheld devices. Furthermore, major challenges faced by m-commerce also include security risks involved in online mobile payment systems and lack of consumer trust in the same. Today, m-commerce applications used widely include mobile banking, mobile purchasing, location-based services, mobile ticketing, and information services. This chapter provides an introduction to the concept of m-commerce. Its meaning is explored through a comparison of definitions published over the last two decades. The evolution and growth of m-commerce is traced parallel to advances in the domains of hardware, software, and networking. Moreover, the advantages, disadvantages, and challenges of m-commerce are described. The applications of m-commerce today in various countries such as Japan, Finland, the United States, the United Kingdom, and India are also outlined. In today’s dynamic world of rapid development, the future of m-commerce is quite difficult to speculate. However, based on the trends related to m-commerce growth as discussed in the chapter, m-commerce can be expected to grow and impact and get impacted by human lives.
1.1 INTRODUCTION
Internet has ushered in a new business era. Though initially developed to share scientific documents, the possibilities for business by communicating latest product information to customers were realized in e-commerce (Herzog and Gottlob, 2001). The rapid developments in telecommunications industry, especially with reference to the proliferation of various handheld devices, such as smartphone, have paved way for a significant increase in the reach of e-commerce, and have crafted an era marked by strong presence of mobile commerce.
The term “m-commerce” comes from the union of two words “mobile” and “commerce.” It was first used in 1997 by Kevin Duffey, and refers to any transaction of monetary value taking place over a wireless mobile telecommunications network. It is considered to be an extension of e-commerce, whereby handheld devices enable users to access Internet-related services such as purchasing, selling, and searching for information, without being tethered to a wired desktop. M-commerce is an integral part of contemporary transactions, providing various services such as mobile banking, location-based information (news, weather, traffic reports, etc.), mobile ticketing, and mobile browsing, to name a few. This chapter deals with the meaning of m-commerce, its evolution, and growth over the years.
1.2 PURPOSE
M-commerce has been spearheading developments in multitudinous domains related to business. The most significant trend associated with m-commerce is its rapid growth especially during the past two decades, due to availability of high-speed Internet and affordable smartphones. This chapter seeks to explore the meaning of m-commerce as defined by numerous authors over the years. It then attempts to trace its origin and evolution parallel to that of communication technologies, especially Internet, and developments in handheld devices. The salient aspects, related to historical timeline for m-commerce evolution and growth, are highlighted. The chapter then focuses on the features of m-commerce, followed by disadvantages and challenges faced by it. Finally, the chapter ends with a discussion on a multitude of applications offered by m-commerce today in different sectors such as banking, education, providing access to information, location-based services, and mobile purchasing.
This chapter seeks to provide readers a review and comparison of definitions of m-commerce published over the past two decades. Readers can understand the evolution of m-commerce in synchronization with that of e-commerce. The paradigm shifts in e-commerce from 1950s to date and synchronization with m-commerce advances over the past two decades are explored. Further, the impact of technology in the domains of hardware, software, and networking catalyzing developments in m-commerce are highlighted. Growth of m-commerce in terms of features and applications available now and expected in the future are also discussed, along with contributions of select countries to m-commerce.
1.3 METHODOLOGY
This chapter is based on a review of existing literature from articles concerning m-commerce, published in reputed journals. A comprehensive set of references available on or related to the domain of m-commerce was obtained by means of a thorough online search of select databases such as ABI/INFORM Global (ProQuest), Academic Search Premier (EBSCO), Emerald, Google Scholar, JSTOR, and SAGE. The keywords used to perform the search include “m-commerce” and “mobile commerce” which were used to obtain a list of references pertaining to literature available on the subject. The search yielded peer-reviewed articles from top-tier journals and articles in a number of conference proceedings published till date. By perusal of both abstract and full text of each article, the list of references was further narrowed by eliminating those articles not directly related to the themes or sub-themes of m-commerce. Furthermore, theses, white papers, and web links on m-commerce were referred. Back referencing of the list of articles thus obtained helped in identifying additional seminal works related to the topic.
1.4 M-COMMERCE: DEFINITIONS, EVOLUTION, AND HISTORY
1.4.1 M-COMMERCE: A REVIEW OF DEFINITIONS
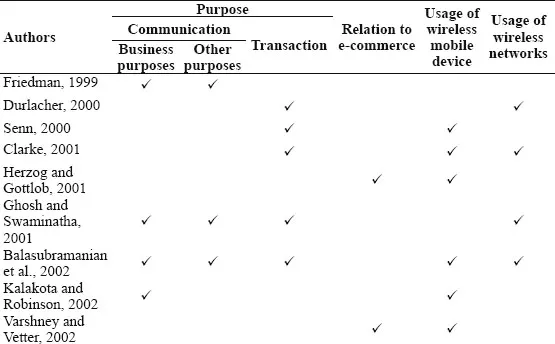
The term “m-commerce” has been defined by a number of researchers, with subtle variations in these definitions over the years. Durlacher (2000) defined m-commerce as “any transaction with a monetary value that is conducted via a mobile telecommunications network.” M-commerce is considered by some as a subset of e-commerce, and is defined as “a natural extension of e-commerce that allows users to interact with other users or businesses in a wireless mode, anytime/anywhere” (Coursaris, 2003).
The definitions of m-commerce are scattered over a number of books (including edited volumes), journal articles, and other forms of academic publications concerning a range of disciplines such as advertising, computing and information technology, electronics, business, and management (Table 1.1). This section focuses on highlighting trends associated with definitions of m-commerce over the years.
TABLE 1.1 M-Commerce: A Review of Definitions (2000–Till Date).
Source: Compiled by authors.
1.4.1.1 PHASE 1: BEFORE 2000
Prior to 2000, mobile commerce has not been explicitly defined in journal articles; rather the focus was on e-commerce. The growing applications and potential of Internet meant that e-commerce was on the rise, whereas the integration of Internet technology and mobile handheld devices had not yet progressed enough to warrant a detailed discussion on m-commerce.
1.4.1.2 PHASE 2: 2000–2005
M-commerce is seen as an extension of e-commerce, with focus on the conduct of commercial transactions and communication for private or business purposes. The ability to purchase goods and services irrespective of the user location using handheld devices such as PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants) or cell phones is highlighted. The purpose of m-commerce is split between communication and commercial transactions. This can be further understood by the fact that mobile payment systems were still in the initial development phase and associated security and privacy risks were considered high.
1.4.1.3 PHASE 3: 2005–2010
The definition of m-commerce has remained the same, with subtle variations. The focus on use of Internet-enabled wireless handheld devices increased. These devices included cell phones, palm-sized devices, or interfaces mounted on vehicles. Though previous definitions focused on the communication aspect of m-commerce, the concept gradually shifted toward incorporating all activities facilitating commercial transactions. This can be accounted for by research and development in mobile payment systems as explained in detail in Section 1.5 later in this chapter. Research into Near-field Communication (NFC) technology and its integration with smartphones paved way for mobile payments as seen today.
1.4.1.4 PHASE 4: 2010–TILL DATE
The pervasiveness of smartphones and associated software and mobile apps has changed the public perception of m-comme...