
- 240 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
MBA Management Models
About this book
If you're a student on an MBA or management course, you'll be expected to demonstrate a knowledge of a range of models. This textbook collects together the 45 models most likely to be required, summarized in a standard format. Each entry contains a diagram of the model; the principles on which it's based; underlying assumptions; guidance on application, and relevant issues; related models; and sources of further reference. Models are organized by subject area: accounting; business strategy; human resources; organizational strategy; and strategic marketing. An alphabetical matrix index means you can find the right model quickly. MBA Management Models will be invaluable to students working on written assignments, projects, case studies or dissertations, and to practising managers too.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Organizational strategy
29 Company position/industry attractiveness screen
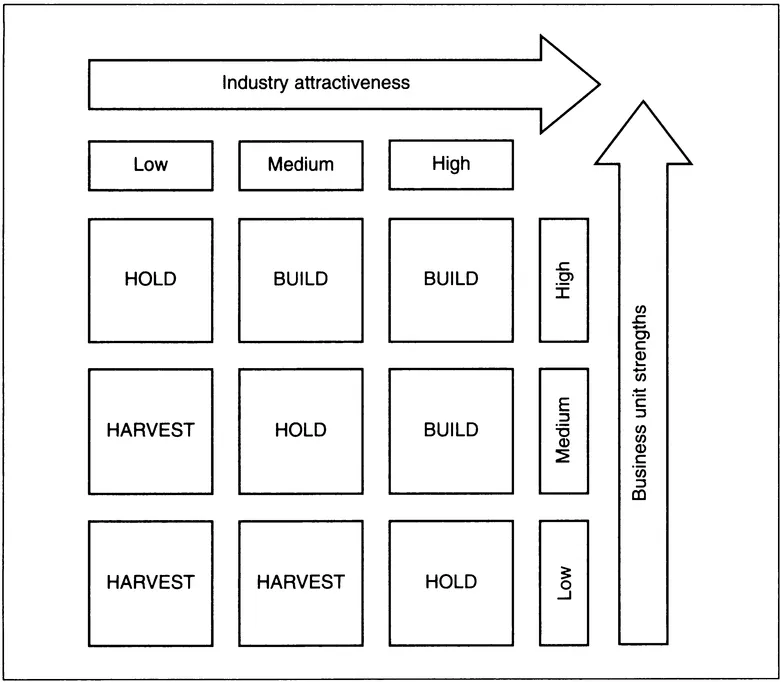
Source: Making strategy work, R.G. Hamermesh, 1986. Reprinted by permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Principle
Portfolio planning can have a significant influence on strategy formulation.
Assumption
Because resources are limited their allocation should be based on a combination of industry attractiveness and the relative strengths of different business units in a diversified organization.
Elements
Industry attractiveness
This includes market growth, size, profitability and price policies.
Business unit strengths
This includes size, market share and technological standing.
Build
Growth through investment is a central objective.
Hold
Investment is maintained and assessed continuously.
Harvest
Remove cash from the business unit and invest elsewhere.
Issues
Business unit definition
Business units should be defined very carefully because definitions shape market perceptions, are influenced by administration and resource considerations and must be responsive to changes in markets, competition and technology.
Negotiations between managers
Portfolio planning tends to centralize the strategic process. If the devolution of strategy setting is an objective, corporate and unit managements must be permitted to negotiate about cash flow and strategic objectives.
Other techniques
Portfolio planning should not be equated with overall strategy; other techniques should also be used.
Applications
Strategy formulation
The model can help in the formulation of organizational and business unit strategy, understanding of markets and the firm's position within them.
Project funding
Portfolio planning is a first step in determining whether a business unit which is proposing a project is worthy of funding at all.
Restructuring
The model may be used to assess an organization's strategic position after a cash crisis in order to effectively divest cash-hungry businesses and promote divestitures and corporate restructuring.
Market planning
Portfolio planning helps in deciding which market to compete in and which resources to use.
Related models
- Ansoff's Box (see pp. 197-9)
- Barriers and profitability (see pp. 47-50)
- Company position/industry attractiveness screen (see pp. 137-40)
- Contrasting characteristics of upstream and downstream companies (see pp. 55-8)
- Five forces (see pp. 59-63)
- Five Ps for strategy (see 65-8)
- Nine specimen standardized strategies (see pp. 201-5)
- PESTLIED (see pp. 83-6)
- PIMS competitive strategy paradigm (see pp. 207-10)
- Porter's Diamond (see pp. 87-90)
- Related diversification grid (see pp. 91-3)
- Resource allocation at corporate level (see pp. 177-80)
- Value chain (see pp. 191—4)
Main reference
R.G. Hamermesh (1986), Making Strategy Work - How Senior Managers Produce Results, Chichester: John Wiley and Sons.
30 Cultural web

Source: Exploring Corporate Strategy, G. Johnson and K. Scholes, Prentice Hall, London, 1993.
Principle
The interaction of key factors influences the way an organization operates (culture).
Assumption
The paradigm, which develops from the key factors, is central to the ongoing success of the organization.
Elements
Paradigm/recipe
The paradigm comprises the combined key beliefs and assumptions and is influenced by the following factors:
- stories: stories of past achievements, procedural activities
- symbols: indications of status - for example titles, office size, job perks
- rituals and routines: any well established formal or informal procedures
- power structures: traditional power base, promotion rights and expectations
- control systems: formal regulation within all functional areas
- organizational structures: the formal relationship between the different elements of an organization - for example, functional/centralized/hierarchical.
Issues
Paradigm changes
Lasting strategic change comes about through changes in the paradigm.
Integration
Art organization's culture is strongest when all factors are integrated and contribute positively to the paradigm, often giving stability and confidence to the organization and its people.
Weakness
If one of the key factors is very weak - for example, there is a lack of internal audit controls - the effect on the organization can be catastrophic.
Ease of change
Some factors - for example, symbols and routines - may be more easily changed than others. Some organizations restructure regularly but at great expense and incurring significant disruption in human terms.
Applications
Analysis
- of a whole organization, a business unit or team
- of an industry - for example banking
- of the interaction between factors - for example, how formal controls may be compromised by power structures.
Cultural change
One or more of the factors, or even the paradigm itself, may be changed - for example with the arrival of a new chief executive.
Related models
- Action-centred leadership (see pp. 101-3)
- Belbin's team roles (see pp. 105-8)
- Dynamics of paradigm change (see pp. 145-8)
- Four organizational cultures (see pp. 149-53)
- Group development (see pp. 109-12)
- Herzberg's Motivator-Hygiene Theory (see pp. 113-15)
- Managerial grid (see pp. 121-4)
- Organic versus mechanistic management styles (see pp. 169-72)
- Related diversification grid (see pp. 91-3)
- The seven 'S's framework (see pp. 181-5)
- Situational leadership (see pp. 131-4)
Main reference
G. John...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Dedication
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Acknowledgements
- Introduction
- Matrix index
- Accounting/economics
- Business strategy
- Human resources
- Organizational strategy
- Strategic marketing
- Appendix
- Subject index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access MBA Management Models by Sue Harding in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Management. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.