
This is a test
- 167 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Engineering Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
Assuming only the most basic knowledge of the physics of fluids, this book aims to equip the reader with a sound understanding of fluid power systems and their uses in practical engineering. In line with the strongly practical bias of the book, maintenance and trouble-shooting are covered, with particular emphasis on safety systems and regulations.
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Engineering Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics by Ian Turner in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Civil Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics in Industry
Aims
At the end of this chapter you should be able to:
1Appreciate a range of industrial applications for pneumatics and hydraulics.
2Appreciate that pneumatics and hydraulics may be used in combination with other technologies in a given system.
3Recognise that fluid power systems may be used for operating, controlling and/or taking measurements of equipment, machinery and plant.
4Have an awareness that fluid power systems can be used in industrial processes requiring emergency and safety shut-down arrangements.
1.1 Industrial applications
Pneumatic and hydraulic systems have been used for many years within industrial processes and as such have acquired an established place in modern industry. Continuous development of fluid power technology over the years has significantly expanded and increased the applications to many areas hitherto not known for adopting pneumatic and hydraulic technology.
Some of the principal users of fluid power technology are:
■manufacturing industries, notably the automotive industry, machine tool manufacturers and domestic and commercial appliance manufacturers
■processing industries, such as chemical, petro-chemical, food processing, textiles, paper, etc.
■transportation systems, including marine and mobile construction plant
■utilities, particularly in the gas industry
■defence systems.
More recent users have been in the fields of offshore oil and gas development, space and aero-nautical systems and nuclear applications.
1.2 Combined technologies
Often, pneumatics and hydraulics are combined with other technologies such as mechanical, electrical and electronic systems to form an overall system. An example of this can be found in robotics.
In addition, safety conscious industries will sometimes adopt a number of technologies operating on different physical principles as a means of achieving diversity of operation, control and measurement on a given process. This is particularly significant as protection against common mode failure whereby if one system fails, the others remain active.
1.3 Uses of fluid power systems
Fluid power systems may be used for:
1Carrying out work by operating plant and machinery using linear, swivel and rotary motion. Some general methods of material handling used in industry, for example, may be:
■ clamping
■ shifting
■ positioning
■ orientating.
a) General applications may be:
■ packaging
■ feeding
■ door or chute control
■ material transfer
■ turning and inverting of parts
■ sorting
■ stacking
■ stamping and embossing.
b)Some general machining and work operations may be:
■drilling
■turning
■milling
■sawing
■finishing and buffing
■forming.

Figure 1.1 A combined wellhead control panel and hydraulic power unit for an offshore oil platform
2Controlling processes and plant. Pneumatic and hydraulic systems may be used to sense the operational status of a process, feed this information back to a controller which will take a necessary control action, for example a limit switch may sense that an actuator needs to be operated.
3Measurements of process and/or machine parameters. Pneumatics and hydraulics can be used to provide measurements of process or machine parameters, act on this information and subsequently display it to an operator.
The processes outlined in 1, 2 and 3 above may be used individually or in combination.
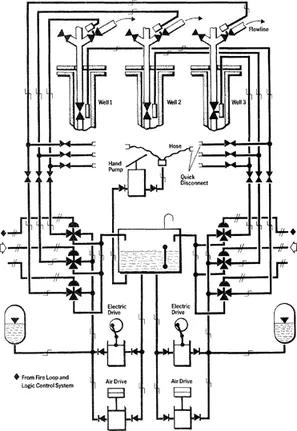
Figure 1.2 Practical hydraulic emergency shut-down system for three sub-sea oil wells
1.4 Hydraulic and pneumatic safety systems
In addition to operating, controlling and measuring parameters of process plant and machinery, hydraulics and pneumatics may be used in high integrity safety systems. This is expanded further in Chapter 14.
The high speed and reliability of operation embodied in good modern pneumatic and hydraulic system design coupled with inherent explosion-proof and overload-safe operation makes the choice of this techno...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- 1 Applications of Pneumatics and Hydraulics in Industry
- 2 Basic Principles of FluidPower Systems
- 3 Features and Characteristics of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
- 4 Component, Equipment and Plant Symbols
- 5 Fluid Power Generation, Supply and Distribution
- 6 ontrol Valves I - Types and Principles of Operation
- 7 Control Valves II - Types and Principles of Operation
- 8 Actuators
- 9 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Circuits and Arrangement of Components
- 10 Electro-pneumatics and Electro-hydraulics
- 11 Fluid Power Measurement Systems
- 12 Troubleshooting and Maintenance
- 13 Basic Principles of Fluid Power Control
- 14 Emergency Shutdown and Safety Systems
- 15 Health and Safety at Work
- Appendix 1 Answers to revision questions
- Appendix 2 City & Guilds specimen examination questions
- Appendix 3 Institution of Plant Engineers: relevant technical guides
- Appendix 4 Standards and standardisation organisations: relevant fluid power
- Appendix 5 Bar litres: calculations
- Index