
Advances in Mobile Computing and Communications
Perspectives and Emerging Trends in 5G Networks
- 397 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Advances in Mobile Computing and Communications
Perspectives and Emerging Trends in 5G Networks
About This Book
By 2020, if not before, mobile computing and wireless systems are expected to enter the fifth generation (5G), which promises evolutionary if not revolutionary services. What those advanced services will look like, sound like, and feel like is the theme of the book Advances in Mobile Computing and Communications: Perspectives and Emerging Trends in 5G Networks. The book explores futuristic and compelling ideas in latest developments of communication and networking aspects of 5G. As such, it serves as an excellent guide for advanced developers, communication network scientists, researchers, academicians, and graduate students.
The authors address computing models, communication architecture, and protocols based on 3G, LTE, LTE-A, 4G, and beyond. Topics include advances in 4G, radio propagation and channel modeling aspects of 4G networks, limited feedback for 4G, and game theory application for power control and subcarrier allocation in OFDMA cellular networks. Additionally, the book covers millimeter-wave technology for 5G networks, multicellular heterogeneous networks, and energy-efficient mobile wireless network operations for 4G and beyond using HetNets. Finally, the authors delve into opportunistic multiconnect networks with P2P WiFi and cellular providers and video streaming over wireless channels for 4G and beyond.
Frequently asked questions
Information
1
ADVANCES IN 4G
COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
STEFAN SCHWARZ
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Evolution toward 5G Networks
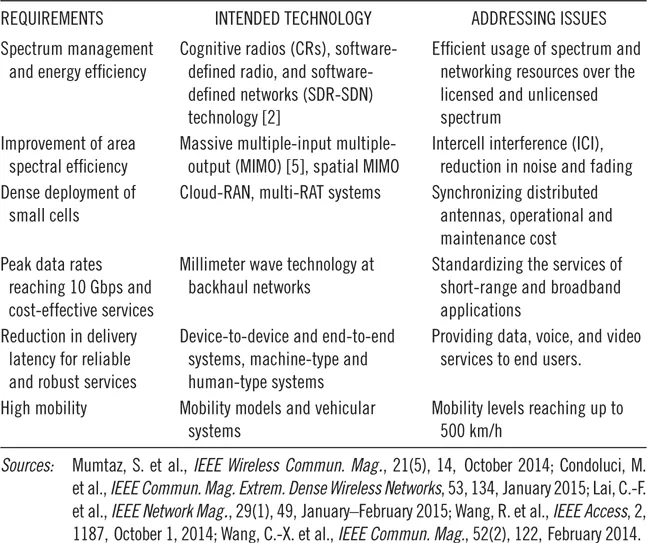
1.3 Challenges in 5G Networks
- Increase in spectrum bandwidth, transmission rate, and traffic density
- Design of small-cell infrastructure [1] (based on femtocells and microcells with eNBs) to increase the spectrum efficiency and decrease the load of base station
- Ultradense networks, multiple radio access technologies (M-RATs), and mobile crowd sensing
- Exponential increase in data traffic based on multimedia live streaming, multivideo conferencing, Internet Protocol television (IP-TV), and so on
- D2D and M2M [2] connectivity
- Mobility management for high-speed vehicular network
- Energy management in cellular communication
- Network virtualization and software-defined network (SDN)
- Mobile vehicular cloud management
1.4 Emerging Trends in 5G Networks
1.4.1 Multiple Radio Access Technology (M-RAT)
1.4.2 OFDM and Multiple MIMO Systems
1.4.3 Device-to-Device Communication Systems
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Other Communications Books
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- Abbreviations
- Chapter 1 Advances in 4G Communication Networks: A 5G Perspective
- Chapter 2 Radio Propagation and Channel Modeling Aspects of 4G and Beyond Networks
- Chapter 3 Limited Feedback for 4G and Beyond
- Chapter 4 Game Theory Application for Power Control and Subcarrier allocation in OFDMA Cellular Networks
- Chapter 5 Millimeter-Wave Technology for 5G Networks
- Chapter 6 Multicellular Heterogeneous Networks: A 5G Perspective
- Chapter 7 Energy-Efficient Mobile Wireless Network Operations for 4G and Beyond Using HetNets
- Chapter 8 Opportunistic MultiConnect with P2P WiFi and Cellular Providers
- Chapter 9 Video Streaming over Wireless Channels: 4G and Beyond
- Index