
eBook - ePub
Dielectrics in Electric Fields
Tables, Atoms, and Molecules
Gorur Govinda Raju
This is a test
Share book
- 776 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Dielectrics in Electric Fields
Tables, Atoms, and Molecules
Gorur Govinda Raju
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
Dielectrics in Electric Fields explores the influence of electric fields on dielectric—i.e., non-conducting or insulating—materials, examining the distinctive behaviors of these materials through well-established principles of physics and engineering.
Featuring five new chapters, nearly 200 new figures, and more than 800 new citations, this fully updated and significantly expanded Second Edition:
-
- Analyzes inorganic substances with real-life applications in harsh working conditions such as outdoor, nuclear, and space environments
- Introduces methods for measuring dielectric properties at microwave frequencies, presenting results obtained for specific materials
- Discusses the application of dielectric theory in allied fields such as corrosion studies, civil engineering, and health sciences
- Combines in one chapter coverage of electrical breakdown in gases with breakdown in micrometric gaps
- Offers extensive coverage of electron energy distribution—essential knowledge required for the application of plasma sciences in medical science
- Delivers a detailed review of breakdown in liquids, along with an overview of electron mobility, providing a clear understanding of breakdown phenomena
- Explains breakdown in solid dielectrics such as single crystals, polycrystalline and amorphous states, thin films, and powders compressed to form pellets
- Addresses the latest advances in dielectric theory and research, including cutting-edge nanodielectric materials and their practical applications
- Blends early classical papers that laid the foundation for much of the dielectric theory with more recent work
The author has drawn from more than 55 years of research studies and experience in the areas of high-voltage engineering, power systems, and dielectric materials and systems to supply both aspiring and practicing engineers with a comprehensive, authoritative source for up-to-date information on dielectrics in electric fields.
Frequently asked questions
How do I cancel my subscription?
Can/how do I download books?
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
What is the difference between the pricing plans?
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
What is Perlego?
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Do you support text-to-speech?
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Is Dielectrics in Electric Fields an online PDF/ePUB?
Yes, you can access Dielectrics in Electric Fields by Gorur Govinda Raju in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Physics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
1 | Introductory Concepts |
The rich and the poor are two locked caskets of which each contains the key to the other.
Karen Blixen
Danish writer
In this chapter, we briefly review some basic concepts that are used in the chapters that follow. Theorems on electrostatics are included as an introduction to the study of the influence of electric fields on dielectric materials. The solution of the Laplace equation to find the electric field within and without dielectric combinations yields expressions that help to develop the various dielectric theories discussed in subsequent chapters. The band theory of solids is discussed briefly to assist in understanding the electronic structure of dielectrics, and a fundamental knowledge of this topic is essential to understand conduction and breakdown in dielectrics. The energy distribution of charged particles is one of the most basic aspects that are required for a proper understanding of the structure of the condensed phase and electrical discharges in gases. Certain theorems are merely mentioned without a rigorous proof, and the student should consult a book on electrostatics to supplement the reading.
1.1 A DIPOLE
A pair of equal and opposite charges situated close enough compared with the distance to an observer is called an electric dipole. The quantity
(1.1) |
where d is the distance between the two charges is called the electric dipole moment. μ is a vector quantity the direction of which is taken from the negative to the positive charge and has the unit of C m. A unit of dipole moment is 1 debye = 3.33 × 10−30 C m.
1.2 THE POTENTIAL DUE TO A DIPOLE
Let two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite polarity, +Q and −Q, be situated d meters apart. It is required to calculate the electric potential at point P, which is situated at a distance of R from the midpoint of the axis of the dipole. Let R+ and R− be the distance of the point from the positive and negative charge, respectively (Figure 1.1). Let R make an angle θ with the axis of the dipole.
The potential at P is equal to
(1.2) |
Starting from this equation, the potential due to the dipole is
(1.3) |
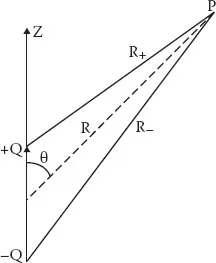
FIGURE 1.1 Potential at a far-awa...