
- 114 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
3D Origami Art
About this book
Easily Create Origami with Curved Folds and Surfaces
Origami—making shapes only through folding—reveals a fascinating area of geometry woven with a variety of representations. The world of origami has progressed dramatically since the advent of computer programs to perform the necessary computations for origami design.
3D Origami Art presents the design methods underlying 3D creations derived from computation. It includes numerous photos and design drawings called crease patterns, which are available for download on the author's website. Through the book's clear figures and descriptions, readers can easily create geometric 3D structures out of a set of lines and curves drawn on a 2D plane.
The author uses various shapes of sheets such as rectangles and regular polygons, instead of square paper, to create the origami. Many of the origami creations have a 3D structure composed of curved surfaces, and some of them have complicated forms. However, the background theory underlying all the creations is very simple. The author shows how different origami forms are designed from a common theory.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Axisymmetric 3D Origami
1.1 Four Basic Types
1.2 Basic Crease Patterns
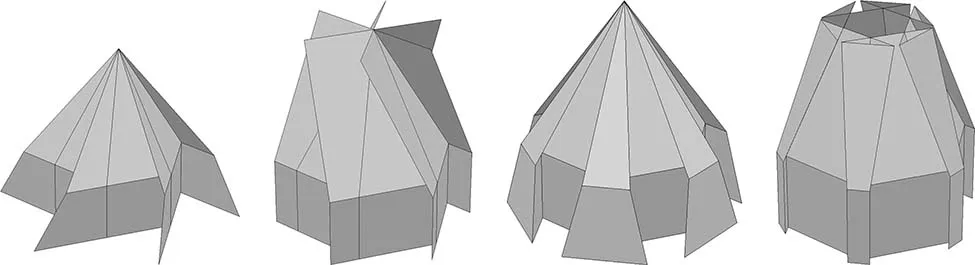
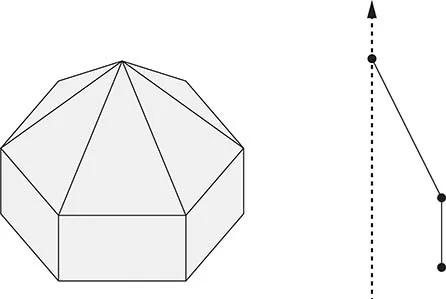
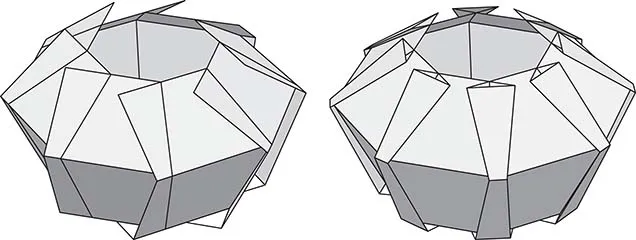
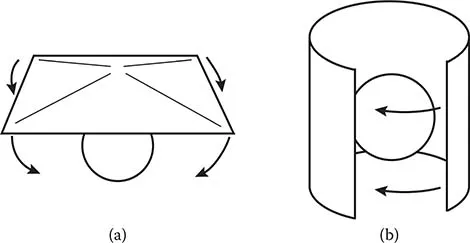
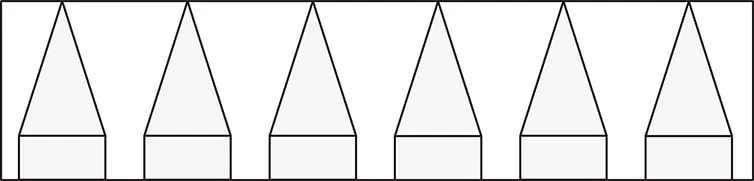
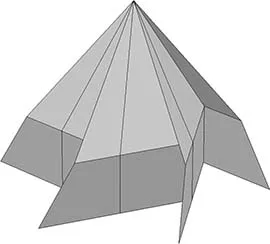
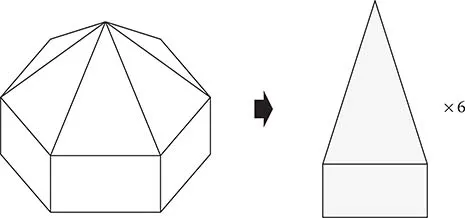
1.3 Flat-Pleat Cone Type
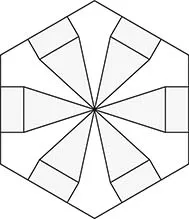
1.4 Flat-Pleat Cylinder Type
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half title
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Prologue: Origami Basics
- Author
- 1 Axisymmetric 3D Origami
- 2 Extension of Axisymmetric 3D Origami
- 3 Connecting Axisymmetric 3D Origami Shapes
- 4 Making Use of Mirror Inversion
- 5 Application of Mirror Inversion
- 6 Voronoi Origami
- 7 Various Origami Designs
- 8 Conclusion
- Afterword
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app