![]()
Chapter 1
Introduction to Causal Analysis
1.1 SITUATIONAL ASSESSMENT
In 2009, one of us (Ryall) had the pleasure of participating as a judge in the McKinsey Case Competition held at the Rotman School of Management, University of Toronto. Case competitions are an established feature of the student experience in modern MBA programs. The details vary from competition to competition, but the essential idea is to provide students with a brief (~15 page) description of a problem facing a particular firm, give them a week to mull it over, then have them present their recommendations and supporting analyses before a panel of experienced judges.1
In order to help the MBA students prepare, two Rotman alumni who had become McKinsey engagement managers (and competition judges) — Paulo Salomao and Erez Eizenman — generously gave a presentation on McKinsey's approach to business problem solving. As they explained, McKinsey uses a technique called issue trees to help structure some of their analyses. An issue tree takes the problem and breaks it down into issues, subissues, subsubissues, and so on. An important requirement is that the direct descendants of any issue constitute a mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive (MECE) set of subissues. This requirement forces the analyst to think broadly about the potential issues at every level.
To illustrate the method, Paulo and Erez posed the question, “How did Robert Maxwell die?” Maxwell was a media tycoon who, in 1991 was presumed to have fallen overboard from his luxury yacht. His death was officially judged to be accidental drowning. However, questions were raised suggesting that the death may have been caused by murder or suicide. Accordingly, the root node of the issue tree they presented was labeled, “How did Robert Maxwell die?” Its direct descendants were: murder, suicide, natural causes, accident and not-really-dead (mutually exclusive collectively exhaustive, MECE!). Then the direct descendants of each of these nodes accounted for (all possible) potential causes of death associated with each of these categories.
Trying to think exhaustively about the issues related to a problem is clearly an important part of making any substantive business decision — and the Maxwell example provided a nice, simple illustration of how to do so. Still, there was something about this example that felt lacking. That “something” was not being told why we care about the answer to, “How did Robert Maxwell die?” Were we considering the issue from the perspective of a policeman pondering whether or not to begin a criminal investigation (is murder sufficiently likely)? From that of Maxwell's life insurance company trying to decide the payout on a claim (is it reasonable to rule out suicide)? From that of a prosecutor assembling a case (what is the theory, what evidence supports it)?
Suppose that instead of asking, “How did Robert Maxwell die?” we ask, “What was Robert Maxwell's cause of death?” Does the different phrasing change your perspective? Most people, saturated with CSI-this or Law & Order-that television programming, read “cause of death” and think in terms of a coroner's report: what was the immediate, physical event that resulted in Maxwell's expiration? Candidates might include: drowning, gunshot, heart attack, poisoning, etc.
Having introduced the notion of causality, though, one's mind naturally begins to frame the question in terms of a longer causal chain (i.e., thinking about causes of causes). If the immediate cause of death was due to a weapon, was the injury self-inflicted (suicide) or other-inflicted (murder). Of course, we do not stop there. What might cause Maxwell to commit suicide? If murder, who did it? If someone did it, what was his or her motive?
Causal thinking leads us not only up the causal chain, but down it as well. Guns cause different trauma to the body than knives. They may also cause other types of evidence to appear — gunpowder residue, bullet casings, projectile markings, etc. Framing the analysis in causal terms points us toward potentially useful sources of information. Moreover, when evidence does present itself, causal analysis allows us to incorporate it in useful ways.
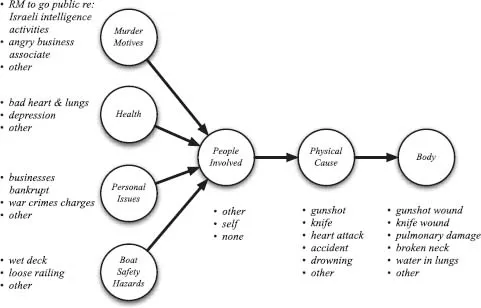
Figure 1.1 gives a preview of the methodology that will be used in this book. The graph is a causal system in which the nodes represent variables that can take on various values or states and the arrows (directed links) indicate direct causal relationships. Thus, a physical cause of gunshot causes a certain type of trauma (gunshot wound) to appear on the body. A gunshot wound could be inflicted by one's self (suicide) or some other person (murder). A murderer typically has some motive that causes him or her to commit that deed. We would say that a motive is an indirect cause of death by murder.
Suppose you are a police inspector interested in determining whether someone other than Maxwell was involved in his death (murder). In our context, then, you are interested in assessing the likelihood that the true value of People Involved
FIGURE 1.1 Robert Maxwell — causes of death
is other. Notice that discovering the values of other variables in this system has implications for the value of People Involved. For example, prior to the coroner's report, learning that the value of Health is bad heart and lungs should cause you to decrease the likelihood that the value of People Involved is other. On the other hand, discovering that Israeli intelligence may have had a motive for killing him would tend to increase that likelihood. In causal systems, evidence has upstream implications as well. For example, other things held constant, discovering that the cause of death was a heart attack should decrease the likelihood that the value of People Involved is other.
A valuable feature of causal analysis is that it permits us to factor in multiple sources of evidence. In the story of Maxwell's death, for example, all of the preceding items were, in fact, discovered (Verkaik, 2006). The muscles on the left side of his body were torn, consistent with falling over the ship's rail and dangling before falling into the ocean. Six months before he died, he was being investigated for war crime World War II. In addition, his corporate empire was on the brink of collapse; he had even illegally raided his employees' pension funds to finance his corporate debt.
As we will see, causal analysis permits all of these facts to be incorporated and used to help assess, e.g., the likelihood of murder. Thus, an important use of causal models is to assess the implications of known information. At the same time, it is worth pointing out that none of the information encoded in the McKinsey issue tree is lost. Indeed, the set of mutually exclusive collectively exhaustive states in which this system may find itself can be enumerated by taking all the combinations of the variable values and eliminating those that are impossible or irrelevant to the task at hand.2
1.2 MANAGERIAL INTERVENTION
Managers manage. This is, of course, true by definition. Yet, what does it mean to manage? In a world without scarcity, there would be no need for managers: firms could undertake every project imaginable. Luckily for managers, resources are limited and, hence, people are needed to make decisions about how they are to be used. This is a key sense in which “managers manage.” Given the rates of return required by investors, which capital projects should be implemented? Should marketing funds be used in a Super Bowl ad or an online guerrilla campaign? Should the cost accountant install better financial reporting software or work with people on the shop floor to improve the measurement of product quality and resolve problems?
To manage is to face a never-ending stream of such decisions, regardless of one's area or level within the firm. Every manager is delegated some measure of control over some co...