
This is a test
- 336 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Hotel Convention Sales, Services, and Operations
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
This text provides a comprehensive look at the fast growing meetings and convention market segment. A useful "how- to" guide, it takes students through all aspects of selling and servicing a convention at a hotel or other group meeting facility. In addition, it profiles the customer for meetings and conventions, the planners in charge of site selection, and facilities they commonly use. Also includes "Industry Insiders" planning tips and case studies direct from professionals in Convention Services departments.
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Hotel Convention Sales, Services, and Operations by Pat Golden-Romero in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Betriebswirtschaft & Gastgewerbe, Reise- & Tourismusbranche. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
The Convention And Meetings Industry: An Overview
Learning Objectives
After studying this chapter, you will be able to discuss:
- The economic impact and multiplier effect of the convention and meetings industry
- The growth of the convention and meetings industry, and current trends
- The types of facilities that house meetings and conventions
- The types of organizations that hold meetings and conventions
Introduction
About 30 years ago, in the mid-1970s, the business of planning and executing meetings in both hotels and convention halls began to undergo changes. At that time, both independent and chain hotels alike relied mostly on business from vacationers and individuals (also known as transient) to fill their rooms. The large function rooms in many hotels, designed and used as banquet and reception facilities, also could accommodate meetings. Today, the group meeting and convention market is recognized as the most significant market segment necessary to ensure the hotels’ room occupancy, as well as food and beverage revenue requirements.
In the 1970s, few hotels in major U.S. cities and resort destinations had enough function space and guest rooms to book convention groups. Overall, convention groups at that time had an image that focused less on meetings and education and more on entertainment. Until recent years, the typical convention attendee was a middle-aged white male; today’s convention-goer is now reflective of the workplace—women and minority groups have altered that demographic profile.
The stereotype of a three-day junket of fun for many convention groups also has been replaced by days of intensive educational programs that upon completion, awarded attendees continuous education credits (CEUs) in their vocation or field. The food and beverage functions at meetings and conventions also have become representative of the creative culinary landscape, replacing the so-called “rubber chicken banquet circuit” of years past. The audiovisual and computer technology needs of groups today require true expertise on-site to ensure that each meeting and presentation goes off without a hitch! Additionally, the meeting planners—people who represent companies and association groups—over the years have become quite knowledgeable of the process.
Therefore, all these requirements have created a need for a department that can seamlessly coordinate and execute these overlapping areas. Thus, the convention services department has become an integral part of the hotel organization chart. This chapter examines how these factors and emerging trends have contributed to the growth of the convention and meetings market. We will look at the financial impact of this global industry in both private and public sectors of the economy. In the last 20 years, state-of-the-art hotel and convention centers have been built to fulfill the need for facilities. This chapter also discusses the key facility requirements for meeting groups. Finally, we will explore the main categories of the group meetings market.
Recently the CIC (Convention Industry Council), conducted a study on the economic impact of this broad, interrelated industry, titled, The Economic Impact of Meetings, Conventions, Exhibitions, and Incentive Travel. Figure 1.1 is a summary of the key points from the 2004 Economic Impact Study, from the CIC Web site. The accompanying pie chart shows the total direct spending by industry segment, with conventions and exhibitions generating the most spending: 55.5 percent ($122.31 billion). Additionally, the study reports that “the largest share of the convention and exhibition dollar (35%) is spent in hotels and other facilities.” These facts further demonstrate just how interdependent these hotel and convention industries are on each other.
FIGURE 1.1
2004 ECONOMIC IMPACT STUDY
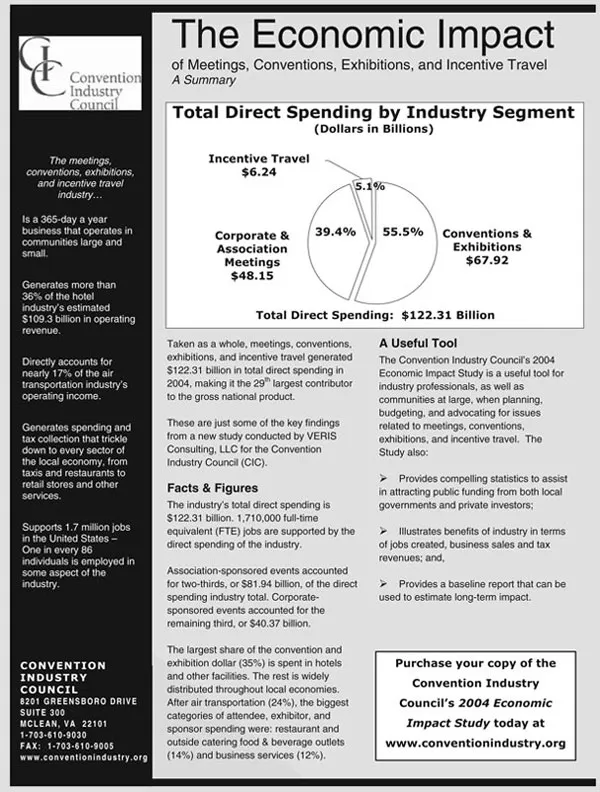
Courtesy: CIC (Convention Industry Council) (2005).
This summary illustrates the usefulness of this report and application to many segments of the meeting and convention industry. Further information on the facts and findings of this study can be located in the appendix at the end of this chapter.
The billions spent in total by all these convention and meetings market segments have a far-reaching financial impact. For example, the U.S. Department of Labor classifies jobs in the hotel, restaurant, and tourism industry as part of the service sector of our economy. Additionally, a large number of jobs are created both directly and indirectly by the convention and meetings industry.
Service Sector Economic Impact
Jobs are created and revenue occurs in other industries indirectly through foreign and domestic delegate spending by conventioneers. This is known as the multiplier effect. As we said in the introduction, by the 1970s and 1980s, hotels and resorts began to expand their facilities to accommodate groups and compete for this emerging market. To remain profitable, most hotels no longer could rely on the leisure vacation and individual business traveler markets to fill their guest rooms year round. At the same time, many people, some with newly earned college degrees in a new program, Hotel and Restaurant Management, began careers in hotel group sales departments. Hotels with 400 or more guest rooms and meeting facilities will have a Group Sales department with a director and sales managers assigned to each of the market segments.
Based on the hotels’ marketing plan, occupancy, and revenue goals, each salesperson must qualify and book a certain amount (or quota) of groups in their respective market.
For example, a group like a national associations’ annual convention may need 200 to 300 rooms for three nights, with meeting space and multiple food and beverage functions. However, association groups traditionally require very low group rates because the majority of the delegates are paying their own way and will not be reimbursed. Additionally, planners for associations expect low room rates and complimentary meeting and exhibit space due to the large quantity of guest rooms they can provide.
This is where the “dance” of negotiating between the seller (facility) and the buyer (group planner) begins. Today, the hotel sales director must train their managers to evaluate every group for the total revenue potential: guest room nights, plus food and beverage and other services. Research is also regularly conducted to determine the groups’ history (did they really use all the guest rooms the hotels held for them in previous years?). However, many association groups like to meet in different regions of the country each year, and this will impact attendance as well.
As you can see, for each group market segment there are many factors for the hotel or facility to consider before it even quotes a group room rate. Regardless, hotels derive much more revenue from any group business and therefore actively advertise and compete for this market. In Chapters 2, 3, and 4, we will also discuss identification of the needs of each type of group customer. Since the 1980s the people who plan the meetings and conventions for associations, corporations, and organizations have become more knowledgeable about the profit centers for hotels. Planners who are responsible for numerous meetings through the year often manage a staff and belong to their own trade association. These organizations offer educational programs at their own conventions so that new and seasoned meeting planners can gain more planning expertise.
However, the growth of the meeting industry is impacted by many factors, most notably, the economy. During the recession of the early 1990s, few corporation meetings were held off-site. Consequently, many hotels went bankrupt by the mid-1990s. The demand for training meetings grew in the late 1990s as a result of daily advancements in computer technology. Every few years the cycle alters so that sometimes it’s a buyer’s market (planners), and other years it’s a seller’s market (facility).
Types of Facilities that Hold Meetings and Conventions
Multinational hotel chains have invested millions in renovating and upgrading their entire hotel properties, to provide facilities and services required by large meeting and convention groups. These well-known and recognized full-service hotels—such as Marriott, Sheraton, Hyatt, Westin, and Holiday Inn— compete with each other as well as other properties within their own chain or brand.
In addition to the traditional hotel, let’s look at other facilities or “venues” used for meetings. Remember, each market or group planning a meeting has different needs and objectives. For example, corporate meeting groups require people (usually employees) to attend, and the corporation (employer) typically pays for everything—including hotel, meals, and travel—related to the meeting. Conversely, attendance at an association convention is optional, and attendees pay out of their own pockets. This results in fluctuating attendance and a greater need for low-cost hotel rooms.
On the other hand, incentive groups need very little meeting space, but they do require a full-service resort with luxurious hotel rooms and amenities. Fortunately, there are more than enough different types of facilities to accommodate these needs. First, we’ll explore conference facilities.
Conference Centers
Conference centers are a relatively new concept that offer state of the art dedicated meeting facilities. Designed with the latest in meeting technology and soundproofing, these self-contained environments often feature built-in theaters and ergonomic chairs that are still comfortable after six hours of meetings. Today, the concept has evolved so that the design features and services provided at a conference center are quite varied. However, their marketing strategies remain focused on providing meeting facilities that are superior to hotels, since they don’t double as banquet rooms. Most conference centers differ from hotels in the following ways:
- Their Meeting package pricing includes rooms, meals, and refreshment breaks
- Their Inclusive package concept ensures no unexpected charges for meeting planners
- They are suitable for small groups of 50 to 200 people who want to be treated like a big group, with an attentive staff and good service
As this concept has grown in popularity with meeting groups, some conference centers have been either acquired or built by some of the leading hotel chains. Therefore, this concept has evolved so that there are now conference facilities built to accommodate each niche. Other...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- About the Author
- 1. The Convention and Meetings Industry: An Overview
- 2. The Associations, Convention, and Meetings Market
- 3. The Corporate Meetings Market
- 4. The Incentive, Smerf, and Other Markets
- 5. The Role of Convention Bureaus and Other Destination Marketing Organizations
- 6. Marketing and Advertising Strategies
- 7. Convention Sales Negotiations and Contracts
- 8. Food and Beverage Function Planning
- 9. Meeting Room and Convention Planning
- 10. On-Site Event Planning: Servicing The Event
- 11. Exhibition and Trade Show Industry Overview
- 12. Industry Trends and Resources
- Index