
eBook - ePub
International Corporate Finance (RLE International Business)
Markets, Transactions and Financial Management
This is a test
- 4 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
International Corporate Finance (RLE International Business)
Markets, Transactions and Financial Management
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
This thorough, comprehensive introduction to international financial management provides an expert guide to the workings of international capital markets, the financing of international business, the complexities of international taxation and the use of financial instruments such as swaps and options. Written by professionals, the book guides the reader through each key topic, targeting the issues underpinning successful financial strategy in the global markets of the 1990s.
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access International Corporate Finance (RLE International Business) by Harvey Poniachek in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & International Business. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
PART I
INTRODUCTION
| 1 | The Framework of International Corporate Finance |
OVER the past forty years, most of the world’s large manufacturing firms—both in the United States and elsewhere—have been transformed from strictly national or domestic to multinational or international enterprises. International business remains the domain of a relatively small number of large multinational corporations (MNCs) with an ever-growing market share. A common definition of a multinational company is one with investment and sales in two or more countries, or one with business activities in two or more countries. MNCs are positioned to take advantage of the complex marketplace, since they are relatively unconstrained in their global activities. International diversification reduces fluctuations in corporate earnings, and enhances their shareholders’ value.
As the world economy becomes more integrated, MNCs’ role is ever increasing, and new companies are joining their ranks. Competition among MNCs in many key industries has intensified in recent years. This phenomenon has been further aggravated by lower global economic growth and the emergence of MNCs from Japan and the newly industrialized countries, such as South Korea.
Operation and financial management of MNCs’ international business occurs in an environment characterized by volatile foreign-exchange rates, a variety of restrictions on capital flows, various levels of country risk, different tax systems, and a wide spectrum of institutional settings. The principles of corporate financial management, however, generally apply for the multinational corporation or the corporation with extensive international business. Environmental and market complexities occasionally modify some of these principles. Moreover, some international financial management applications have no domestic counterparts and arise entirely because of a unique institutional setting.
Recent dramatic changes in the international financial markets have significant implications for corporate operation, financial management, survival, and competitive position. In this environment, management’s ability to seize opportunities and avoid unnecessary risk depends on its knowledge of the international environment and its proficiency in various management principles. By focusing on the international market environment and financial management issues, particularly of the MNCs, this book provides a comprehensive framework for international corporate finance and a balanced and integrated treatment of environmental and institutional settings, business transactions, and management aspects. It discusses the international financial and foreign-exchange markets, trade and investment, and issues concerning financial management and techniques for operating in the financial markets. Considerable attention is paid to financial innovations in funding and hedging methods through currency swaps and options.
MNCS AND THEIR ACTIVITIES
The involvement of multinational corporations in international business is growing. Of the more than 10,000 multinational corporations in the world, the fifty largest (of which about half are American) conduct about 50 percent of their operations abroad and account for 80 percent of global direct foreign investment and international production activities. The United States has about 3,500 MNCs (a multinational corporation is defined as having at least one operation abroad). Of these, about 300 corporations or, about 8.5 percent, are billion-dollar companies in terms of assets; they account for 80 percent of the total assets of the group.
The largest U.S. nonbank companies derive about 33 percent of their revenues from abroad and have the same proportion of assets there. The ratios are much higher for the largest companies. U.S. MNCs operate about 24,000 affiliates around the world, of which the 850 largest account for 53 percent of total assets.
About two-thirds of U.S. affiliates abroad are located in industrial countries, and the remaining third operate in the less developed countries (LDCs). Japan and the Asia Pacific region are likely to assume greater importance; they now host only 11 percent of U.S. subsidiaries.
The very high growth rate that U.S. MNCs and international transactions displayed between the mid-1960s and mid-1970s has now subsided, apparently because their positioning abroad has been largely completed. Price stability substantially deflated trade flows, and country risk and portfolio balance considerations suggest more subdued expansion. MNCs are the most important actors in the world economy. They are heavily engaged in international trade and capital flows, and generate the bulk of direct international investment. Japanese and European MNCs’ foreign production and investment grew considerably faster in the current decade than foreign production and investment of U.S. based companies. The U.S. emerged as the largest host country to MNCs from Western Europe and Japan. The importance of the U.S. MNCs as foreign investors peaked in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
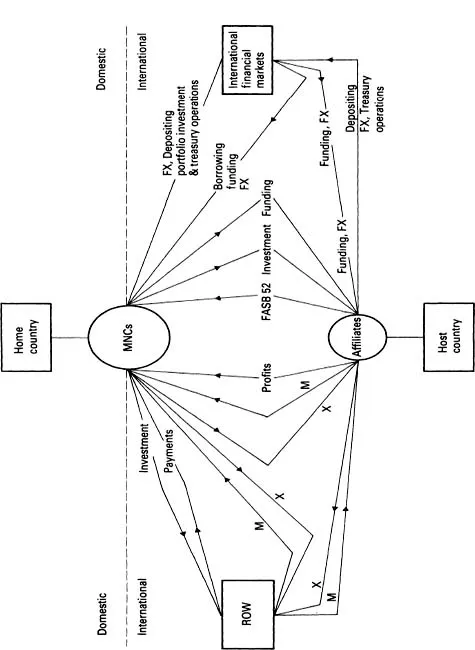
Figure 1–1. International Transactions of MNCs.
| ROW = Rest of the World | I = Import |
| X = Export | FX = Foreign Exchange |
Table 1–1.
INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS OF MNCs.
INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS OF MNCs.
International trade:
Export
Import
Services:
Remittances:
Dividends
Royalties
Fees
Various services:
Transportation
Insurance
Interest
Financial transactions:
Banking:
Deposits
Loans
Other funding:
Notes-issuing facilities (NIFs)
Revolving underwriting facilities (RUFs)
Eurocommercial paper
Payments
Investment:
Portfolio investment
Direct foreign investment
Hedging instruments:
Foreign exchange:
Forward markets
Futures
Options
Swaps
Interest:
Futures
Options
Swaps
Financial markets:
Home
Host
Offshore:
Eurocurrency
Eurobond
MNCs are involved in a broad spectrum of international transactions that give rise to financial intermediation. The average MNC exports and imports, has outstanding short- and long-term foreign-currency loans, assets, and liabilities, and operates numerous subsidiaries and affiliates abroad. These transactions are summarized in Figure 1–1 and Table 1–1. The unique position held by MNCs affords them access to a variety of capital markets to obtain competitive financing, position profits and minimize taxation, and diversify internationally in order to reduce risk.
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT POLICIES
The objective of the MNCs is to maximize their shareholders’ investments. To meet this objective, financial management addresses three major decisions concerning investment, financing, and dividend policy. An optimal combination of the three financial decisions that financial managers are concerned with are; 1. Capital budgeting decision, 2. Financing decision, and 3. Dividend policy decision. The capital budgeting on investment decision is concerned with how to allocate funds to competing projects and assets in such a way that shareholders’ wealth is maximized. The financing decision involves generating funds either internally or from external sources at the least possible cost. The dividend policy involves decisions concerning the distribution of profit to stockholders and the level of retained earnings, which, in turn, affects liquidity, risk and the value of the firm. See Table 1–2.
Generally, corporate decisionmaking authority is decentralized, with substantial authority afforded to subsidiaries and affiliates abroad. There is, however, considerable variation among companies, depending on their size, experience, and type of business. Capital budgeting is usually controlled by the parent company, but it is not clear to what degree international treasury operations are centralized. Companies with advanced management information systems and efficient communications networks are likely to tightly manage treasury operations across geographic regions.
Table 1–2.
FINANCIAL DECISION PRINCIPLES
FINANCIAL DECISION PRINCIPLES
| MNCs’ objectives; maximizing the value of the firm, or stockholders’ wealth | |
| I @ @ @ @ | Investment (capital budgeting) assessment criteria and selection of assets selection among competing projects growth strategy—m&a, natural growth assets management |
| II @ @ | Financing (capital structure) debt/equity cost and risk |
| III @ @ @ | Dividend policy payout ratio retained earnings funding considerations |
FINANCING AND FINANCIAL MARKET TRENDS
MNCs have access to a wide range of international sources of funds, of which the most important are the Eurocurrency and the Eurobond markets. In addition, MNCs have access to the capital markets of host countries in which their affiliates are located and to their home country’s financial markets.
Because of the sharp acceleration in deregulation and development in the global economy, dramatic changes have occurred in the capital markets, financial inst...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Original Title Page
- Original Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- About the Editor and Contributors
- Preface
- Part I Introduction
- Part II International Financial and Capital Markets
- Part III International Business and its Financing
- Part IV International Corporate Financial Management
- Part V Utilizing Currency Swaps and Options
- Part VI Summary and Conclusion
- Appendixes
- Index