
ODE/PDE Analysis of Antibiotic/Antimicrobial Resistance
Programming in R
- 122 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About This Book
ODE/PDE Analysis of Antibiotic/Antimicrobial Resistance: Programming in R presents mathematical models for antibiotic/antimicrobial resistance based on ordinary and partial differential equations (ODE/PDEs). Sections cover the basic ODE model, the detailed PDE model that gives the spatiotemporal distribution of four dependent variable components, including susceptible bacteria population density, resistant bacteria population density, plasmid number, and antibiotic concentration. The computer-based implementation of the example models is presented through routines coded (programmed) in R, a quality, open-source scientific computing system that is readily available from the Internet. As such, formal mathematics is minimized and no theorems and proofs are required.
The PDE analysis is based on the method of lines (MOL), an established general algorithm for PDEs that is implemented with finite differences. Routines are available from a download link so that the example models can be executed without having to first study numerical methods and computer coding. Routines can then be applied to variations and extensions of the antibiotic/antimicrobial models, such as changes in the ODE/PDE parameters (constants) and the form of the model equations.
- Includes PDE routines based on the method of lines (MOL) for computer-based implementation of PDE models
- Offers transportable computer source codes for readers in R, with line-by-line code descriptions as it relates to mathematical model and algorithms
- Authored by a leading researcher and educator in PDE models
Frequently asked questions
Information
1: Introductory ODE model
Abstract
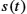
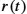
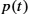
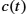
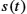
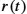
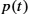
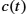
Keywords
Introduction
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- 1: Introductory ODE model
- 2: Analysis of the ODE model equations
- 3: ODE analysis of antibiotic/antimicrobial resistance
- 4: Introductory PDE model
- 5: Parameter analysis of the PDE model
- 6: Parameter time variation
- A1: Functions dss004, dss044
- Index